Featured
What Is The Effect Of Exercise On Bones?
Published: October 2, 2023
Explore the featured article to discover the remarkable impact of exercise on bones and how it can strengthen and improve overall bone health.
Introduction
Bones are an essential component of our body’s structure, providing support and protection for vital organs. They also play a crucial role in mobility, enabling us to perform everyday activities. However, maintaining bone health is not something that should be taken for granted. Various factors, such as genetics, age, and lifestyle choices, can influence bone density and strength.
One lifestyle factor that greatly impacts bone health is exercise. Exercise has long been known to have numerous benefits for overall health and well-being, but its effect on bones is often overlooked. Engaging in regular physical activity can have a significant positive impact on bone density, strength, and overall bone health.
In this article, we will explore in detail the relationship between exercise and bone health. We will delve into the structure and function of bones, the bone remodeling process, and why exercise is vital for maintaining healthy bones. We will also discuss how exercise affects bone density, strength, and mineral content, and explore specific types of exercises that are beneficial for bone health.
Furthermore, we will examine exercise’s role in preventing bone loss and reducing the risk of osteoporosis, a condition characterized by weakened and fragile bones. Finally, we will provide exercise recommendations to help you optimize your bone health and ensure that you reap the many benefits that physical activity offers to your bones.
By the end of this article, you will have a comprehensive understanding of the effect of exercise on bones and be equipped with the knowledge to prioritize exercise for maintaining strong and healthy bones throughout your life.
The Structure and Function of Bones
Bones are remarkable structures that provide support, protect vital organs, and facilitate movement. They are composed of a combination of dense, hard outer tissue called compact bone, and a honeycomb-like inner tissue called trabecular bone. This combination gives bones their strength and flexibility.
The primary function of bones is to provide a framework for the body. They act as anchors for muscles, allowing us to perform various movements such as walking, running, and lifting. Bones also protect delicate organs such as the brain, heart, and lungs. For example, the skull protects the brain, while the ribcage shields the heart and lungs.
Another critical function of bones is mineral storage. They act as reservoirs for essential minerals like calcium and phosphorus, which are crucial for numerous bodily functions. When the body needs these minerals, such as for muscle contraction or nerve function, it can draw upon the stores in the bones.
Bones are not static structures; they are constantly undergoing a process known as bone remodeling. This process involves the removal of old bone tissue by cells called osteoclasts and the formation of new bone tissue by cells called osteoblasts. Bone remodeling helps to maintain bone strength, repair micro-damage, and adapt to changing mechanical stresses.
Understanding the structure and function of bones is essential because it forms the basis for comprehending how exercise affects bone health. By engaging in specific types of exercise, we can stimulate bone remodeling, enhancing bone strength and density.
Now, let’s dive deeper into the bone remodeling process and explore the importance of exercise in maintaining optimal bone health.
Bone Remodeling Process
The bone remodeling process is a continuous and dynamic cycle that occurs throughout our lives. It involves the coordinated activity of two types of cells: osteoclasts and osteoblasts.
Osteoclasts are responsible for breaking down old and damaged bone tissue. They secrete enzymes and acids that dissolve the bone material, allowing for its resorption. This process is essential for removing old bone tissue that may be weak or damaged, making way for the formation of new, healthy bone.
Osteoblasts, on the other hand, are responsible for the formation of new bone tissue. They synthesize and deposit collagen, a protein that serves as the framework for new bone formation. Osteoblasts also mineralize the collagen matrix by depositing calcium and other minerals, making the bone denser and stronger.
