Featured
How Has Technology Improved Health Care
Published: September 10, 2023
Discover how technology has revolutionized the healthcare industry with our featured article. Explore the advancements that have improved patient care and transformed the way medical professionals operate.
Introduction
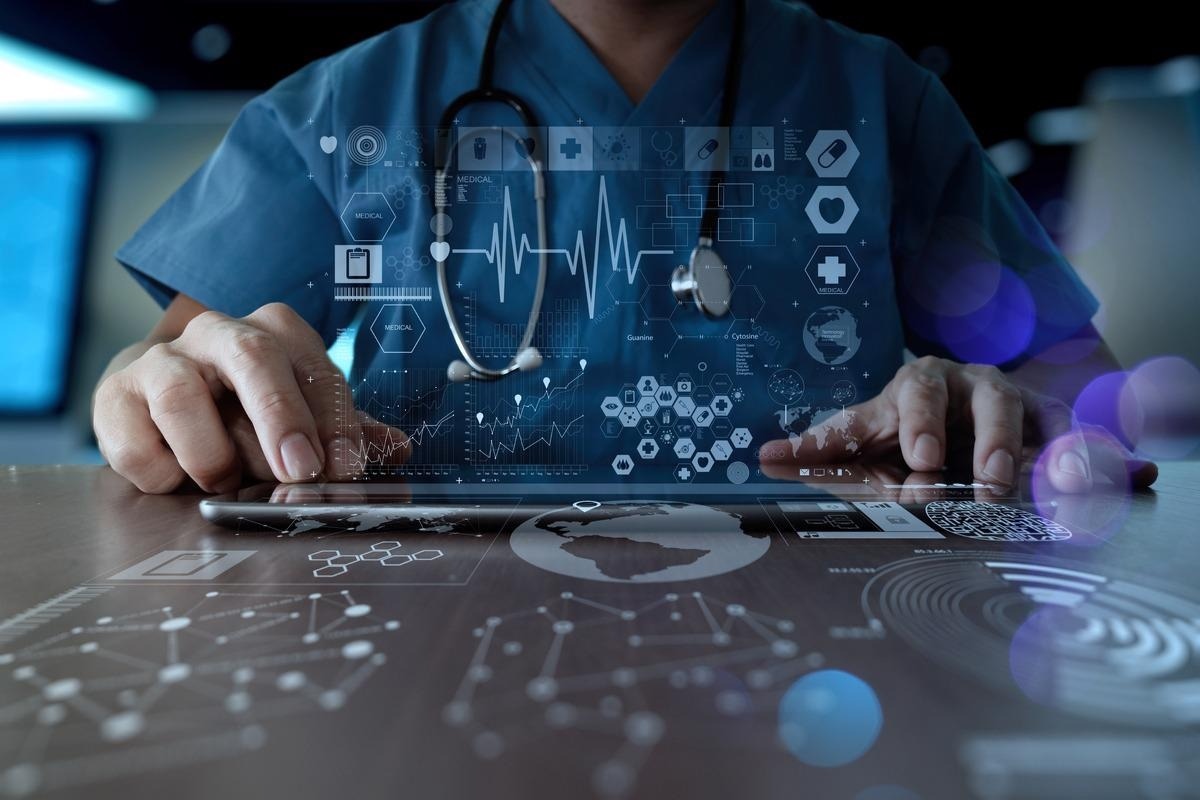
Technology has revolutionized every aspect of our lives, including the field of healthcare. Over the past few decades, advancements in technology have transformed the way we access medical information, receive treatment, and manage our health. From digital health records to remote monitoring devices, technology has improved the efficiency, accuracy, and accessibility of healthcare services.
The increased availability of medical information has empowered patients to take a more active role in their own health and well-being. With a few taps on a smartphone, individuals can access a vast amount of health-related information, ranging from symptoms and treatments to medical research and lifestyle tips. This easy access to medical knowledge allows patients to make more informed decisions about their health and collaborate more effectively with their healthcare providers.
