Home>Misc>Featured>What Is The Difference Between Muscular Endurance And Cardiovascular Endurance


Featured
What Is The Difference Between Muscular Endurance And Cardiovascular Endurance
Modified: January 2, 2024
Discover the featured difference between muscular endurance and cardiovascular endurance. Enhance your fitness knowledge and optimize your training routine for improved performance.
Introduction
Muscular endurance and cardiovascular endurance are two essential components of physical fitness that contribute to overall health and performance. While they both involve endurance, they target different aspects of the body and have distinct benefits. Understanding the difference between muscular endurance and cardiovascular endurance is crucial for designing an effective fitness routine and achieving optimal results.
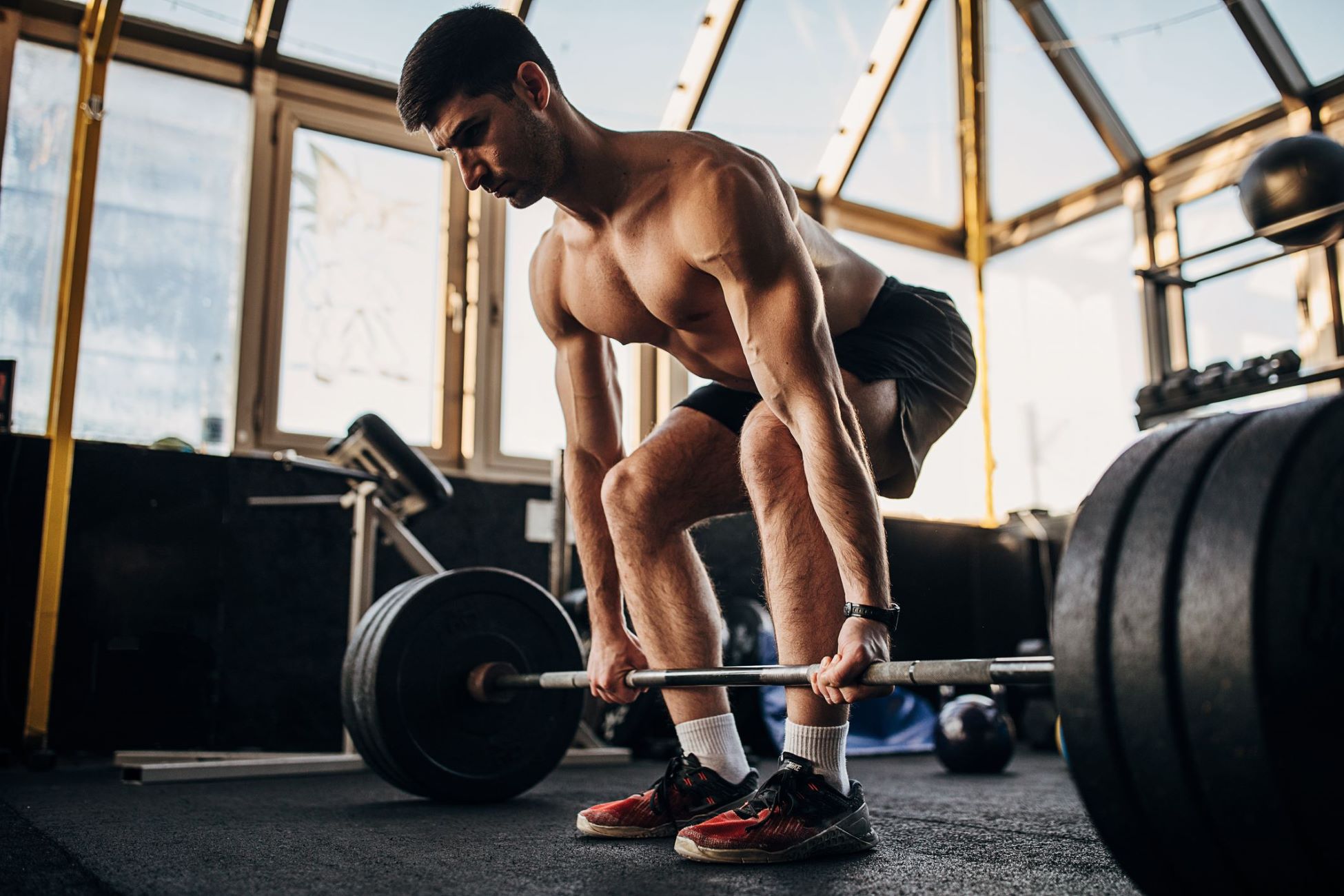
Muscular endurance refers to the ability of a muscle or group of muscles to exert force repeatedly over an extended period. It involves the capacity to sustain muscle contractions without fatigue. On the other hand, cardiovascular endurance, also known as cardiorespiratory endurance, refers to the ability of the heart, lungs, and circulatory system to supply oxygenated blood to the working muscles during prolonged periods of physical activity.
