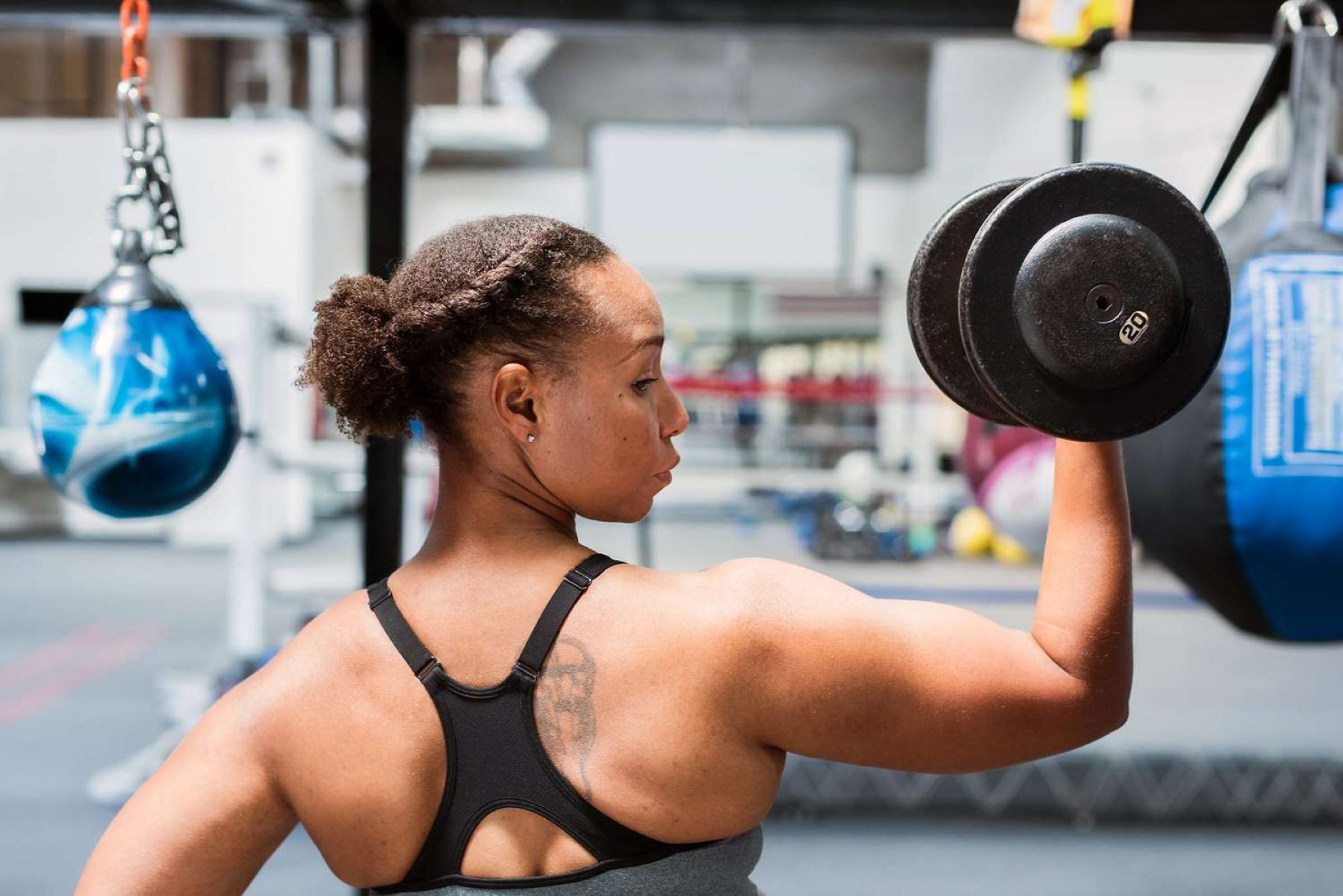Home>Misc>Featured>What Is The Difference Between Muscular Strength And Muscular Endurance?


Featured
What Is The Difference Between Muscular Strength And Muscular Endurance?
Modified: January 22, 2024
Learn about the distinction between muscular strength and muscular endurance in this featured article. Discover how these two concepts affect your fitness journey.
Introduction
The terms “muscular strength” and “muscular endurance” are often used interchangeably, but they actually refer to two different aspects of muscle performance. Understanding the difference between these two terms is crucial for individuals seeking to improve their overall fitness and achieve their specific goals.
Muscular strength refers to the maximum amount of force that a muscle or group of muscles can generate. It is determined by factors such as muscle size, muscle fiber type, and neurological factors. On the other hand, muscular endurance is the ability of a muscle or group of muscles to repeatedly exert force over a period of time. It is influenced by factors such as muscle fiber efficiency, aerobic capacity, and resistance to fatigue.
