Home>Misc>Featured>How Does Caffeine Affect A Treadmill Stress Test

Featured
How Does Caffeine Affect A Treadmill Stress Test
Modified: January 2, 2024
Discover the effects of caffeine on treadmill stress tests. Find out how this featured substance impacts your cardiovascular health during exercise.
Introduction
Welcome to the world of fitness and exercise! Treadmill stress tests are a common tool used by medical professionals to evaluate heart health and determine an individual’s cardiovascular fitness. These tests involve running or walking on a treadmill while being monitored for heart rate, blood pressure, and other vital signs. They provide valuable insights into a person’s overall cardiovascular function and can help detect any underlying issues or potential risks.
But have you ever wondered how certain factors, such as caffeine consumption, can impact the results of a treadmill stress test? Caffeine is a stimulant found in many everyday products, such as coffee, tea, energy drinks, and chocolate. It has been shown to have various effects on the body, including its influence on heart rate, blood pressure, and exercise performance. Understanding the relationship between caffeine and treadmill stress tests can provide valuable information for individuals undergoing the test, as well as for medical professionals interpreting the results.
In this article, we will explore the effects of caffeine on a treadmill stress test. We will delve into how caffeine affects heart rate, blood pressure, and exercise performance. Additionally, we will examine the findings of research studies that have investigated the impact of caffeine on treadmill stress tests. Finally, we will discuss some precautions and considerations that should be taken into account when consuming caffeine before undergoing a treadmill stress test. So, grab a cup of coffee and let’s dive in!
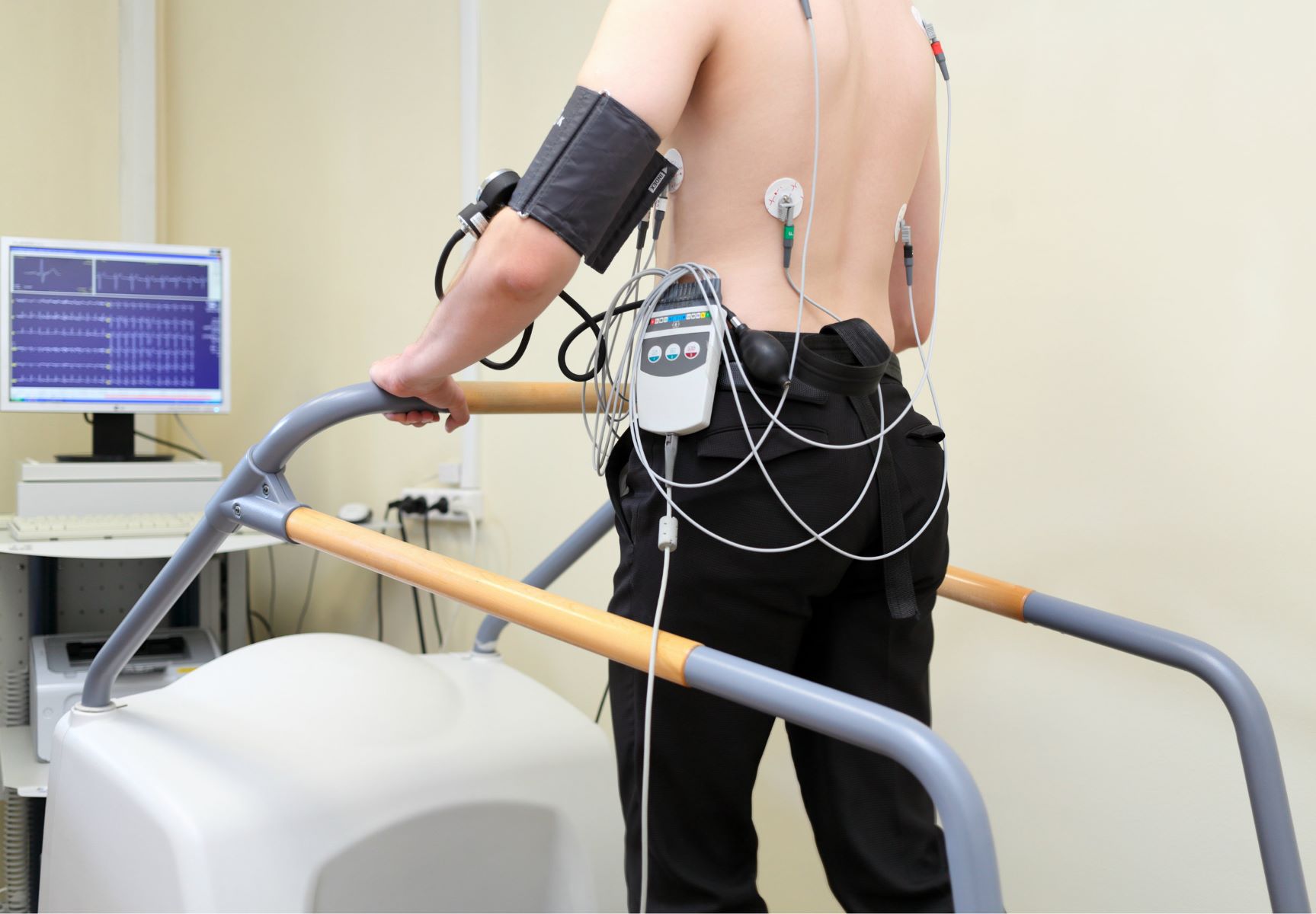
What is a Treadmill Stress Test?
A treadmill stress test, also known as an exercise stress test or a cardiac stress test, is a diagnostic tool used to evaluate the cardiovascular health of an individual. It involves the individual walking or running on a treadmill while their heart rate, blood pressure, and other vital signs are monitored. The purpose of this test is to assess how well the heart functions under physical stress.
During a treadmill stress test, the intensity and incline of the treadmill are gradually increased at specified intervals, simulating the exertion of physical activity. The individual is required to continue exercising until reaching their target heart rate or until they are unable to continue due to fatigue or any symptoms such as chest pain or shortness of breath.