Both types of endurance play significant roles in various activities, from everyday tasks to sports performance. However, they differ in terms of the physiological demands placed on the body and the specific benefits they provide. This article will explore the key differences between muscular endurance and cardiovascular endurance and highlight the importance of each for overall fitness and well-being.
Definition of Muscular Endurance
Muscular endurance refers to the ability of a muscle or group of muscles to perform repeated contractions against resistance without fatigue. It is the muscle’s ability to sustain physical activity or exercise over an extended period. Muscular endurance is an essential component of overall fitness, as it directly impacts our ability to perform daily tasks and participate in physical activities.
When we engage in activities that require muscular endurance, our muscles are able to maintain a level of force for an extended period without experiencing significant fatigue. This endurance can be specific to a particular muscle group, such as the arms or legs, or it can be generalized to include multiple muscle groups throughout the body.
Several factors influence muscular endurance, including muscle fiber composition, muscle size, and the energy systems utilized during exercise. Slow-twitch muscle fibers, also known as Type I fibers, are primarily responsible for endurance activities, as they have a high capacity for energy production and are resistant to fatigue. On the other hand, fast-twitch muscle fibers, or Type II fibers, are better suited for short bursts of intense power but fatigue quickly.
Improving muscular endurance involves training the muscles and energy systems to withstand prolonged periods of activity. This can be achieved through various exercises, such as bodyweight exercises, resistance training, and circuit training. By gradually increasing the repetitions, resistance, or duration of the exercises, the muscles adapt and become more efficient at sustaining contractions over time.
Muscular endurance has numerous practical applications in everyday life. It allows us to perform activities such as lifting and carrying heavy objects, maintaining proper posture, and withstanding prolonged periods of physical exertion. Additionally, it plays a crucial role in sports performance, as it enhances the ability to maintain consistent performance over an entire match, game, or race.
Overall, muscular endurance is essential for maintaining functional fitness and performing physical tasks efficiently. By incorporating exercises that target muscular endurance into our fitness routines, we can improve our ability to perform daily activities with ease and enhance our overall physical performance.
Definition of Cardiovascular Endurance
Cardiovascular endurance, also referred to as cardiorespiratory endurance, is the ability of the heart, lungs, and circulatory system to supply oxygen-rich blood to the working muscles during prolonged periods of physical activity. It is a measure of the body’s efficiency in supplying oxygen to meet the demands of exercise.
When we engage in activities that demand cardiovascular endurance, such as running, cycling, swimming, or brisk walking, our heart rate increases to pump more oxygenated blood to the muscles. This sustained increase in heart rate helps improve the cardiovascular system’s capacity to deliver oxygen and nutrients to the working muscles while removing waste products, such as carbon dioxide.
The key component of cardiovascular endurance is the aerobic system, which utilizes oxygen to convert stored carbohydrates and fats into energy. This system allows for sustained, low-to-moderate intensity exercise over an extended duration. It is characterized by the efficient functioning of the heart, lungs, blood vessels, and respiratory system.