While both muscular strength and muscular endurance are important components of physical fitness, they serve different purposes. Muscular strength is essential for activities that require short bursts of intense exertion, such as lifting heavy weights or performing explosive movements. Muscular endurance, on the other hand, is crucial for activities that require sustained effort over an extended period of time, such as running a marathon or participating in endurance sports.
Throughout this article, we will explore the definitions of muscular strength and muscular endurance, the factors that affect each of them, and their respective importance in achieving optimal fitness. We will also discuss different training techniques that can be employed to enhance both muscular strength and muscular endurance.
Understanding the difference between muscular strength and muscular endurance is key to developing a well-rounded fitness program that addresses both aspects effectively. By integrating specific exercises and training methods for each component, individuals can optimize their overall performance and reach their fitness goals.
Definition of Muscular Strength
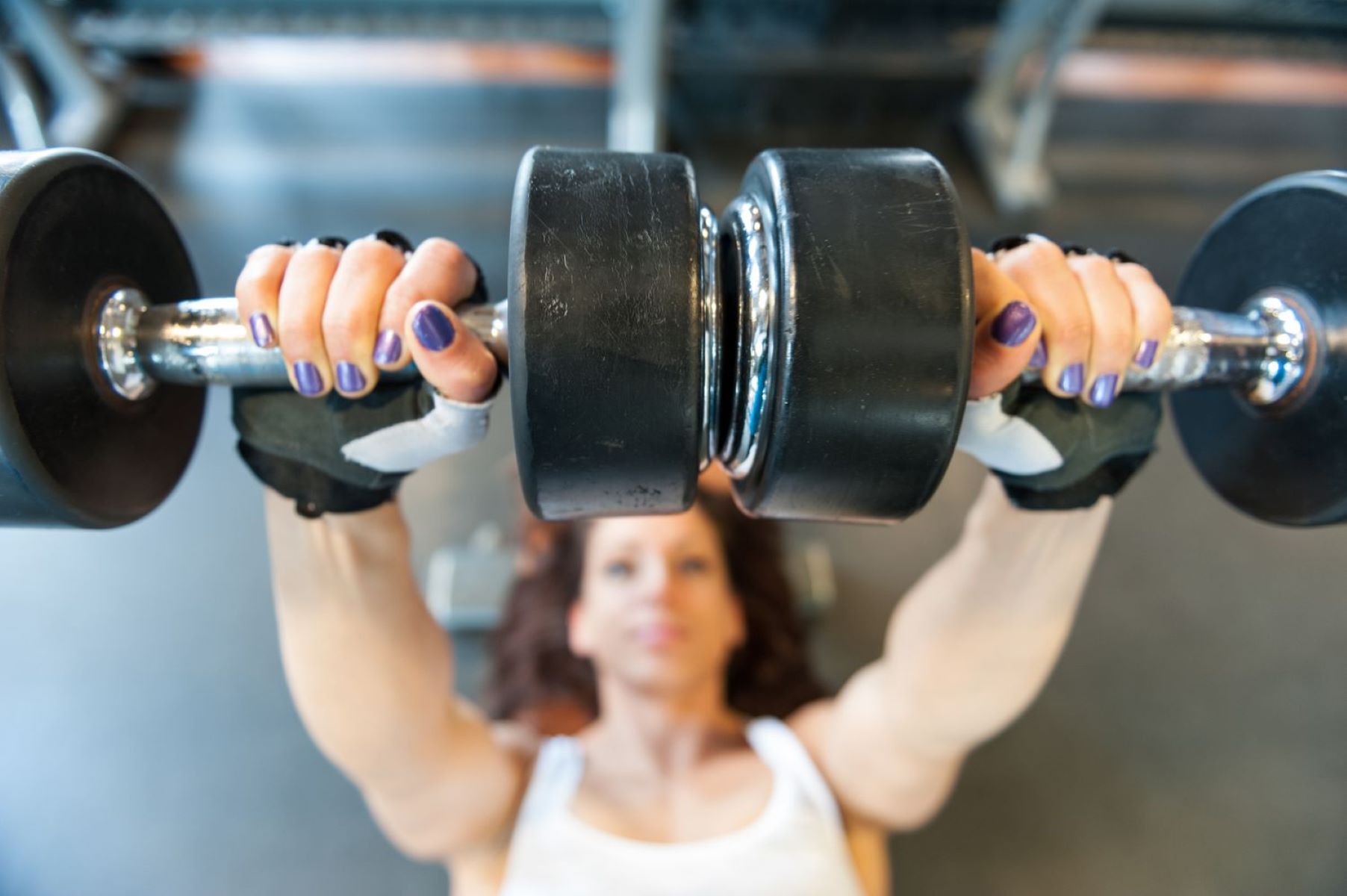
Muscular strength is the measure of the maximum amount of force that a muscle or group of muscles can generate. It is determined by various factors including muscle size, muscle fiber type, and neurological factors.