The test provides valuable information about the overall health of the cardiovascular system. It can help diagnose underlying heart conditions, assess the effectiveness of treatments, determine a person’s exercise capacity, and evaluate the risk of cardiovascular events such as heart attacks.
During the test, various measurements are taken, including heart rate, blood pressure, electrocardiogram (ECG) readings, and oxygen consumption. These data help medical professionals evaluate the heart’s response to exercise and identify any abnormalities or irregularities.
Treadmill stress tests are commonly performed in a medical facility or doctor’s office under the supervision of trained professionals. The procedure usually takes around 15 to 30 minutes, depending on the individual’s fitness level and overall health.
This non-invasive test is generally safe, but it may not be suitable for individuals with certain medical conditions or risk factors. It is essential to consult with a healthcare professional before undergoing a treadmill stress test to ensure it is appropriate and safe for you.
Now that we understand what a treadmill stress test entails, let’s explore the purpose of this test and what it aims to achieve.
Purpose of a Treadmill Stress Test
The primary purpose of a treadmill stress test is to assess the cardiovascular health and function of an individual under physical stress. This test helps medical professionals evaluate the overall condition of the heart and detect any abnormalities or potential risks.
There are several specific objectives and purposes for performing a treadmill stress test:
- Diagnosing heart conditions: A treadmill stress test can help diagnose various heart conditions, such as coronary artery disease, heart rhythm disorders, and valvular heart disease. By monitoring changes in heart rate, blood pressure, and ECG patterns during exercise, medical professionals can identify any indications of these underlying issues.
- Assessing exercise capacity: The test provides information about an individual’s exercise tolerance and capacity. It evaluates their ability to sustain physical activity and exertion and determines their cardiovascular fitness level. This information can be valuable for creating personalized exercise programs, assessing the effectiveness of treatments or interventions, and guiding lifestyle modifications.
- Evaluating the risk of heart attacks and cardiovascular events: Treadmill stress tests can help estimate an individual’s risk of experiencing a heart attack or other cardiovascular events. By monitoring changes in blood pressure, heart rate, and ECG readings during exercise, medical professionals can identify any signs of reduced blood flow to the heart muscle or decreased oxygen supply, indicating an increased risk of future complications.