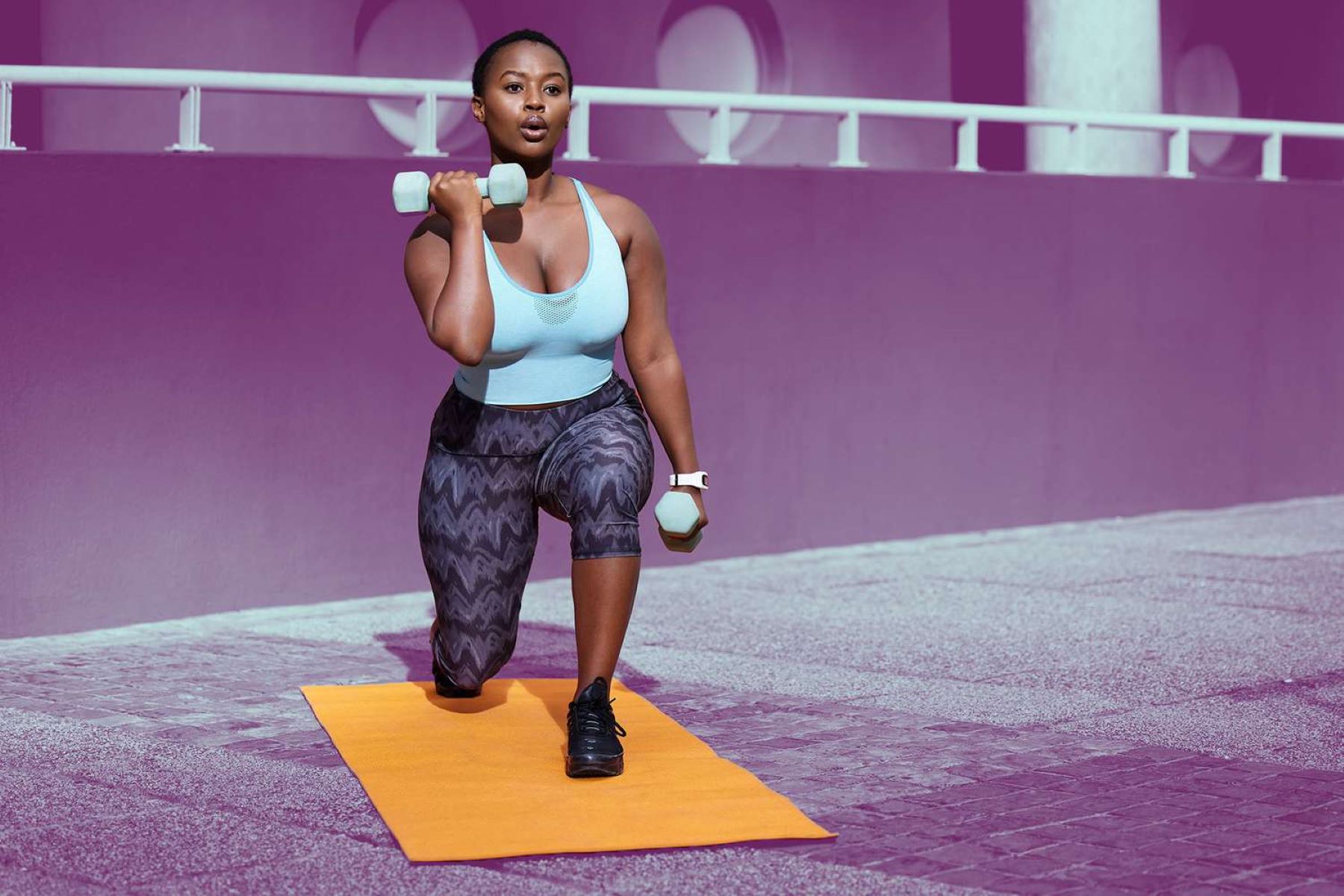
Improving cardiovascular endurance involves regular aerobic exercise that elevates the heart rate and challenges the cardiovascular system. Activities such as running, cycling, swimming, and aerobic classes are effective ways to improve cardiovascular endurance. Gradually increasing the duration or intensity of the exercise helps stimulate adaptations within the cardiovascular system, leading to improved endurance over time.
Having good cardiovascular endurance offers numerous benefits for overall health and well-being. It improves the efficiency of the cardiovascular system, strengthens the heart muscle, reduces the risk of cardiovascular diseases, such as heart disease and high blood pressure, and aids in weight management. Additionally, it can enhance stamina, energy levels, and mental clarity.
Cardiovascular endurance is crucial not only for athletes and fitness enthusiasts but also for individuals seeking to maintain a healthy lifestyle. It enables us to engage in daily activities without experiencing excessive fatigue, shortness of breath, or elevated heart rate. Moreover, it lays the foundation for more intense physical activities and sports by providing a solid cardiovascular base.