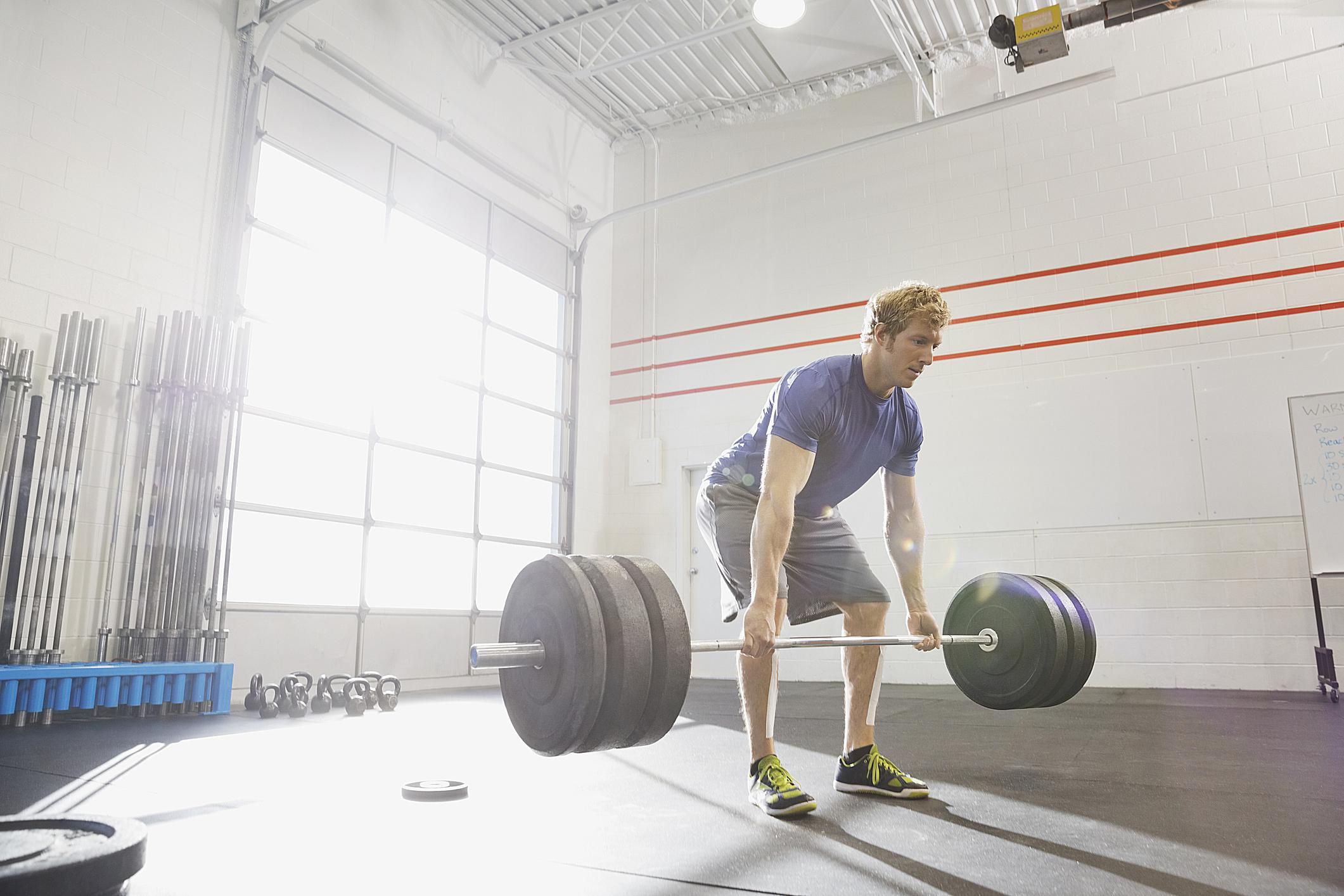
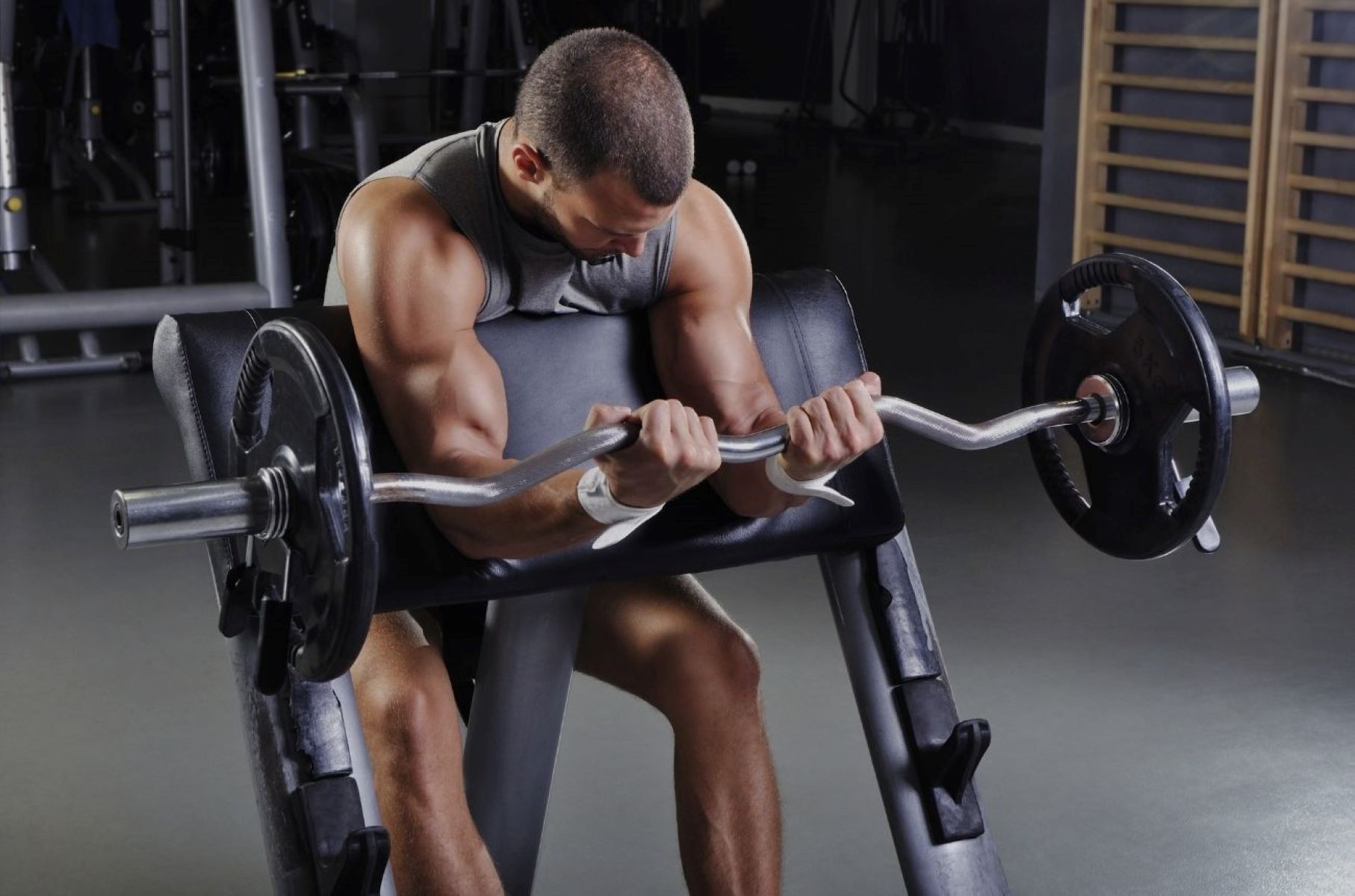
Muscular strength is often quantified by the ability to lift or move heavy weights. It is commonly assessed through exercises like the bench press, squat, or deadlift, where individuals aim to lift as much weight as they can for a given number of repetitions. Professional athletes and strength trainers often prioritize developing muscular strength to improve performance in sports that demand explosive power.
Strength training is the primary method used to improve muscular strength. It involves performing exercises with heavy weights and low repetitions, focusing on challenging the muscles to the point of fatigue. This type of training stimulates muscle growth and increases the number of contractile proteins within the muscle fibers, leading to greater force production.
The benefits of muscular strength extend beyond athletic performance. Having a good level of muscular strength is essential in performing daily tasks such as lifting heavy objects, maintaining proper posture, and preventing injuries. It also plays a crucial role in maintaining bone density and muscle mass as individuals age.
It’s important to note that muscular strength is not synonymous with muscle size. While muscle hypertrophy (increased muscle size) can contribute to greater muscular strength, factors such as muscle fiber type and neural adaptations also play a significant role. Some individuals may have smaller muscles but possess exceptional muscular strength due to their specific muscle fiber composition and neural control.
Overall, muscular strength is a vital component of physical fitness and is cultivated through strength training exercises. By continuously challenging the muscles and progressively increasing the resistance, individuals can enhance their muscular strength and improve their performance in various physical activities.
Definition of Muscular Endurance
Muscular endurance refers to the ability of a muscle or group of muscles to repeatedly exert force over a period of time. It is influenced by factors such as muscle fiber efficiency, aerobic capacity, and resistance to fatigue.
Muscular endurance is commonly assessed through exercises like push-ups, pull-ups, or planks, where individuals aim to perform as many repetitions or hold a position for as long as possible. Unlike muscular strength, which focuses on lifting heavy weights for a short duration, muscular endurance emphasizes sustaining submaximal contractions over an extended period.
Improving muscular endurance involves training the muscles and cardiovascular system to efficiently supply oxygen and nutrients, as well as to remove waste products during prolonged activity. This type of training typically involves moderate loads or bodyweight exercises performed for high repetitions or prolonged durations.