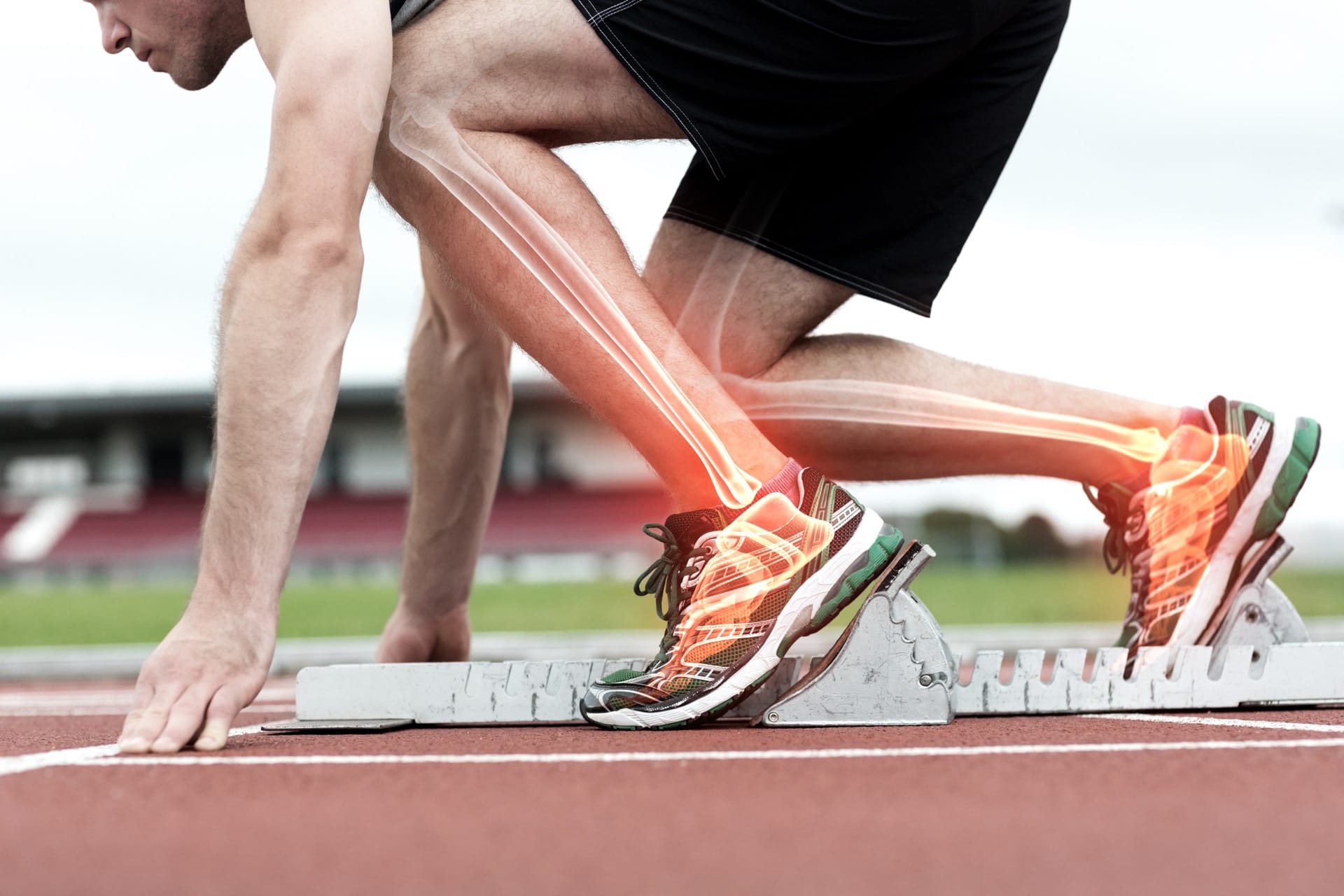
The bone remodeling process is tightly regulated by various signaling factors, hormones, and mechanical stresses. When bones experience mechanical forces, such as weight-bearing activities or impact exercises, it triggers a response in the bone cells, stimulating the remodeling process. This response is known as bone adaptation.
During bone adaptation, the bone tissue experiences micro-damage. This activates the osteoclasts to resorb the damaged tissue, while the osteoblasts initiate the formation of new bone in response to the mechanical stress. Through this process, bones can remodel and strengthen themselves to withstand the forces they encounter.
Exercise plays a crucial role in the bone remodeling process. Weight-bearing exercises and activities that involve impact or resistance stimulate the bone cells, leading to increased osteoblast activity and bone formation. By regularly subjecting our bones to these forces, we can promote the remodeling process and enhance bone density and strength.
Now that we understand the bone remodeling process, let’s explore why exercise is essential for maintaining healthy bones.
The Importance of Exercise for Bone Health
Exercise plays a vital role in maintaining and improving bone health. Engaging in regular physical activity not only benefits our cardiovascular system and overall well-being but also has a positive impact on our bones. Here are some reasons why exercise is essential for bone health:
1. Increased Bone Density: Exercise, particularly weight-bearing activities and resistance training, promotes the formation of new bone tissue. When we put stress on our bones through exercise, it stimulates the osteoblasts to deposit more minerals and collagen, increasing bone density.
