Home>Misc>Featured>How Much Beetroot Should You Eat To Boost Athletic Performance


Featured
How Much Beetroot Should You Eat To Boost Athletic Performance
Modified: January 2, 2024
Discover the ideal amount of beetroot to consume for enhanced athletic performance with our featured article. Maximize your workouts and optimize results!
Introduction
Athletes, both professional and recreational, are constantly seeking ways to enhance their performance and gain a competitive edge. While there are various supplements and nutritional strategies available, one natural ingredient that has gained attention for its potential benefits is beetroot.
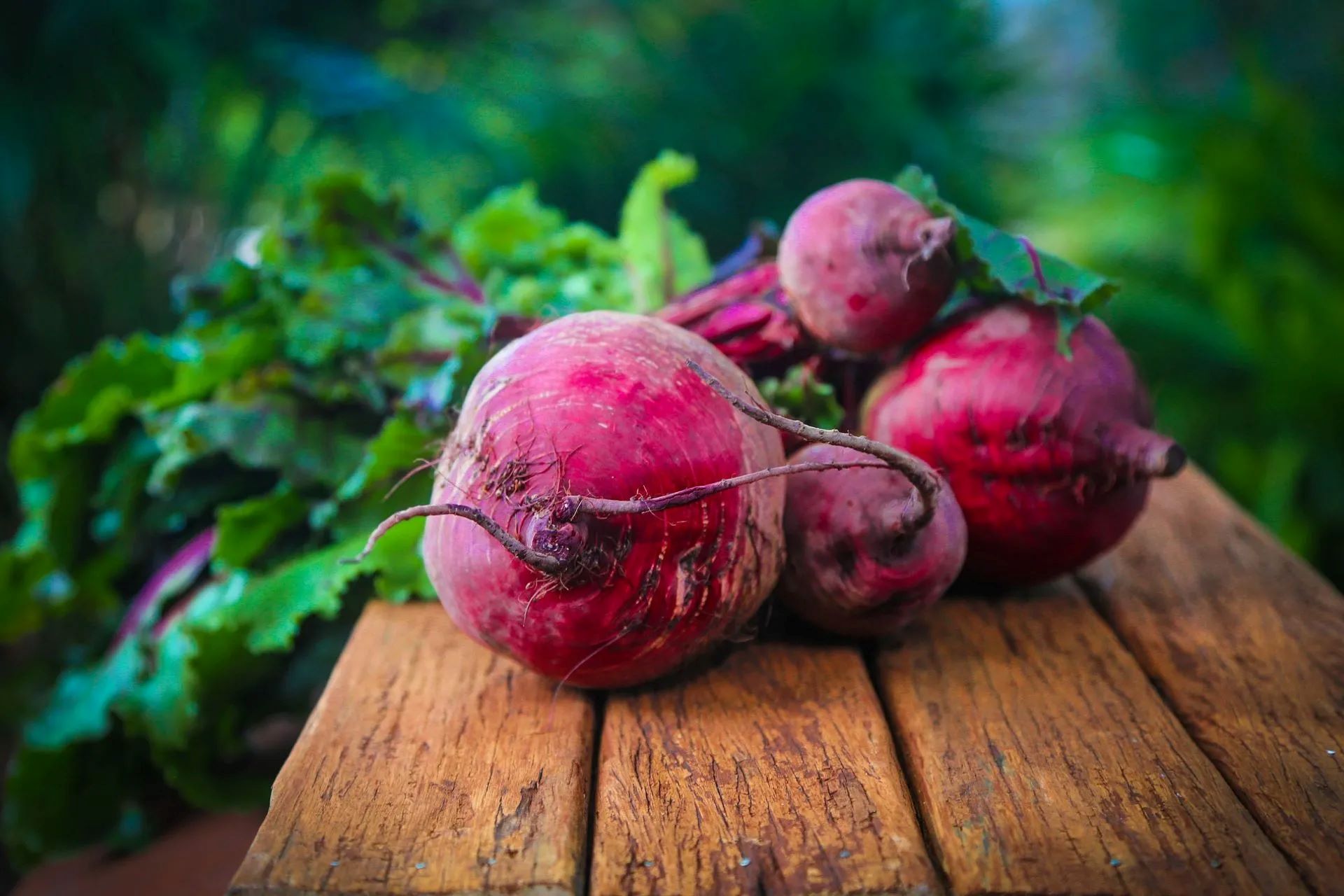
Beetroot, commonly known as beets, is a vibrant and nutrient-rich vegetable that has been used for centuries for its medicinal properties. Its deep purple color is a result of the presence of betalains, a group of antioxidants that have been linked to various health benefits.