Another significant improvement in healthcare technology is the rise of remote monitoring and telemedicine. These technologies enable healthcare professionals to remotely monitor patients’ vital signs, provide consultations through video calls, and even perform certain medical procedures from a distance. This opens up opportunities for individuals in remote areas to receive quality healthcare without the need for long and costly travels to the nearest medical facilities.
Efficient and accurate record-keeping is also greatly facilitated by technology. Digital health records have replaced the conventional paper-based system, reducing the risk of errors and making patient information easily accessible to healthcare providers. This streamlines administrative processes and allows for better coordination of care among different medical professionals involved in a patient’s treatment.
Furthermore, technology has vastly improved communication and collaboration among healthcare professionals. With the use of secure messaging platforms and video conferencing, doctors, nurses, and specialists can easily communicate and share information, leading to more coordinated and comprehensive care. This enhanced collaboration not only improves patient outcomes but also enables healthcare providers to stay updated on the latest advancements and best practices.
Increased Access to Medical Information
One of the key benefits of technology in healthcare is the increased access to medical information. In the past, patients had to rely solely on their healthcare providers for information about their conditions, treatments, and medications. However, with the advent of the internet and mobile technology, access to medical knowledge has become more democratized.
Today, individuals can easily search for medical information online, accessing a wide range of resources such as reputable health websites, forums, and medical journals. This easy access to information allows patients to educate themselves about their health conditions, understand treatment options, and make better-informed decisions about their care.
Furthermore, technology has given rise to numerous health-related apps and platforms that provide users with tailored information and tools to manage their health. These apps offer features such as symptom checkers, medication reminders, and personalized fitness plans, helping individuals take charge of their health on a day-to-day basis.
Moreover, the advent of wearable devices, such as smartwatches and fitness trackers, provides individuals with real-time health data. These devices can track vital signs, monitor sleep patterns, and even detect irregularities in heart rate or blood sugar levels. This valuable information allows individuals to better understand their overall health and take proactive steps towards improving it.
However, it is important to note that not all medical information available online is accurate or reliable. Misinformation and misleading advice can spread easily, potentially causing harm or leading to unnecessary worry. It is essential that individuals evaluate the credibility of the sources they rely on and consult with healthcare professionals to ensure they receive accurate and evidence-based information.
Overall, technology has undoubtedly improved access to medical information, empowering individuals to actively participate in their healthcare journey. By arming themselves with knowledge, patients can engage in meaningful discussions with their healthcare providers, make informed decisions, and become partners in their own care.
Remote Monitoring and Telemedicine
Technology has transformed healthcare delivery by enabling remote monitoring and telemedicine. These advancements have revolutionized the way medical consultations and care are provided, especially for individuals in remote areas or those with limited mobility.
Remote monitoring allows healthcare providers to remotely track and monitor patients’ health conditions. This is particularly beneficial for individuals with chronic illnesses or those recovering from surgical procedures. Devices such as wearable sensors or mobile applications can collect and transmit data, including vital signs, blood glucose levels, or medication adherence, to healthcare professionals. This real-time information enables early detection of any abnormalities or changes in a patient’s condition, allowing for timely interventions and adjustments to the treatment plan.
Telemedicine, on the other hand, refers to the use of telecommunications technology for medical consultations and follow-ups. Through video calls or secure messaging platforms, individuals can consult with healthcare providers without the need for face-to-face visits. This is particularly useful in situations where physical distances or travel limitations make in-person visits difficult or costly. Telemedicine not only improves access to healthcare services for individuals in remote areas but also reduces the burden on healthcare facilities by minimizing unnecessary visits and wait times.
Telemedicine has also proven to be invaluable during times of crisis, such as pandemics or natural disasters, when physical distancing measures are necessary. It allows individuals to receive medical advice, prescriptions, or even mental health support from the comfort and safety of their own homes.
Furthermore, telemedicine has facilitated specialized care by enabling consultations with specialists who may be located in a different city or even a different country. This eliminates the need for patients to travel long distances, incur travel expenses, and endure the stress associated with seeking specialized care. It allows healthcare professionals to collaborate on complex cases, share expertise, and provide the best possible care to patients regardless of geographic limitations.