Muscular endurance is a key component of fitness for endurance athletes, such as long-distance runners, cyclists, or swimmers. It allows them to maintain a consistent effort over a prolonged period, delaying the onset of muscular fatigue.
In addition to its importance in endurance sports, muscular endurance also has practical benefits in everyday life. It aids in performing activities that require sustained effort, such as yard work, house cleaning, or participating in group fitness classes. Individuals with good muscular endurance are less likely to experience muscle fatigue and can maintain performance for longer periods without succumbing to exhaustion.
It’s essential to differentiate muscular endurance from cardiovascular endurance, also known as aerobic endurance. While muscular endurance focuses on the ability of muscles to sustain contractions, cardiovascular endurance relates to the efficiency of the heart and lungs to supply oxygen to the working muscles. Both aspects are interconnected and contribute to overall physical fitness.
To improve muscular endurance, individuals can engage in exercises that target specific muscle groups and gradually increase the duration or number of repetitions performed. Through consistent training, the muscles’ ability to resist fatigue improves, allowing individuals to perform demanding activities for longer durations.
Factors Affecting Muscular Strength
Several factors contribute to an individual’s muscular strength, determining their ability to generate maximum force. These factors include muscle size, muscle fiber type, and neurological factors.
1. Muscle Size: One of the primary factors influencing muscular strength is the size of the muscles involved. Generally, larger muscles have a greater capacity to generate force. This is because larger muscles contain more muscle fibers, allowing for a higher potential force production. Through resistance training and progressive overload, individuals can increase muscle size, thereby enhancing their muscular strength.
2. Muscle Fiber Type: Muscle fibers are classified into two main types – fast-twitch (Type II) and slow-twitch (Type I). Fast-twitch fibers have a greater capacity for generating force, but they fatigue more quickly. Slow-twitch fibers, on the other hand, have better endurance but produce less force. The proportion of each fiber type varies among individuals and can affect their muscular strength. Those with a higher percentage of fast-twitch fibers tend to have greater explosive power and muscular strength.
3. Neurological Factors: The nervous system plays a vital role in muscle contractions and strength. Neural adaptations, such as motor unit recruitment and motor unit synchronization, impact muscular strength. Motor unit recruitment refers to the activation of a greater number of motor units within a muscle, leading to increased force production. Motor unit synchronization involves the coordination of motor units to generate force more efficiently. Improvements in neural factors can significantly enhance muscular strength.
4. Sex and Age: Biological differences between males and females can contribute to variations in muscular strength. On average, males tend to have greater muscle mass and higher levels of testosterone, which can result in higher muscular strength compared to females. Additionally, muscular strength tends to peak in early adulthood and gradually decline with age, due to factors such as hormonal changes, reduced muscle mass, and decreased neurological efficiency.
5. Training Status: Regular resistance training is a key factor in developing and maintaining muscular strength. Through progressive overload and consistent training, individuals can increase their muscular strength over time. Conversely, detraining or a lack of exercise can lead to a decline in muscular strength.
While individual factors contribute to muscular strength, it’s important to note that the interplay between these factors is complex and can vary among individuals. Understanding these factors can help individuals tailor their training programs to effectively improve their muscular strength and overall physical performance.
Factors Affecting Muscular Endurance
Various factors influence an individual’s muscular endurance, which refers to their ability to sustain contractions over a period of time. These factors include muscle fiber efficiency, aerobic capacity, and resistance to fatigue.
1. Muscle Fiber Efficiency: Muscular endurance is influenced by the proportion and type of muscle fibers present in the muscles involved. Slow-twitch (Type I) muscle fibers have a higher aerobic capacity and are more resistant to fatigue. These fibers are efficient at utilizing oxygen and can sustain contractions for extended periods. In contrast, fast-twitch (Type II) muscle fibers have limited endurance but can generate more force. The composition of muscle fiber types can vary among individuals, affecting their muscular endurance.
2. Aerobic Capacity: Muscular endurance is closely linked to cardiovascular fitness or aerobic capacity. Aerobic exercise improves the body’s ability to deliver oxygen-rich blood to the working muscles, enabling them to sustain contractions for longer durations. Individuals with higher aerobic capacities have enhanced muscular endurance as their muscles receive sufficient oxygen and nutrients to delay the onset of fatigue.
3. Resistance to Fatigue: The ability of muscles to resist fatigue is crucial for maintaining muscular endurance. Fatigue occurs when the muscles are no longer able to generate or sustain force due to the accumulation of metabolites and waste products. Factors such as muscle glycogen stores, levels of intramuscular pH, and the body’s ability to remove waste products influence resistance to fatigue. Proper nutrition, hydration, and rest are important for optimizing muscular endurance and delaying the onset of fatigue.
4. Training Specificity: Similar to muscular strength, training specificity plays a significant role in muscular endurance. Engaging in activities or exercises that target the specific muscles and energy systems involved in the desired endurance activity is essential. By progressively increasing the duration or repetitions performed during training, individuals can improve their muscular endurance and adapt to the demands of their chosen activity.