- Assessing the effectiveness of treatments: For individuals with known heart conditions or those who have undergone cardiac procedures or interventions, treadmill stress tests can evaluate the effectiveness of these treatments. By comparing the results of pre- and post-treatment stress tests, medical professionals can determine if the interventions have improved the individual’s cardiovascular function and overall health.
- Determining the need for further testing: In some cases, a treadmill stress test may be a preliminary step to determine if further diagnostic procedures, such as cardiac imaging or angiography, are necessary. If abnormalities or significant changes are observed during the stress test, additional tests may be recommended to provide more detailed information about the heart’s structure and function.
By fulfilling these purposes, treadmill stress tests serve as a valuable tool in assessing cardiovascular health and providing crucial information for medical professionals to make informed diagnoses and treatment decisions.
Effects of Caffeine on Heart Rate
Caffeine, being a stimulant, can have a significant impact on heart rate. When consumed, caffeine stimulates the central nervous system, leading to an increase in heart rate. The primary mechanism behind this effect is the inhibition of an enzyme called phosphodiesterase, which results in the accumulation of cyclic AMP (cAMP) and enhances the release of norepinephrine.
Norepinephrine is a hormone and neurotransmitter that plays a role in the “fight or flight” response of the body. It stimulates the heart’s beta-adrenergic receptors, leading to an increased heart rate. Consequently, the consumption of caffeine can cause an elevation in heart rate.
The extent of the increase in heart rate varies from person to person, depending on factors such as sensitivity to caffeine, the amount consumed, and individual metabolic differences. Some individuals may experience a more pronounced increase in heart rate after consuming caffeine, while others may be less affected.
It is worth noting that the effects of caffeine on heart rate can be influenced by several factors, such as the individual’s tolerance, habitual caffeine consumption, and the presence of any underlying heart conditions. Individuals who regularly consume caffeine may develop some level of tolerance, resulting in a less significant increase in heart rate compared to those who are not accustomed to caffeine intake.
Additionally, individuals with certain heart conditions or cardiovascular risk factors should exercise caution when consuming caffeine. Conditions such as arrhythmias or high blood pressure may be more susceptible to the effects of caffeine, potentially leading to irregular heart rhythms or exacerbating existing symptoms.
It is important to note that the effects of caffeine on heart rate are generally temporary and return to baseline once the stimulant properties of caffeine wear off. However, individuals who have concerns about their heart health or those with known heart conditions should consult with a medical professional before consuming caffeinated beverages or products.
Now that we have explored the effects of caffeine on heart rate, let us move on to discussing the impact of caffeine on blood pressure.
Effects of Caffeine on Blood Pressure
The consumption of caffeine can have significant effects on blood pressure. Caffeine stimulates the release of adrenaline, a hormone that can constrict blood vessels, leading to an increase in blood pressure. This effect is due to the activation of the sympathetic nervous system, which is responsible for the “fight or flight” response in the body.
While the increase in blood pressure caused by caffeine is generally temporary, it can be more pronounced in individuals who are sensitive to the effects of caffeine or who consume large amounts of it. The extent of the blood pressure increase may also depend on individual factors such as overall health, underlying medical conditions, and genetic predisposition.
It is important to note that while caffeine may cause a short-term increase in blood pressure, regular caffeine consumption does not appear to have a long-term or sustained effect on blood pressure levels. In individuals with normal blood pressure, the increase is usually within a moderate range and returns to baseline within a few hours.
However, for individuals with hypertension (high blood pressure) or those at risk of developing hypertension, the effects of caffeine on blood pressure may be more significant. It is advisable for these individuals to exercise caution and limit their caffeine intake to prevent excessive and prolonged increases in blood pressure.
It is worth mentioning that not everyone responds to caffeine in the same way. Some individuals may be more sensitive and have a greater increase in blood pressure after consuming caffeine, while others may experience a lesser effect. It is important for individuals to monitor their own blood pressure and pay attention to any adverse reactions after consuming caffeine-containing products.