While remote monitoring and telemedicine have undeniably improved access to healthcare, it is important to recognize that certain limitations exist. Not all medical conditions or situations can be adequately addressed through remote means, and in-person medical evaluations or procedures may still be necessary. Additionally, the digital divide and lack of access to technology can present barriers to widespread adoption, particularly for vulnerable populations and underserved communities.
Nevertheless, remote monitoring and telemedicine have opened up new frontiers in healthcare delivery, providing convenience, accessibility, and improved outcomes for both patients and healthcare providers.
Efficient and Accurate Record-Keeping
Technology has revolutionized record-keeping in the healthcare industry, replacing traditional paper-based systems with efficient and accurate digital health records. This shift has brought numerous benefits to both healthcare providers and patients alike.
Digital health records, also known as electronic health records (EHRs), provide a centralized and comprehensive collection of a patient’s medical history, diagnoses, treatments, and healthcare interactions. These records are stored electronically, making them easily accessible to authorized healthcare professionals across different specialties and settings.
One of the key advantages of digital health records is improved efficiency. With the click of a button, healthcare providers can access a patient’s complete medical history, eliminating the need to search through stacks of paper documents or wait for physical records to be transferred. This streamlines the workflow, reduces administrative burdens, and allows healthcare professionals to allocate more time to direct patient care.
Moreover, digital health records facilitate more accurate and complete documentation. Automated prompts and templates built into the EHR system help healthcare providers capture essential information, reducing the likelihood of errors or omissions. This enhances the quality of documentation, ensuring that critical details are recorded and minimizing the risk of miscommunication or misunderstanding between healthcare professionals.
The interoperability of digital health records also improves care coordination and communication among healthcare team members. Different healthcare providers involved in a patient’s care, such as primary care physicians, specialists, and pharmacists, can access and contribute to the patient’s EHR, ensuring seamless communication and continuity of care. This avoids the duplication of tests, reduces medication errors, and facilitates the sharing of vital information that is crucial for effective treatment planning.
Digital health records also offer enhanced security and privacy compared to physical records. Access to electronic records can be restricted to authorized personnel, and measures can be implemented to protect against unauthorized access or data breaches. This helps safeguard sensitive patient information, ensuring compliance with privacy regulations and maintaining patient trust.
However, despite these benefits, the adoption and implementation of digital health records come with certain challenges. Transitioning from a paper-based system to an electronic one requires proper training, resources, and infrastructure. It also requires careful consideration of data integrity, data migration, and ongoing maintenance to ensure the accuracy and security of the records.
Overall, the shift towards digital health records has revolutionized record-keeping in healthcare, leading to improved efficiency, accuracy, and collaboration among healthcare providers. It has transformed the way patient information is managed, ensuring that vital medical data is accessible, secure, and up-to-date, ultimately leading to better patient outcomes.
Enhanced Communication and Collaboration
Technology has significantly improved communication and collaboration among healthcare professionals, leading to more efficient and coordinated patient care. Gone are the days of relying solely on phone calls, faxes, or physical paper-based communication. Today, healthcare providers have access to a wide range of digital tools and platforms that facilitate seamless communication and collaboration.
One of the key benefits of technology in healthcare is the ability to securely exchange information and communicate in real-time. Secure messaging platforms, electronic health records (EHRs), and teleconferencing tools allow healthcare professionals to share patient information, discuss treatment plans, and collaborate on complex cases. This enables more efficient communication and eliminates the need for time-consuming phone calls or back-and-forth exchanges.
With the use of EHR systems, healthcare providers can access patient records and share critical information instantaneously. This eliminates the need for multiple phone calls or physical transfers of records, minimizing the risk of miscommunication or delays in care. It also allows for better coordination among different healthcare team members, ensuring that all providers have access to the most up-to-date patient information.