5. Body Composition: Body composition, including the amount of muscle mass and body fat, can affect muscular endurance. Having a higher percentage of lean muscle mass, as opposed to excess body fat, contributes to improved muscular endurance. This is because muscles play a vital role in sustaining contractions and providing the necessary force during endurance activities.
It’s important to consider that factors influencing muscular endurance can vary among individuals and are influenced by genetics, training history, and lifestyle choices. By incorporating proper training techniques, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and gradually challenging the muscles, individuals can enhance their muscular endurance and excel in activities that require prolonged effort.
Comparison between Muscular Strength and Muscular Endurance
Muscular strength and muscular endurance are two distinct aspects of muscle performance, each with its own characteristics and importance in physical fitness. Understanding the differences between these two components allows individuals to design training programs that address their specific goals.
1. Definition: Muscular strength refers to the maximum amount of force that a muscle or group of muscles can generate in a single contraction. It is measured by the ability to lift or move heavy weights for a few repetitions. In contrast, muscular endurance refers to the ability of a muscle or group of muscles to sustain contractions over a period of time. It involves performing exercises for higher repetitions or prolonged durations without experiencing fatigue.
2. Intensity vs. Duration: Muscular strength training focuses on high-intensity, low-duration exercises, involving heavy weights and low repetitions. The goal is to challenge the muscles to exert maximum force. In contrast, muscular endurance training emphasizes lower intensity, longer duration exercises with lighter weights or bodyweight, targeting the ability to sustain contractions over extended periods.
3. Muscle Fiber Recruitment: Muscular strength primarily activates fast-twitch (Type II) muscle fibers, which have high force production but fatigue quickly. These fibers are responsible for explosive movements. Muscular endurance, on the other hand, predominantly engages slow-twitch (Type I) muscle fibers, which have better endurance and resistance to fatigue. These fibers are used in activities requiring prolonged effort.
4. Performance in Sports: Muscular strength is crucial for power-based and explosive activities, such as weightlifting, sprinting, and jumping. It allows individuals to generate high force in a short amount of time. Muscular endurance is vital for endurance-based activities like long-distance running, cycling, or swimming, where sustained effort over time is required.
5. Practical Application: Muscular strength plays a significant role in daily tasks that require short bursts of force, such as lifting heavy objects or performing intense physical activities. Muscular endurance, on the other hand, is beneficial in activities that demand sustained effort, like participating in fitness classes, hiking, or performing repetitive tasks.
6. Training Methods: Muscular strength is developed through exercises such as heavy weightlifting, resistance training, and explosive movements. Training focuses on low repetitions and high loads. Muscular endurance is enhanced through exercises like bodyweight exercises, circuit training, and high repetition workouts, gradually increasing duration or repetitions to improve endurance capacity.
Both muscular strength and muscular endurance are important for overall physical fitness. The specific goals, sports or activities, and individual preferences determine the emphasis placed on each component in training programs. A balanced approach that includes both strength and endurance exercises can provide a well-rounded fitness routine and optimal performance in various physical activities.
Importance of Muscular Strength
Muscular strength plays a crucial role in overall physical fitness and has several important benefits for individuals of all ages and fitness levels. Understanding the importance of developing and maintaining muscular strength can motivate individuals to incorporate strength training exercises into their fitness routines.
1. Functional Strength: Muscular strength is essential for performing everyday tasks, such as lifting, carrying, and pushing objects. Having a good level of muscular strength enables individuals to handle these tasks with ease and prevents the risk of injuries associated with poor strength and muscle imbalances.
2. Sports Performance: Muscular strength is vital for athletes participating in sports that require explosive power, such as sprinting, jumping, and throwing. It directly impacts performance by enabling athletes to generate maximum force and produce rapid and forceful movements that are critical to success in these sports.
3. Injury Prevention: Building muscular strength helps protect joints, ligaments, and tendons by providing stability and support. Strengthening the muscles surrounding these structures helps to absorb impact, reducing the risk of injuries and enhancing joint integrity.
4. Bone Health: Strength training exercises that promote muscular strength have a positive impact on bone health. The stress placed on the bones during resistance training stimulates the production of new bone tissue, leading to increased bone density. This can help prevent or slow down the progression of conditions such as osteoporosis.
5. Metabolic Boost: Muscular strength training can boost metabolism, increasing the number of calories burned at rest. Muscle tissue is metabolically more active than fat tissue, so individuals with higher muscle mass have a higher resting metabolic rate. This can assist in weight management and promoting a healthy body composition.
6. Aging Well: As individuals age, they naturally experience a decline in muscle mass and strength, known as sarcopenia. Engaging in regular strength training exercises can help counteract this decline by preserving and building muscle mass, maintaining functional strength, and reducing the risk of age-related muscle and bone-related issues.
7. Mental Well-being: Strength training has positive effects on mental health. Engaging in resistance exercises releases endorphins, which are natural mood enhancers, promoting a sense of well-being and reducing stress and anxiety. Additionally, achieving personal strength goals can boost self-confidence and improve overall self-esteem.