2. Enhanced Bone Strength: Exercise helps to improve the overall strength and mechanical properties of our bones. Activities that involve impact or resistance, such as running, jumping, and weightlifting, subject the bones to forces that stimulate bone adaptation. This leads to stronger bones that are better able to withstand everyday activities and reduce the risk of fractures.
3. Prevention of Bone Loss: As we age, bone loss becomes more prevalent, especially in women after menopause. Regular exercise can help slow down the rate of bone loss and reduce the risk of osteoporosis. By engaging in weight-bearing exercises, we stimulate bone remodeling and prevent excessive bone resorption.
4. Improved Balance and Posture: Exercise can help improve our balance and posture, reducing the risk of falls and fractures. As we age, maintaining good balance becomes crucial in preventing injuries. Activities like yoga, tai chi, and strength training can help enhance our stability and coordination.
5. Overall Health Benefits: Regular exercise has numerous health benefits, and many of these indirectly contribute to better bone health. Exercise helps maintain a healthy body weight, reduces the risk of chronic diseases like cardiovascular disease and diabetes, and improves overall muscle strength and flexibility.
It is important to note that not all types of exercise have the same impact on bone health. Weight-bearing activities, such as walking, jogging, dancing, and aerobics, are particularly effective in promoting bone strength. Resistance exercises, like weightlifting and bodyweight exercises, also have a positive impact on bone health by stimulating bone formation.
Incorporating a variety of exercises into our routine, including cardiovascular exercises, strength training, and balance exercises, can provide a well-rounded approach to improving bone health.
Now that we understand the importance of exercise for maintaining optimal bone health, let’s delve into how exercise specifically affects bone density.
How Exercise Affects Bone Density
Exercise has a profound impact on bone density, which refers to the amount of mineralized bone tissue present in a given volume of bone. Engaging in regular physical activity can help increase bone density and prevent bone loss, particularly in areas that experience the greatest mechanical stress.
Weight-bearing exercises, such as walking, jogging, and dancing, are particularly effective in promoting bone density. When we engage in these activities, the mechanical forces generated by our muscles and the impact with the ground stimulate bone cells, specifically the osteoblasts, to deposit more minerals and collagen in our bones.
The impact forces experienced during weight-bearing exercises create a type of stress called mechanical loading. This stress signals the bones to adapt and become stronger. The weight-bearing nature of these exercises means that our bones are supporting our body weight, which provides an optimal stimulus for bone remodeling and increased bone density.
Resistance exercises, such as weightlifting and bodyweight exercises, also contribute to increased bone density. These exercises involve exerting force against a resistance, whether it be free weights, weight machines, or our body weight. By placing stress on the bones, we trigger the bone cells to remodel and add more mineralized tissue, increasing bone density.
It is important to note that the effect of exercise on bone density is site-specific. That means that exercise can have a more substantial impact on bone density in areas that bear the greatest load during physical activity. For example, weight-bearing exercises like walking or running have a greater effect on bone density in the bones of the lower body, such as the hips, legs, and spine.
Another factor that influences the effect of exercise on bone density is the intensity and duration of the exercise. Higher-intensity activities and longer durations tend to have more significant effects on bone density. However, it is crucial to find a balance and avoid excessive training, as overtraining can have detrimental effects on bone health.
Increasing bone density through exercise is particularly important for individuals at risk of osteoporosis or those who have low bone density. Regular exercise, combined with a balanced diet rich in calcium and vitamin D, can help improve bone density and reduce the risk of fractures.
Now that we understand how exercise affects bone density, let’s explore the impact of exercise on bone strength and structure.
Impact of Exercise on Bone Strength and Structure
Exercise plays a crucial role in enhancing bone strength and improving the overall structure of our bones. Regular physical activity, particularly weight-bearing and resistance exercises, stimulates the bone remodeling process, leading to increased bone strength and improved bone structure.
When we engage in weight-bearing exercises, such as walking, running, and jumping, the mechanical stress placed on our bones triggers the deposition of minerals, particularly calcium and phosphorus, making the bones stronger and more resistant to fractures. These exercises also stimulate the production of collagen, which provides flexibility and resilience to the bone structure.