Teleconferencing tools and video consultations have also revolutionized communication in healthcare. Healthcare professionals can now conduct virtual meetings and consultations, no matter where they are located. This is particularly beneficial in situations where face-to-face meetings are not feasible, such as during emergencies or when dealing with remote patients. Video consultations allow for visual assessments, discussions of treatment plans, and the ability to share visuals such as medical images or test results.
Moreover, technology has facilitated interdisciplinary collaboration and team-based care. Healthcare professionals from different specialties can easily communicate and share expertise through collaborative platforms. This fosters a holistic approach to patient care, where medical professionals can work together to develop comprehensive treatment plans and provide the best possible care to patients.
Technology has also improved communication between healthcare providers and patients. Online patient portals, secure messaging systems, and mobile healthcare applications allow patients to communicate with their healthcare providers, ask questions, seek advice, and receive updates on their care. This promotes active patient engagement and empowers individuals to actively participate in their own healthcare journey.
While technology has greatly enhanced communication and collaboration in healthcare, it is important to recognize some limitations. Not all healthcare professionals or organizations have equal access to technology, and there may be variations in the adoption and use of digital platforms. Additionally, the reliance on technology may also pose challenges in terms of privacy and data security. Ongoing efforts need to be made to mitigate these challenges and ensure the responsible and ethical use of technology in healthcare communication.
Overall, technology has revolutionized communication and collaboration in healthcare, enabling more efficient information exchange, facilitating interdisciplinary teamwork, and empowering patients to take an active role in their care. The use of digital platforms and tools has improved the quality and efficiency of patient care, leading to better health outcomes.
Advanced Diagnostic Tools
Technology has brought remarkable advancements in diagnostic tools, revolutionizing the way medical conditions are identified and diagnosed. These tools enable healthcare professionals to detect diseases earlier, with greater accuracy, and in a minimally invasive manner.
One of the key advancements in diagnostic technology is medical imaging. Technologies such as X-rays, computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and ultrasound provide detailed images of the internal structures of the body. These imaging techniques help healthcare professionals visualize and identify abnormalities, such as fractures, tumors, or organ damage, aiding in the diagnosis and treatment planning process.
Another significant advancement is the development of molecular diagnostic tools. These tools allow healthcare professionals to analyze DNA, RNA, and proteins to identify specific genetic variations, mutations, or markers associated with diseases. Molecular diagnostics play a crucial role in the early detection and personalized treatment of various conditions, including cancer, infectious diseases, and genetic disorders.
Laboratory diagnostics have also greatly benefited from technological innovations. Automated laboratory systems and high-throughput analyzers enable faster and more accurate analysis of blood samples, urine samples, and other bodily fluids. This enables rapid detection of infections, monitoring of chronic diseases, and assessment of organ function.
Furthermore, the advancement of point-of-care testing devices has revolutionized diagnostics, particularly in resource-limited settings or during emergency situations. Portable devices allow healthcare professionals to perform immediate tests and obtain fast results, eliminating the need for sending samples to a central laboratory and waiting for the results. Point-of-care testing is particularly valuable in diagnosing conditions such as infectious diseases, cardiovascular events, or diabetes.
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning have also made significant contributions to diagnostic capabilities. These technologies can analyze large sets of medical data, including imaging studies, laboratory results, and patient histories, to detect patterns and make accurate predictions. AI-powered diagnostic tools can assist healthcare professionals in interpreting data, supporting clinical decision-making, and improving diagnostic accuracy.
While the advancements in diagnostic tools have greatly improved patient care, it is important to recognize certain challenges. The cost of acquiring and maintaining advanced diagnostic equipment can be prohibitive, particularly for healthcare facilities with limited resources. Additionally, the interpretation of diagnostic results, especially in complex cases, still requires the expertise and experience of trained healthcare professionals.
Overall, technology has revolutionized the field of diagnostics, enabling earlier, more accurate, and less invasive identification of diseases and conditions. The continued development and implementation of advanced diagnostic tools hold great promise in improving patient outcomes, optimizing treatment plans, and enhancing healthcare delivery.