Furthermore, it is essential to consider other lifestyle and dietary factors that can influence blood pressure when assessing the impact of caffeine. These factors include overall diet, exercise habits, stress levels, and medication use. Adhering to a healthy lifestyle, including a well-balanced diet and regular physical activity, can help manage and control blood pressure effectively.
Now that we have explored the effects of caffeine on blood pressure, let us move on to discussing the impact of caffeine on exercise performance during a treadmill stress test.
Effects of Caffeine on Exercise Performance
Caffeine has long been recognized for its potential to enhance exercise performance. As a stimulant, caffeine can provide several benefits that may positively impact physical performance during a treadmill stress test or any other form of exercise.
One of the primary ways caffeine improves exercise performance is by reducing fatigue and increasing alertness. It acts on the central nervous system, blocking adenosine receptors in the brain, which helps promote wakefulness and a sense of alertness. This can lead to improved cognitive function and concentration during exercise, allowing individuals to push themselves further and maintain a higher level of performance for a longer period of time.
Caffeine has also been shown to have a direct effect on muscle contraction. It enhances muscle contractility by increasing calcium release within the muscle fibers. This can result in improved strength and power output during physical exertion, allowing individuals to perform at a higher intensity.
Furthermore, caffeine has been found to have a positive impact on endurance performance. It can help delay the onset of fatigue by increasing the utilization of free fatty acids as a fuel source. This shift in energy utilization can help preserve glycogen stores in the muscles, which are essential for sustaining endurance exercise. This, in turn, can extend the time to exhaustion and improve overall endurance performance.
Research studies have demonstrated the ergogenic effects of caffeine on various aspects of exercise performance. For example, a study published in the Journal of Applied Physiology found that consuming caffeine prior to endurance exercise resulted in increased time to exhaustion by 20-30%. Another study published in Sports Medicine revealed that caffeine ingestion improved strength and power output during resistance exercise.
It is important to note that the effects of caffeine on exercise performance can vary among individuals. Factors such as caffeine sensitivity, habitual caffeine consumption, and genetics can influence the response to caffeine. Additionally, it is crucial to consider the dosage and timing of caffeine consumption, as excessive amounts or consuming it too close to bedtime can lead to negative effects such as jitteriness, increased heart rate, and sleep disturbances.
While caffeine can be beneficial for improving exercise performance, it is important to approach its use with caution and individualize consumption based on personal tolerance and preferences. Consulting with a healthcare professional or sports nutritionist can be helpful in determining the most appropriate dosage and timing of caffeine intake for optimal performance.
Now that we have explored how caffeine can impact exercise performance, let us delve into the findings of research studies that have investigated the effects of caffeine on treadmill stress tests.
Research Studies on the Impact of Caffeine on Treadmill Stress Tests
The impact of caffeine on treadmill stress tests has been a topic of interest among researchers, leading to several studies investigating its effects on various parameters measured during these tests.
A study published in the Journal of Applied Physiology examined the influence of caffeine on heart rate and blood pressure during a treadmill stress test. The researchers found that consuming caffeine prior to the test resulted in an increase in both heart rate and blood pressure compared to a placebo. These effects were more pronounced in individuals who were not habitual caffeine consumers, suggesting a greater sensitivity to caffeine’s cardiovascular effects.
Another study published in the American Journal of Cardiology focused on the impact of caffeine on the exercise capacity of individuals undergoing treadmill stress tests. The researchers found that consuming caffeine prior to the test led to a significant improvement in exercise duration and distance covered. This suggests that caffeine’s stimulant properties can enhance an individual’s physical performance during the test.
However, it is worth noting that not all research studies have reported positive outcomes. A meta-analysis published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology analyzed multiple studies and concluded that while caffeine consumption may result in a slight increase in heart rate and blood pressure, it does not significantly affect exercise duration or maximal workload during treadmill stress tests. These findings suggest that the impact of caffeine on treadmill stress test results may vary among individuals and be influenced by factors such as caffeine sensitivity and dosage.
It is important to interpret the findings of these studies in the context of individual characteristics and precautions. Factors such as caffeine tolerance, overall health, and the presence of any cardiovascular conditions can influence the response to caffeine during a treadmill stress test. It is recommended to consult with a healthcare professional before consuming caffeine prior to the test, especially for individuals with known heart conditions or other risk factors.