Research has suggested that beetroot can improve athletic performance, making it a popular choice among athletes looking for natural and effective ways to boost their abilities. Whether it’s running, cycling, swimming, or any other endurance-based activity, incorporating beetroot into your diet may help you reach new heights.
In this article, we will explore the potential benefits of beetroot for athletic performance, delve into the science behind its effectiveness, and provide guidance on determining the right amount of beetroot to consume for optimal results. It’s important to note that while beetroot can be an incredible addition to your training routine, it’s always best to consult with a healthcare professional or nutritionist before making any significant changes to your diet.
Benefits of Beetroot for Athletic Performance
Beetroot has gained popularity among athletes due to its potential performance-enhancing properties. Let’s explore some of the key benefits of incorporating beetroot into your diet:
1. Improved Endurance: One of the main benefits of beetroot is its ability to improve endurance during physical activities. This is primarily attributed to its high nitrate content, which is converted into nitric oxide in the body. Nitric oxide helps to relax blood vessels, improving blood flow and oxygen delivery to the muscles, ultimately enhancing stamina and reducing fatigue.
2. Increased Oxygen Efficiency: Beetroot has been found to increase the efficiency with which your body utilizes oxygen during exercise. Research suggests that the nitric oxide produced from beetroot consumption can enhance mitochondrial function, the powerhouse of the cells responsible for energy production. This increased oxygen efficiency can allow athletes to perform at a higher intensity for longer durations.
3. Boosted Energy Levels: Beetroot contains carbohydrates, which are a primary source of energy for physical activities. The natural sugars in beetroot provide a quick energy boost, making it an ideal pre-workout snack. Additionally, the high antioxidant content of beetroot helps to reduce exercise-induced inflammation, allowing for faster recovery and sustained energy levels.
4. Muscle Recovery: Intense exercise can lead to muscle damage and inflammation. The anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties of beetroot can aid in reducing exercise-induced muscle damage and inflammation. This, in turn, supports faster recovery and reduces muscle soreness, allowing athletes to bounce back quicker and perform at their best.
5. Improved Blood Pressure: Beetroot has been shown to have positive effects on blood pressure. The nitric oxide produced from beetroot consumption can help relax and dilate blood vessels, leading to a decrease in blood pressure levels. Maintaining healthy blood pressure is crucial for overall cardiovascular health and optimal athletic performance.
6. Enhanced Brain Function: Beetroot contains natural nitrates that have been linked to improved cognitive function. Studies have suggested that beetroot’s ability to increase blood flow to the brain can enhance cognitive performance, including decision-making, reaction time, and memory. This can be particularly beneficial for athletes participating in sports that require mental focus and quick decision-making.
Incorporating beetroot into your diet can provide a range of benefits for athletic performance. However, it’s important to note that individual results may vary, and the extent of these benefits can depend on factors such as overall diet, training regimen, and individual physiology. It’s always best to experiment and find the approach that works best for you.
The Role of Nitric Oxide
Nitric oxide, a gas produced naturally in the body, plays a crucial role in various physiological processes. When it comes to athletic performance, nitric oxide has garnered attention due to its vasodilatory effects and its impact on endurance and recovery. Let’s take a closer look at the role of nitric oxide in relation to beetroot and athletic performance:
1. Vasodilation: Nitric oxide acts as a vasodilator, meaning it helps relax and widen blood vessels. This dilation allows for increased blood flow, which is essential for delivering oxygen and nutrients to the muscles during exercise. By expanding the blood vessels, nitric oxide promotes efficient oxygen utilization and nutrient delivery to the working muscles, contributing to enhanced endurance and improved performance.
2. Improved Oxygen Delivery: One of the primary benefits of nitric oxide is its ability to enhance the delivery of oxygen to the muscles. During exercise, the demand for oxygen increases, and the production of nitric oxide helps facilitate the efficient transport of oxygen-rich blood to the working muscles. This increased oxygen supply supports energy production, delays muscle fatigue, and promotes overall athletic performance.