Precision Medicine and Personalized Treatments
One of the most exciting advancements in healthcare is the emergence of precision medicine and personalized treatments, made possible by advancements in technology and the availability of vast amounts of data. Precision medicine aims to provide tailored and targeted treatments, taking into account an individual’s unique genetic makeup, environmental factors, and lifestyle choices.
Advancements in genomic sequencing technology have revolutionized the field of precision medicine. With the ability to sequence an individual’s genome, healthcare professionals can identify specific genetic variations or mutations that may be associated with certain diseases or drug responses. This genetic information allows for more precise diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment selection.
By analyzing an individual’s genetic profile, healthcare providers can determine whether a patient is predisposed to certain diseases or conditions. This enables proactive monitoring, lifestyle modifications, or early interventions to prevent or mitigate the onset of certain diseases.
Moreover, personalized treatments based on an individual’s genetic information can enhance the efficacy and safety of medications. Pharmacogenomics, the study of how genetic variations influence drug response, helps healthcare professionals determine the most appropriate medications and their dosages for each individual. This minimizes the risk of adverse reactions and improves treatment outcomes.
Another aspect of precision medicine is the use of biomarkers to guide treatment decisions. Biomarkers are measurable indicators, such as specific molecules or genetic markers, that can provide information about the progression of a disease or a patient’s response to treatment. By monitoring these biomarkers, healthcare professionals can tailor treatment regimens and adjust therapies as needed, leading to more effective and personalized care.
Technology has also enabled the integration of various types of data, such as clinical data, genomic data, and lifestyle data, to provide a comprehensive understanding of an individual’s health. By analyzing this diverse set of data, healthcare professionals can identify patterns, risk factors, and treatment options that are most effective for each patient.
While precision medicine holds great promise, it also presents certain challenges. The interpretation and integration of large amounts of diverse data require advanced analytics and computational capabilities. Additionally, there are ethical, legal, and privacy considerations associated with the collection and use of genetic and personal health information.
Overall, precision medicine and personalized treatments have the potential to revolutionize healthcare by moving away from a one-size-fits-all approach to a more individualized and precise approach. As technology continues to advance and our understanding of human genetics deepens, the benefits of precision medicine in improving patient outcomes and optimizing treatment plans will become increasingly apparent.
Improved Patient Care and Outcomes
Technology has played a significant role in improving patient care and outcomes across various aspects of healthcare delivery. From enhanced monitoring and treatment options to improved patient engagement, technological advancements have transformed the way healthcare is provided and experienced.
One of the key contributions of technology to patient care is the ability to monitor individuals more closely and in real-time. Wearable devices and remote monitoring tools allow for continuous tracking of vital signs, symptoms, and treatment adherence. This enables healthcare professionals to identify early warning signs of complications, detect changes in a patient’s condition, and intervene promptly. By providing a more comprehensive view of a patient’s health, these technologies facilitate proactive care and management of chronic conditions, ultimately improving patient outcomes.
Furthermore, technology has empowered patients to become more engaged in their own care. Patient portals, mobile applications, and online health resources facilitate access to personal health records, medical information, and educational resources. Patients can schedule appointments, view test results, and communicate securely with their healthcare providers, promoting active participation and collaboration in the decision-making process. Additionally, technologies that promote self-management, such as medication reminder apps or activity trackers, help individuals take control of their health and adhere to treatment plans, leading to better health outcomes.
With the use of telemedicine and remote consultations, access to specialized care has also improved. Individuals in remote or underserved areas can now seek expert medical opinions without the need for extensive travel or long waiting periods. This timely access to specialized care allows for earlier interventions, improved coordination among healthcare providers, and more efficient treatment planning. As a result, patients can receive more targeted and appropriate care, leading to better outcomes.
Technology has also improved communication and coordination among healthcare providers, reducing medical errors and promoting safer care. Electronic health records facilitate the sharing of critical patient information among different healthcare professionals involved in a patient’s care. This eliminates the need for redundant tests or procedures and ensures that all providers have access to up-to-date and comprehensive medical information. Increased communication and collaboration among providers reduce the likelihood of miscommunication, enhances care coordination, and ultimately improves patient safety.