In addition to increasing bone strength, exercise can also improve the overall structure of our bones. Regular physical activity helps promote proper alignment and distribution of the bone tissue, preventing deformities and abnormalities. This is particularly important during growth and development, as exercise can positively influence bone growth and prevent conditions like osteogenesis imperfecta.
Resistance exercises, such as weightlifting and bodyweight exercises, are also beneficial for bone strength and structure. These exercises create a direct load or force on the bones, stimulating bone cells to remodel and adapt to the imposed stress. As a result, bone density and strength increase, reducing the risk of fractures and enhancing overall bone health.
Furthermore, exercise has been shown to have positive effects on bone geometry, which refers to the shape and size of the bones. Weight-bearing activities and resistance exercises can improve bone geometry by increasing the cortical thickness (outer layer of dense bone) and trabecular bone volume, leading to stronger bones that are more resistant to fracture.
It is important to note that the impact of exercise on bone strength and structure is influenced by various factors, including the intensity, duration, and frequency of the exercise, as well as individual factors such as age, sex, and genetics. Therefore, it is important to develop an exercise routine that is appropriate for your fitness level and consult with a healthcare professional or exercise specialist if needed.
Now that we have examined the impact of exercise on bone strength and structure, let’s take a closer look at specific types of exercises recommended for bone health.
Specific Types of Exercise for Bone Health
When it comes to promoting bone health, certain types of exercises are particularly beneficial. Incorporating these exercises into your routine can help improve bone density, strength, and overall bone health. Here are some specific types of exercises recommended for bone health:
1. Weight-Bearing Exercises: Weight-bearing exercises involve supporting your body weight while engaging in activities that put stress on your bones. These types of exercises include walking, jogging, hiking, dancing, and stair climbing. They help stimulate bone growth and increase bone density in the weight-bearing bones of the hips, legs, and spine.
2. Resistance Training: Resistance training, also known as strength or weight training, involves using external resistance, such as free weights, weight machines, or resistance bands, to strengthen muscles and bones. The load placed on the bones during resistance training stimulates the bone tissue, promoting bone formation. Focus on exercises that target multiple muscle groups, such as squats, lunges, deadlifts, and push-ups.
3. Impact Exercises: Impact exercises involve activities that subject your bones to brief periods of high impact and mechanical stress. Examples of impact exercises include jumping rope, plyometrics (jumping exercises), and sports such as basketball and volleyball. These exercises help enhance bone strength by stimulating bone remodeling and increasing bone density.
4. Balance and Coordination Exercises: Balance and coordination exercises, such as yoga, tai chi, and Pilates, can help improve your posture, stability, and proprioception (awareness of your body’s position in space). These exercises contribute to reducing the risk of falls and fractures by enhancing balance and reducing the likelihood of accidents.
5. Flexibility and Range of Motion Exercises: While not directly impacting bone health, flexibility exercises play a supportive role in maintaining overall musculoskeletal health. Stretching exercises help improve joint mobility, enhance muscle flexibility, and reduce the risk of muscle imbalances and injuries.
It is important to note that a well-rounded exercise routine that incorporates a combination of these types of exercises is most effective for promoting bone health. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise, along with two or more days of strength training exercises each week.
It is recommended to consult with a healthcare professional or a certified exercise specialist to create an exercise plan tailored to your individual needs and abilities.
Now that we have explored the specific types of exercises for bone health, let’s examine the impact of exercise on bone mineral content.
Impact of Exercise on Bone Mineral Content
Exercise plays a crucial role in influencing bone mineral content, which refers to the amount of minerals, particularly calcium and phosphorus, present in the bone tissue. Regular physical activity, particularly weight-bearing and resistance exercises, can positively impact bone mineral content and contribute to improved bone health.
Weight-bearing exercises, such as walking, running, and dancing, stimulate the bone cells to deposit more minerals in the bones, increasing bone mineral content. The mechanical stress placed on the bones during weight-bearing activities signals the body to allocate more calcium and phosphorus to strengthen the bones and promote healthy bone remodeling.