3. Muscle Efficiency: Nitric oxide also plays a role in improving the efficiency of muscle contractions. It helps regulate calcium levels within muscle cells, allowing for better control and coordination of muscle contractions. This can result in smoother and more powerful movements during physical activities, enhancing athletic performance and reducing the risk of injury.
4. Muscle Recovery: In addition to its effects during exercise, nitric oxide contributes to post-workout recovery. It aids in reducing inflammation and oxidative stress, both of which can occur as a result of intense exercise. By mitigating these processes, nitric oxide supports faster muscle recovery and reduces muscle soreness, allowing athletes to bounce back quicker and continue training at a high level.
While the body naturally produces nitric oxide, it can also be obtained through dietary sources such as beetroot. Beetroot’s high nitrate content can increase nitric oxide production, thus benefiting athletic performance. However, it’s important to note that the effectiveness of nitric oxide supplementation can vary among individuals, and it’s best to experiment and find the approach that works best for you.
As always, consult with a healthcare professional or nutritionist to determine the appropriate dosage and to ensure that nitric oxide supplementation is suitable for your specific needs and health conditions.
Determining the Right Amount of Beetroot
When it comes to incorporating beetroot into your diet for athletic performance, finding the right amount is key. While there is no “one size fits all” approach, there are a few factors to consider to determine the optimal amount of beetroot to consume:
1. Nitrate Content: The primary component in beetroot that contributes to its performance-enhancing benefits is its nitrate content. Nitrate is converted into nitric oxide in the body, which helps improve blood flow and oxygen delivery. Different varieties of beetroot can vary in their nitrate content, so it’s beneficial to check the labels or consult with a nutritionist to find the best option.
2. Athletic Goals: Your specific athletic goals can also inform how much beetroot you should consume. If you’re looking to improve endurance and stamina, a higher intake of beetroot may be necessary. On the other hand, if you’re primarily focused on muscle recovery and reducing inflammation, a smaller amount may be sufficient. Experiment with different amounts and monitor how your body responds to determine the optimal dosage for your goals.
3. Timing: Consider when to consume beetroot for maximum benefit. Some research suggests that consuming beetroot in the hours leading up to exercise can enhance performance. Additionally, consuming beetroot after exercise may aid in the recovery process. Experiment with different timings and observe how your body performs and recovers to find what works best for you.
4. Individual Tolerance: It’s important to listen to your body and adjust the amount of beetroot based on your individual tolerance. Some individuals may experience gastrointestinal discomfort or changes in urine color due to the betalain pigments in beetroot. Start with a smaller amount and gradually increase to find the right balance that suits your body’s tolerance and preferences.
5. Variation in Diet: Remember that beetroot should be part of a well-rounded and varied diet. While it offers numerous benefits, it’s important to consume a variety of other fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains to ensure you’re meeting your overall nutritional needs for optimal athletic performance.
As with any dietary changes, it’s always a good idea to consult with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian to ensure that adding beetroot to your diet aligns with your overall health goals and any specific dietary requirements or restrictions you may have.
Finding the right amount of beetroot to consume is a personal journey that may require some experimentation. Pay attention to how your body responds and make adjustments accordingly to maximize the benefits of incorporating beetroot into your diet.
Factors to Consider
When incorporating beetroot into your diet for athletic performance, there are several factors to consider to ensure you maximize the benefits and minimize any potential drawbacks. Take these factors into account when determining if beetroot is the right choice for you:
1. Overall Diet and Nutrition: While beetroot offers numerous benefits, it’s important to remember that it should be part of a balanced and nutrient-dense diet. Consider the composition of your overall diet and ensure you’re consuming a variety of fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains to support your athletic performance and overall health.
2. Individual Sensitivities and Allergies: Some individuals may have sensitivities or allergies to beetroot or its components. If you’ve experienced any adverse reactions to beets in the past, it’s important to exercise caution when incorporating beetroot into your diet. Consult with a healthcare professional or allergist to identify any potential risks or alternatives.
3. Medication Interactions: If you are taking any medications, it’s crucial to check whether there are any potential interactions with beetroot. Beetroot, especially in supplement form, can affect blood pressure and blood clotting. Consult with your healthcare provider or pharmacist to ensure beetroot is safe to consume alongside your medications.
4. Quality and Sourcing: Opt for high-quality and organic beetroot to ensure you’re getting the maximum nutritional benefits. Be mindful of the source and ensure that the beetroot is grown in clean and pesticide-free environments. This will ensure the beetroot is free from harmful substances and maximize its nutritional value.