It’s important to note that developing muscular strength requires consistent and progressive resistance training. Proper technique, appropriate progression, and allowing for adequate rest and recovery are essential for reaping the benefits of strength training while minimizing the risk of injury.
Importance of Muscular Endurance
Muscular endurance is a vital component of physical fitness and plays a significant role in various aspects of daily life and sports performance. Understanding the importance of developing and improving muscular endurance can motivate individuals to incorporate endurance-based exercises into their fitness routines.
1. Sports Performance: Muscular endurance is crucial in sports and activities that require sustained effort over time. Endurance athletes, such as long-distance runners, swimmers, and cyclists, rely on their muscular endurance to maintain a consistent level of performance for extended durations. Building and enhancing muscular endurance can enhance performance in these sports and activities.
2. Functional Stamina: Muscular endurance is essential for performing activities of daily living that require repeated contractions over an extended period of time. Whether it’s gardening, cleaning the house, or participating in group fitness classes, having good muscular endurance allows individuals to sustain effort and perform tasks efficiently without getting excessively fatigued.
3. Improved Cardiovascular Health: Muscular endurance training often involves aerobic exercises that increase heart rate and improve cardiovascular fitness. Regular endurance-based exercises, such as jogging, cycling, or swimming, strengthen the cardiovascular system, improve blood circulation, and enhance the body’s ability to use oxygen efficiently.
4. Delayed Fatigue: Muscular endurance training helps the muscles become more resistant to fatigue. By performing exercises for higher repetitions or prolonged durations, individuals can train their muscles to endure sustained contractions without experiencing early fatigue. This increased fatigue resistance enables individuals to perform physical activities for longer periods, delaying the onset of muscular fatigue.
5. Weight Management: Endurance-based exercises are effective for burning calories and maintaining a healthy body weight. Engaging in activities that require sustained effort can significantly increase energy expenditure, contributing to weight loss or weight maintenance when combined with a balanced diet.
6. Enhanced Mental Stamina: Building muscular endurance requires mental willpower and discipline to push through challenges and persevere. Engaging in endurance exercises can improve mental stamina, focus, and resilience, helping individuals overcome physical and mental barriers not only in fitness pursuits but also in other areas of life.
7. Overall Health and Longevity: Muscular endurance exercises, particularly aerobic exercises, offer numerous health benefits. Regular endurance training can lower the risk of chronic diseases such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and obesity. It also contributes to overall physical and mental well-being, promoting a healthier and longer life.
To improve muscular endurance, individuals should gradually increase the intensity, duration, or repetitions of their endurance exercises over time. Additionally, proper nutrition, hydration, and recovery play essential roles in optimizing muscular endurance and overall performance.
Training Techniques for Muscular Strength
When it comes to developing muscular strength, incorporating specific training techniques can optimize results. These techniques target the muscles, stimulate growth, and progressively increase the muscles’ ability to generate maximum force. By implementing these techniques, individuals can effectively build muscular strength and enhance their overall performance.
1. Progressive Overload: Progressive overload is a key principle in strength training. It involves systematically increasing the demands placed on the muscles over time. This can be achieved by progressively increasing the weight lifted, the number of repetitions performed, or the intensity of the exercise. By consistently challenging the muscles, individuals stimulate muscle growth and adaptation, leading to increased muscular strength.
2. Compound Exercises: Compound exercises are multi-joint movements that engage multiple muscle groups simultaneously. Examples include squats, deadlifts, bench press, and overhead press. These exercises recruit a larger number of muscle fibers, allowing for greater force production and a more efficient use of time in training sessions. Incorporating compound exercises into a strength training routine targets multiple muscles and promotes overall muscular strength development.
3. High-Intensity Training: High-intensity training involves lifting heavy weights for a low number of repetitions. This technique focuses on challenging the muscles to exert maximum force. Using weights that are close to an individual’s maximum capacity stimulates muscle growth and strength gains. However, it’s essential to maintain proper form and technique to prevent injuries and ensure effective muscle activation.
4. Eccentric Training: Eccentric training involves emphasizing the eccentric phase, or the lowering phase, of an exercise. This phase involves lengthening the muscle under tension. Eccentric training has been shown to promote greater muscle hypertrophy and strength gains compared to concentric (lifting) training alone. Incorporating slower, controlled eccentric movements can be beneficial for maximizing muscular strength development.
5. Rest and Recovery: Adequate rest and recovery are essential for optimizing muscular strength gains. Muscles need time to repair and grow stronger after intense workouts. It is recommended to allow at least 48 hours of recovery between strength training sessions targeting the same muscle groups. Additionally, ensuring quality sleep, proper nutrition, and hydration support optimal recovery and muscle growth.