Incorporating regular aerobic exercise into our fitness routines is key to improving cardiovascular endurance. By engaging in activities that elevate the heart rate and challenge the cardiovascular system, we can enhance our endurance, overall fitness, and quality of life.
Key Differences between Muscular Endurance and Cardiovascular Endurance
Muscular endurance and cardiovascular endurance are two distinct components of physical fitness that differ in terms of the physiological systems involved, the specific demands placed on the body, and the benefits they provide. Here are the key differences between muscular endurance and cardiovascular endurance:
- Physiological Systems: Muscular endurance primarily depends on the muscle fibers’ ability to sustain repeated contractions without fatigue. It involves the efficiency of the muscles in generating and maintaining force over time. In contrast, cardiovascular endurance focuses on the efficiency of the heart, lungs, and circulatory system in supplying oxygen to the working muscles during sustained physical activity. It revolves around the aerobic system’s capacity to provide energy for prolonged exercise.
- Specific Demands: Muscular endurance is more directly related to muscle strength and power. It is essential for activities that require repetitive muscle contractions, such as lifting weights, performing bodyweight exercises, or holding a yoga pose. On the other hand, cardiovascular endurance is particularly crucial for activities that involve continuous, rhythmic movement over an extended period. Running, swimming, cycling, and aerobic exercises are examples of activities that challenge and improve cardiovascular endurance.
- Training Methods: Improving muscular endurance typically involves performing exercises that target specific muscle groups and gradually increasing the repetitions, duration, or resistance. Bodyweight exercises, resistance training, and circuit training are effective ways to enhance muscular endurance. On the other hand, cardiovascular endurance is improved through aerobic exercises that elevate the heart rate and challenge the cardiovascular system. Running, cycling, swimming, and aerobic classes are popular methods for boosting cardiovascular endurance.
- Benefits: Muscular endurance enhances the ability to perform tasks that require sustained muscle contractions, such as carrying heavy objects or maintaining proper posture. It also plays a crucial role in sports performance by allowing athletes to maintain consistent performance throughout a match or game. Cardiovascular endurance, on the other hand, improves the overall efficiency of the cardiovascular system, strengthens the heart muscle, reduces the risk of cardiovascular diseases, and enhances stamina and energy levels. It can also aid in weight management and improve mental clarity.
- Interplay: While muscular endurance and cardiovascular endurance are distinct components, they are interconnected and can influence each other. For example, improved cardiovascular endurance can enhance the ability to sustain muscular endurance activities by increasing oxygen delivery to the muscles. Similarly, enhanced muscular endurance can contribute to improved cardiovascular efficiency by reducing the effort required for subsequent physical activity.
Incorporating exercises that target both muscular endurance and cardiovascular endurance into a well-rounded fitness routine is important for overall fitness and performance. By understanding the differences between these two forms of endurance, individuals can design effective training programs and optimize their physical fitness levels.
Importance of Muscular Endurance
Muscular endurance plays a significant role in overall fitness and daily life activities. Here are some key reasons why muscular endurance is important:
- Functional Fitness: Muscular endurance is crucial for performing everyday tasks that require sustained muscular effort. It allows us to lift and carry heavy objects, perform repetitive movements, and maintain proper posture for extended periods. Whether it’s carrying groceries, moving furniture, or engaging in household chores, muscular endurance helps us perform these tasks efficiently and without excessive fatigue.
- Sports Performance: Muscular endurance is vital for athletes and individuals involved in sports. It enables athletes to maintain consistent performance throughout a game, match, or race. In sports like soccer, basketball, and tennis, where continuous movement, repetitive actions, and sustained effort are required, having good muscular endurance can provide a competitive advantage, allowing athletes to perform at a high level without fatigue.
- Injury Prevention: Building muscular endurance helps reduce the risk of injuries. Muscles that have good endurance can better stabilize joints, absorb impact, and withstand repetitive movements. It can help prevent overuse injuries, such as tendonitis or strains, by enabling the muscles to handle the demands placed on them without becoming fatigued and compromising form.