5. Individual Performance Goals: Consider your specific performance goals when incorporating beetroot into your diet. Different sports and activities may require different nutritional strategies, and the amount of beetroot you consume may vary accordingly. Consult with a sports nutritionist or registered dietitian who can customize a nutrition plan to align with your specific goals.
6. Preparation and Cooking Methods: The way you prepare and cook beetroot can affect its nutrient content. To retain the maximum amount of nutrients, opt for steaming or roasting rather than boiling, as this helps to preserve the water-soluble nutrients. Additionally, avoid overcooking, as excessive heat can destroy some of the beneficial compounds.
7. Individual Response: Every individual’s body may respond differently to beetroot. While research suggests numerous benefits, it’s important to pay attention to your own body’s response. Monitor how you feel, perform, and recover after incorporating beetroot into your diet, and make adjustments as needed.
By taking these factors into consideration, you can ensure that you are incorporating beetroot into your diet in a way that aligns with your individual needs and preferences, optimizing its benefits for your athletic performance.
Potential Side Effects
While beetroot is generally safe for most people when consumed in moderation, it’s important to be aware of potential side effects that may occur, especially when consumed in large quantities or if you have certain health conditions. Here are some potential side effects to consider:
1. Gastrointestinal Discomfort: Some individuals may experience gastrointestinal discomfort such as bloating, gas, or an upset stomach when consuming beetroot. This is typically due to the high fiber content of beets. If you notice these symptoms, start with smaller amounts of beetroot and gradually increase to allow your digestive system to adapt.
2. Kidney Stone Formation: Beetroot is high in oxalates, which can contribute to the formation of kidney stones in susceptible individuals. If you have a history of kidney stones or are prone to them, it’s best to limit your intake of beetroot or consult with a healthcare professional to determine a safe amount for you.
3. Beeturia: Some individuals may experience a harmless condition called “beeturia,” where the consumption of beetroot causes a reddish or pinkish discoloration in urine or stool. This is due to the pigments present in the beetroot and is considered a harmless side effect.
4. Blood Pressure Management: While beetroot can help lower blood pressure due to its nitric oxide content, individuals with already low blood pressure levels should be cautious. Consuming excessive amounts of beetroot can potentially lower blood pressure to unsafe levels. It’s essential to monitor your blood pressure regularly and consult with a healthcare professional if you have any concerns.
5. Allergic Reactions: Although rare, some individuals may have an allergic reaction to beetroot. Symptoms may include itching, swelling, hives, or difficulty breathing. If you experience any signs of an allergic reaction, seek immediate medical attention.
6. Interactions with Medications: Beetroot, especially in large amounts or as a concentrated supplement, can interact with certain medications such as blood thinners or medication for high blood pressure. If you are taking any medications, it’s important to consult with your healthcare provider before incorporating beetroot into your diet to ensure there are no potential interactions.
It’s crucial to note that these side effects are relatively uncommon and typically occur when consuming large amounts of beetroot. Moderation is key, and it’s always advisable to consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian before making any significant changes to your diet, especially if you have underlying health conditions or are taking medications.
By being aware of these potential side effects and monitoring your body’s response, you can enjoy the benefits of beetroot while minimizing any risks.
Conclusion
Beetroot can be a valuable addition to the diet of athletes looking to improve their performance. Its high nitrate content and subsequent conversion to nitric oxide offer potential benefits such as enhanced endurance, increased oxygen efficiency, and improved muscle recovery. Incorporating beetroot into your diet may contribute to improved athletic performance and overall well-being.
When determining the optimal amount of beetroot to consume, consider factors such as your athletic goals, individual tolerance, and overall diet. It’s important to start with smaller amounts and gradually increase to find the right balance that works for you. Additionally, be mindful of potential side effects, such as gastrointestinal discomfort or interactions with certain medications.
As with any dietary change, it’s advisable to consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian to ensure that incorporating beetroot aligns with your individual health needs and goals. They can provide personalized guidance and help you tailor your nutrition plan to optimize your athletic performance.
Remember, beetroot is just one piece of the puzzle. It should be part of a balanced and varied diet that includes a wide range of nutrient-dense foods. By considering all of these factors and monitoring your body’s response, you can harness the potential benefits of beetroot while supporting your athletic endeavors.