In summary, research studies indicate that caffeine consumption can lead to an increase in heart rate and blood pressure during a treadmill stress test. Furthermore, some studies suggest that caffeine can improve exercise capacity and performance during the test, while others suggest more modest effects. The variability in findings highlights the need for individualized approaches when considering caffeine consumption and encourages further research to better understand its impact on treadmill stress test results.
Precautions and Considerations when Consuming Caffeine before a Treadmill Stress Test
While caffeine consumption can have both positive and negative effects on the results of a treadmill stress test, there are several precautions and considerations that individuals should take into account before consuming caffeine prior to the test.
1. Talk to your healthcare professional: It is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional before deciding to consume caffeine before a treadmill stress test, especially if you have any underlying cardiovascular conditions or risk factors. They can provide personalized advice based on your individual health status and determine if caffeine consumption is appropriate for you.
2. Timing of consumption: Consider the timing of your caffeine intake before the test. It is generally recommended to consume caffeine at least 30 minutes to one hour before the test to allow sufficient time for its effects to kick in. Avoid consuming caffeine too close to the test, as it may lead to increased heart rate and nervousness during the test.
3. Individual sensitivity: Take into account your own sensitivity to caffeine. Some individuals may be more sensitive to its effects, while others may have developed a tolerance. Monitoring your reaction to caffeine in day-to-day situations can help provide insight into how it might affect your body during a treadmill stress test.
4. Dosage: Pay attention to the amount of caffeine you consume. Different beverages and products contain varying amounts of caffeine. It is essential to be aware of the caffeine content and limit your consumption accordingly. Excessive caffeine intake can lead to adverse effects such as increased heart rate, jitteriness, and anxiety.
5. Hydration: Stay hydrated before and during the test. Caffeine has diuretic properties, which can increase urine production and potentially lead to dehydration. Proper hydration is essential for maintaining cardiovascular function and overall well-being during the test.
6. Consider other lifestyle factors: Evaluate other factors that can influence your cardiovascular health and exercise performance. Factors such as sleep quality, nutrition, and stress levels can have a significant impact on your overall well-being and the results of a treadmill stress test. Incorporating healthy habits and maintaining a well-rounded lifestyle can contribute to optimal test outcomes.
7. Individualize your approach: Ultimately, every individual is unique, and the effects of caffeine will vary. It is crucial to listen to your body, monitor your own response to caffeine, and make informed decisions based on your personal health circumstances and preferences.
By considering these precautions and individualizing your approach, you can make an informed decision about consuming caffeine before a treadmill stress test. Always prioritize your health and work closely with healthcare professionals to ensure the most appropriate and safe approach for your unique situation.
Conclusion
The impact of caffeine on a treadmill stress test is a topic of interest, as it can have significant effects on heart rate, blood pressure, and exercise performance. Caffeine consumption has been found to increase heart rate and blood pressure, although the extent of these increases may vary among individuals. Caffeine has also been shown to enhance exercise performance by reducing fatigue, increasing alertness, and improving muscle contractility and endurance.
Research studies have provided insight into the effects of caffeine on treadmill stress tests, with findings suggesting that caffeine consumption can lead to an increase in heart rate and blood pressure during the test. There is evidence supporting improvements in exercise duration and performance, although the magnitude of these effects may vary among individuals. It is important to consider individual sensitivity, dosage, timing of consumption, and other lifestyle factors when deciding to consume caffeine before a treadmill stress test.
Precautions and considerations are necessary to ensure the safe and appropriate use of caffeine before a treadmill stress test. Consulting with a healthcare professional, timing caffeine intake appropriately, monitoring personal sensitivity, being mindful of dosage, staying hydrated, and considering other lifestyle factors are important factors to take into account.
In conclusion, while caffeine can have both positive and negative effects on a treadmill stress test, it is essential to approach its consumption with caution and individualize the approach based on personal circumstances. By doing so, individuals can optimize their treadmill stress test experience and obtain more accurate results in evaluating their cardiovascular health and exercise performance.