Moreover, technology has enabled the development of personalized treatment approaches, tailoring care to an individual’s unique characteristics and needs. Precision medicine, as discussed previously, utilizes genetic information and biomarkers to guide treatment decisions, leading to more targeted therapies and improved treatment outcomes. By considering an individual’s specific genetic makeup, lifestyle factors, and disease characteristics, healthcare professionals can design treatment plans that are more effective, minimize side effects, and optimize outcomes.
While technology has brought significant improvements to patient care, challenges do exist. The digital divide, lack of access to technology, and variations in technological literacy can create barriers to the widespread adoption and benefits of these advancements. Additionally, ethical considerations such as data privacy and security need to be addressed to ensure the responsible and ethical use of patient information.
Overall, technology has revolutionized patient care, delivering improved outcomes through closer monitoring, patient engagement, access to specialized care, enhanced communication and collaboration, and personalized treatment approaches. Continued advancements in technology hold great promise in further improving patient care and outcomes, making healthcare more efficient, effective, and patient-centered.
Streamlined Administrative Processes
Technology has played a pivotal role in streamlining administrative processes within the healthcare industry, reducing inefficiencies, and improving workflow. From appointment scheduling to billing and insurance claims, technological advancements have transformed the way administrative tasks are managed and executed.
One of the key areas that technology has greatly impacted is appointment scheduling and management. Digital appointment scheduling systems allow patients to book appointments online, eliminating the need for phone calls and reducing wait times. Automated reminders and notifications can be sent to patients, reducing no-show rates and ensuring better management of healthcare resources. Additionally, digital scheduling systems provide healthcare providers with a centralized platform to manage appointments, allowing for efficient allocation of time and resources.
Technology has also revolutionized medical billing and insurance claims processes. Electronic billing systems have replaced paper-based billing, making the submission and processing of claims faster and more accurate. By automating billing processes, healthcare providers can reduce errors and turnaround times, enabling faster reimbursement and improved cash flow. Additionally, electronic claim submission allows for quicker communication with insurance providers, reducing payment delays and improving the overall efficiency of the billing process.
Moreover, technology has facilitated efficient and secure storage and retrieval of patient records. Digital record-keeping systems, such as electronic health records (EHRs), have replaced traditional paper-based systems, reducing the need for physical storage space and minimizing the risk of lost or misplaced records. EHRs allow for quick and easy access to patient information, eliminating the need to search through paper files and improving the speed and accuracy of data retrieval.
Another area where technology has streamlined administrative processes is inventory management. Automated inventory tracking systems help healthcare providers monitor and manage medical supplies and equipment more effectively. These systems ensure that stock levels are optimized, minimizing wastage and reducing the likelihood of shortages. By automating inventory management, healthcare institutions can reduce costs, improve efficiency, and ensure the availability of necessary supplies when needed.
Furthermore, technology has simplified communication with patients and among healthcare professionals. Secure messaging platforms and patient portals allow for efficient and secure communication, reducing the reliance on phone calls and physical correspondence. Healthcare professionals can collaborate and share information seamlessly, improving communication and coordination of care. These digital communication channels also enhance patient engagement, allowing patients to ask questions, receive updates, and access vital information conveniently.
While technology has streamlined administrative processes, there are certain challenges that need to be addressed. Implementation and adoption of new technology require proper training, investment, and change management. Maintaining data security and privacy is also a crucial consideration, given the sensitive nature of patient information.
Overall, technology has played a significant role in streamlining administrative processes within the healthcare industry. From appointment scheduling to billing, record-keeping, inventory management, and communication, technological advancements have improved efficiency, accuracy, and overall productivity. By automating and digitizing administrative tasks, healthcare providers can focus more on delivering quality patient care and improving the overall healthcare experience.
Ethical Considerations and Potential Challenges
While technology has brought significant advancements to the healthcare industry, it also raises important ethical considerations and potential challenges that need to be addressed. These considerations revolve around privacy, data security, equity in access, and the responsible use of emerging technologies.