6. Periodization: Periodization is a training approach that involves dividing a training program into specific cycles or phases. Each phase focuses on different training variables such as volume, intensity, and exercise selection. This helps prevent plateaus and ensures continuous progress in muscular strength development. Periodization also allows for planned recovery periods, reducing the risk of overtraining and injuries.
7. Proper Technique and Form: Maintaining proper technique and form during exercises is crucial for effective and safe strength training. It ensures that the targeted muscles are effectively engaged, minimizing the risk of injury. Learning proper form and seeking guidance from a qualified trainer can help individuals optimize their training technique and maximize muscular strength gains.
By incorporating these training techniques into a well-rounded strength training program, individuals can effectively develop muscular strength, increase force production, and achieve their fitness goals.
Training Techniques for Muscular Endurance
To improve muscular endurance, specific training techniques can be incorporated into a fitness routine. These techniques target the muscles and the cardiovascular system, allowing individuals to sustain contractions over extended periods and delay the onset of fatigue. By implementing these techniques, individuals can effectively enhance their muscular endurance and excel in activities that require prolonged effort.
1. High-Repetition Training: Performing exercises for high repetitions is a fundamental training technique for muscular endurance. This technique challenges the muscles to sustain contractions for a prolonged duration, improving their endurance capacity. It is important to maintain proper form and control throughout each repetition to effectively engage the targeted muscle groups.
2. Circuit Training: Circuit training involves performing a series of exercises targeting different muscle groups with minimal rest between exercises. This training method combines strength and cardiovascular exercises, allowing for an increased training density and improved muscular endurance. It helps to elevate heart rate, improve cardiovascular fitness, and increase the endurance capacity of the muscles.
3. Interval Training: Interval training involves alternating periods of high-intensity exercise with periods of active recovery or lower-intensity exercise. This technique can be applied to both cardiovascular exercises and resistance exercises to enhance both aerobic and muscular endurance. By incorporating short bursts of intense effort followed by active recovery, individuals can improve their endurance capacity and delay the onset of fatigue.
4. Tempo Training: Tempo training focuses on the speed or tempo at which exercises are performed. Slowing down the eccentric (lowering) phase of an exercise and controlling the concentric (lifting) phase can increase time under tension and challenge the muscles to sustain contractions for an extended period. This technique improves muscular endurance and increases muscle fibers’ resistance to fatigue.
5. Supersets and Tri-Sets: Supersets and tri-sets involve performing two or three exercises consecutively without rest. These exercises typically target different muscle groups or movement patterns. By minimizing rest intervals between exercises, individuals increase the training density and intensity, improving both muscular endurance and cardiovascular fitness.
6. Fartlek Training: Fartlek, a Swedish term meaning “speed play,” is a training technique commonly used in endurance sports. It involves alternating between periods of varying intensities during cardiovascular exercises. By incorporating intervals of faster or slower pace within a longer endurance session, individuals can improve their cardiovascular capacity and train their muscles to sustain effort over varying intensities.
7. Progressive Duration: Gradually increasing the duration of exercises or the overall training session is essential for improving muscular endurance. Progressive overload can be achieved by adding a few more repetitions, increasing the time under tension, or extending the duration of the training session. This gradual progression challenges the muscles and advances their endurance capacity over time.
By incorporating these training techniques into a well-rounded fitness routine, individuals can effectively improve their muscular endurance, increase their capacity to sustain contractions, and excel in activities that demand prolonged effort.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the difference between muscular strength and muscular endurance is crucial for individuals looking to enhance their overall fitness and achieve specific goals. Muscular strength refers to the maximum amount of force a muscle or group of muscles can generate, while muscular endurance is the ability to sustain contractions over an extended period. Both components are important in physical fitness and serve different purposes.
Factors such as muscle size, muscle fiber type, neurological factors, aerobic capacity, and resistance to fatigue influence both muscular strength and muscular endurance. By incorporating specific training techniques, individuals can optimize their development in each area. Progressive overload, compound exercises, high-intensity training, and proper rest and recovery are vital for improving muscular strength. High-repetition training, circuit training, interval training, and progressive duration exercises are effective in enhancing muscular endurance.
Developing muscular strength and muscular endurance offers numerous benefits. Muscular strength improves functional strength, enhances sports performance, prevents injuries, promotes bone health, boosts metabolism, and supports healthy aging. Muscular endurance enhances sports performance, functional stamina, cardiovascular health, delays fatigue, aids in weight management, improves mental stamina, and contributes to overall health and longevity.
To achieve optimal results, it is essential to design a well-rounded fitness program that includes a combination of strength and endurance exercises tailored to individual goals and preferences. Gradually progress the intensity, duration, or repetitions over time, and ensure proper form and technique to maximize effectiveness and minimize the risk of injury.
By focusing on both muscular strength and muscular endurance, individuals can improve their overall physical performance, enhance their ability to perform daily tasks, excel in sports or recreational activities, and maintain good health throughout their lifespan. Prioritizing the development and maintenance of both components leads to a well-rounded and balanced fitness routine for optimal results.