- Muscle Tone and Definition: Muscular endurance training can contribute to improved muscle tone and definition. The sustained contractions and continuous effort involved in endurance exercises can help develop lean muscle mass and increase muscular density. This can lead to a more sculpted and defined physique.
- Metabolic Health: Muscular endurance training has positive effects on metabolic health. It can increase the body’s basal metabolic rate, leading to greater calorie expenditure even at rest. Additionally, building muscle through endurance exercises can improve insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism, lowering the risk of metabolic disorders like diabetes.
Overall, muscular endurance is crucial for maintaining functional fitness, improving sports performance, preventing injuries, enhancing muscle tone and definition, and promoting metabolic health. By incorporating exercises that target muscular endurance into our fitness routines, we can reap these benefits and enhance our overall physical well-being.
Importance of Cardiovascular Endurance
Cardiovascular endurance plays a crucial role in overall fitness and well-being. Here are some key reasons why cardiovascular endurance is important:
- Heart Health: Engaging in activities that improve cardiovascular endurance strengthens the heart muscle and enhances its efficiency. Regular aerobic exercise helps lower resting heart rate, improve blood circulation, and reduce the risk of heart disease. It can also regulate blood pressure and lower LDL (bad) cholesterol levels, promoting cardiovascular health.
- Enhanced Stamina: Improving cardiovascular endurance increases stamina and energy levels. It enables individuals to engage in physical activity for longer durations without feeling excessively fatigued. This endurance can be beneficial in various settings, from performing daily tasks to participating in recreational activities or sports.
- Weight Management: Cardiovascular exercise aids in weight management by increasing calorie expenditure. Engaging in activities that elevate heart rate and challenge the cardiovascular system helps burn calories and reduce body fat. Combined with a balanced diet, regular cardiovascular exercise can contribute to achieving and maintaining a healthy weight.
- Mental Well-being: Cardiovascular exercise has profound effects on mental health. It promotes the release of endorphins, also known as “feel-good” hormones, which can alleviate stress, anxiety, and depression. Regular aerobic exercise has been shown to enhance cognitive function, improve memory, and increase overall mental clarity and focus.
- Disease Prevention: Cardiovascular endurance has been linked to a decreased risk of various chronic diseases. Regular aerobic exercise helps reduce the risk of conditions such as type 2 diabetes, stroke, metabolic syndrome, and certain types of cancer. It can also improve immune function, leading to better overall health and a stronger defense against illnesses.
Improving cardiovascular endurance is a key component of maintaining a healthy lifestyle. By incorporating aerobic exercises that challenge the heart and respiratory system into our fitness routines, we can experience the benefits of improved heart health, enhanced stamina, better weight management, boosted mental well-being, and reduced risk of chronic diseases.
How to Improve Muscular Endurance
Improving muscular endurance involves specific exercises and training methods that target the muscles’ ability to sustain contractions over an extended period. Here are some effective strategies to enhance muscular endurance:
- Circuit Training: Circuit training involves performing a series of exercises targeting different muscle groups with minimal rest in between. This type of training helps improve muscular endurance by challenging the muscles to sustain multiple contractions within a short period. Incorporate a combination of bodyweight exercises, resistance exercises, and cardiovascular exercises into your circuit training routine.
- High Repetition, Low Resistance: To improve muscular endurance, focus on performing exercises with higher repetitions and lower resistance. This approach helps train the muscles to sustain contractions for a longer duration without fatiguing quickly. For example, instead of lifting heavy weights with fewer repetitions, opt for lighter weights or resistance bands and perform 15-20 repetitions per set.
- Bodyweight Exercises: Bodyweight exercises are an excellent way to improve muscular endurance as they engage multiple muscle groups simultaneously. Examples of bodyweight exercises include push-ups, squats, lunges, planks, and burpees. Incorporate these exercises into your routine and gradually increase the number of repetitions or duration of each exercise.
- Tempo Training: Tempo training involves controlling the speed of your movements during exercises. By slowing down the eccentric (lengthening) phase of the exercise, you challenge the muscles to work harder and sustain contractions for a longer time. For example, perform squats by taking 3-4 seconds to lower yourself down and explosively raise back up.