One of the primary ethical concerns is the protection of patient privacy and the security of personal health information. As more data is collected and shared digitally, there is an increased risk of data breaches and unauthorized access. Healthcare organizations must ensure robust data security measures are in place to protect patient confidentiality and comply with privacy regulations. Patients should be made aware of how their data is being used, and their consent must be obtained before sharing their information.
Another ethical consideration is the equitable access to technology and healthcare services. While technology has the potential to improve healthcare outcomes, there are disparities in access to technology, particularly among disadvantaged populations or those in rural and underserved areas. Efforts should be made to bridge this digital divide and ensure that the benefits of technology are accessible to all, regardless of socioeconomic status or geographic location.
With the rapid pace of technological advancements, it is imperative to use emerging technologies responsibly and ethically. For instance, the use of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning algorithms in healthcare decision-making should be transparent, explainable, and accountable. The algorithms should be regularly audited and validated to ensure fairness, accuracy, and mitigation of bias. Unintended consequences or biases in the algorithms should be continuously monitored and addressed to prevent discrimination or disparities in healthcare delivery.
Additionally, healthcare professionals must navigate the ethical implications of personal health data ownership and usage. As patients increasingly share health data through wearable devices or health-tracking apps, it is essential to establish clear guidelines on how this data is collected, stored, and shared. Patients should have control over their data and be informed about how it may be used for research or other purposes. Proper informed consent processes should be in place to ensure individuals understand the potential risks and benefits of sharing their data.
Moreover, the reliance on technology should not lead to a loss of human connection and empathy in healthcare. While technology can improve efficiency and access to care, it is essential to maintain a balance that preserves the importance of the patient-provider relationship. Healthcare professionals must continue to prioritize compassionate and holistic care, leveraging technology to augment their abilities rather than replacing the human touch.
Finally, there are ongoing debates surrounding the cost-effectiveness of technological advancements and their impact on healthcare affordability. While technology can lead to improved outcomes and efficiency, the costs associated with implementing and maintaining these technologies can create financial burdens for healthcare organizations. Ensuring that these advancements are cost-effective and provide value for patients and healthcare systems is vital to achieve equitable healthcare delivery.
Addressing these ethical considerations and potential challenges requires collaboration among healthcare professionals, policymakers, and technology developers. By establishing clear guidelines, regulations, and ethical frameworks, we can harness the benefits of technology while minimizing risks and ensuring that healthcare remains patient-centered, equitable, and ethically sound.
Conclusion
The integration of technology in healthcare has brought about tremendous advancements, improving access to medical information, enhancing patient care, and transforming the way healthcare is delivered and experienced. From increased access to medical information to remote monitoring devices, advanced diagnostic tools, and personalized treatments, technology has revolutionized the healthcare landscape.
With the use of technology, individuals have unprecedented access to a wealth of medical knowledge, empowering them to take a more active role in their health and well-being. Remote monitoring and telemedicine have made healthcare more accessible and convenient, particularly for those in remote areas or with limited mobility. Advanced diagnostic tools enable earlier and more accurate detection of diseases, while personalized treatments based on individual genetic profiles have paved the way for targeted and effective interventions.
Technology has also streamlined administrative processes, optimizing efficiency, reducing errors, and improving communication and collaboration among healthcare professionals. Additionally, ethical considerations, such as privacy and data security, equity in access, and responsible use of emerging technologies, must be addressed to ensure that the benefits of technology are maximized while minimizing risks and disparities.
In conclusion, technology has transformed the healthcare industry, enhancing patient care, improving outcomes, and paving the way for more personalized and precise approaches to medicine. As technology continues to advance, it is essential for healthcare professionals, policymakers, and technology developers to work together to ensure responsible and ethical use of technology, foster equal access to healthcare, and maintain the human touch in healthcare delivery. By harnessing the power of technology, we can continue to create a healthcare system that is more efficient, patient-centered, equitable, and ultimately leads to better health outcomes for individuals worldwide.