- Progressive Overload: To continuously improve muscular endurance, gradually increase the intensity of your workouts over time. This can be achieved by increasing the number of repetitions, sets, or resistance. By consistently challenging your muscles with progressively higher demands, you promote adaptation and improvement in muscular endurance.
- Active Recovery: Allow your muscles to recover properly between workouts to prevent overuse injuries and optimize performance. Incorporate active recovery exercises, such as stretching, foam rolling, and low-intensity cardiovascular exercises, into your routine. Active recovery promotes blood flow to the muscles, aids in muscle repair, and reduces post-workout soreness.
Remember to listen to your body and gradually progress your workouts to avoid overexertion or injury. Consistency is key when it comes to improving muscular endurance, so aim for regular workouts that challenge and progressively push your limits.
How to Improve Cardiovascular Endurance
Improving cardiovascular endurance involves exercises that challenge the heart, lungs, and circulatory system. Here are some effective strategies to enhance cardiovascular endurance:
- Aerobic Exercises: Engage in activities that elevate your heart rate and sustain it for an extended period. Running, cycling, swimming, brisk walking, and dancing are excellent aerobic exercises that can improve cardiovascular endurance. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic activity per week.
- Interval Training: Incorporate high-intensity interval training (HIIT) into your routine. Alternate between periods of intense effort and active recovery. For example, sprint for 30 seconds, followed by 1 minute of jogging or walking, then repeat the cycle several times. HIIT workouts challenge the cardiovascular system and improve its capacity to recover and perform at higher intensities.
- Long Slow Distance (LSD) Training: Include longer-duration workouts at a lower intensity, such as steady-state cardio. These workouts involve maintaining a moderate level of intensity for an extended period. Going for a long run, bike ride, or swim at a sustainable pace helps build endurance and improves the cardiovascular system’s efficiency.
- Cross-Training: Incorporate a variety of exercises into your routine to work different muscle groups and challenge your cardiovascular system. Mixing aerobic exercises like running with activities such as swimming or cycling helps prevent boredom, overuse injuries, and provides a more comprehensive cardiovascular workout.
- Progressive Overload: Gradually increase the intensity, duration, or frequency of your cardiovascular workouts to continuously challenge and improve your endurance. Progressively overload your cardiovascular system by increasing the distance, speed, or resistance of your exercises. This gradual progression ensures that your cardiovascular system adapts and becomes more efficient over time.
- Rest and Recovery: Adequate rest and recovery are essential for improving cardiovascular endurance. On rest days, give your body time to recover and repair. This allows the cardiovascular system to adapt and become stronger. Include active recovery exercises, such as light cardio or gentle stretching, to promote blood circulation and reduce muscle soreness.
Consistency is key when it comes to improving cardiovascular endurance. Aim for regular workouts, gradually increase the intensity and duration of your exercises, and listen to your body to avoid overexertion. By incorporating a variety of cardiovascular exercises and challenging your cardiovascular system progressively, you can enhance your endurance and overall cardiovascular health.
Conclusion
Developing both muscular endurance and cardiovascular endurance is crucial for overall fitness and well-being. While they are distinct components of physical fitness, they work together to enhance our performance in various activities and improve our health.
Muscular endurance focuses on the ability of muscles to sustain contractions over an extended period, allowing us to perform repetitive movements and maintain proper posture. It is important for everyday tasks and sports performance. On the other hand, cardiovascular endurance revolves around the efficiency of the heart, lungs, and circulatory system to supply oxygen-rich blood to the working muscles during sustained physical activity. It supports overall heart health, stamina, and energy levels.
To improve muscular endurance, incorporating circuit training, high repetitions with low resistance, bodyweight exercises, and gradually increasing intensity are effective strategies. For cardiovascular endurance, engaging in aerobic exercises, interval training, long slow distance training, cross-training, and progressively overloading workouts are recommended.
Both forms of endurance offer numerous benefits beyond physical fitness. They contribute to weight management, reduce the risk of chronic diseases, enhance mental well-being, and promote overall health and longevity.
Incorporating exercises that challenge both muscular endurance and cardiovascular endurance into our fitness routines is essential for a well-rounded approach to fitness. By understanding the differences between these two forms of endurance and implementing strategies to improve them, we can optimize our physical performance, improve our health, and lead active and fulfilling lives.