Resistance exercises, such as weightlifting and resistance band workouts, also have a positive impact on bone mineral content. These exercises create an additional load on the bones, stimulating the bone cells to deposit more minerals. By regularly engaging in resistance training, you can promote the accumulation of minerals in the bones, making them stronger and more resistant to fractures.
It is important to note that the impact of exercise on bone mineral content is influenced by various factors, including the intensity, duration, and frequency of the exercise, as well as individual factors such as age, sex, and genetics. In addition, proper nutrition is crucial for maintaining adequate mineral levels in the bones. Consuming a balanced diet rich in calcium, vitamin D, and other essential nutrients can support bone mineralization and enhance the effects of exercise.
Furthermore, regular weight-bearing and resistance exercises promote bone health by improving the absorption and utilization of minerals, ensuring that the bones receive the necessary nutrients for optimal strength and density. This emphasizes the importance of combining exercise with a nutrient-rich diet for maximizing bone mineral content.
It’s important to note that the impact of exercise on bone mineral content is particularly significant during growth and development, when bones are still forming and mineralizing. However, exercise continues to play a crucial role in maintaining bone health throughout adulthood and into old age.
Now that we understand the impact of exercise on bone mineral content, let’s explore the role of exercise in preventing bone loss.
Exercise’s Role in Preventing Bone Loss
As we age, our bones naturally undergo a decline in density and strength, making them more susceptible to fractures and conditions like osteoporosis. However, regular exercise can play a significant role in preventing bone loss and maintaining optimal bone health throughout life.
Exercise helps to counteract the natural age-related decline in bone density by stimulating bone remodeling and promoting bone formation. Weight-bearing exercises, such as walking, jogging, and hiking, help maintain bone density and reduce the risk of bone loss. The mechanical forces generated during these activities stimulate the bone cells to deposit more minerals and collagen, enhancing bone strength and density.
Resistance exercises, such as weightlifting and resistance band workouts, are particularly effective in preventing bone loss. These exercises create a direct load on the bones, stimulating bone remodeling and promoting bone formation. By regularly engaging in resistance training, you can help preserve bone density and prevent excessive bone resorption, reducing the risk of osteoporosis.
Exercise also helps to improve balance, stability, and coordination, which are important factors in preventing falls and fractures, especially in older adults. Falls can significantly impact bone health, leading to fractures and further bone loss. By enhancing balance and stability through exercises like tai chi, yoga, and specific balance training exercises, you can reduce the risk of falls and protect your bones.
Furthermore, the impact of exercise on bone health extends beyond density and strength. Regular physical activity has been shown to improve bone quality by enhancing bone structure and promoting optimal bone geometry. This contributes to overall bone health and reduces the risk of fractures.
It is important to note that the benefits of exercise in preventing bone loss are most pronounced when combined with a well-balanced diet rich in calcium, vitamin D, and other essential nutrients. Proper nutrition provides the necessary building blocks for bone health and supports the effects of exercise on bone density and strength.
By incorporating weight-bearing exercises, resistance training, balance and coordination exercises, and maintaining proper nutrition, you can effectively combat bone loss and minimize the risk of osteoporosis.
Now that we understand exercise’s role in preventing bone loss, let’s explore some exercise recommendations for optimal bone health.
Exercise Recommendations for Bone Health
To optimize bone health, it is important to incorporate specific types of exercise into your routine. Here are some exercise recommendations to promote bone health:
1. Weight-Bearing Exercises: Include weight-bearing exercises such as walking, jogging, dancing, and stair climbing in your routine. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity each week.
2. Resistance Training: Engage in resistance training exercises at least two days a week. Use free weights, weight machines, or resistance bands to target major muscle groups and stimulate bone growth.
3. Impact Exercises: Include impact exercises such as jumping rope, plyometrics, and sports like basketball and volleyball. These activities subject your bones to brief periods of high impact, promoting bone strength.
4. Balance and Coordination Exercises: Incorporate exercises like yoga, tai chi, and specific balance training exercises. These exercises enhance stability, coordination, and reduce the risk of falls and fractures.
5. Flexibility and Range of Motion Exercises: Include stretching exercises to improve joint mobility, flexibility, and reduce the risk of muscle imbalances and injuries.
It is important to note that exercise intensity, duration, and frequency should be tailored to your fitness level and abilities. If you are new to exercise or have any medical conditions, it is recommended to consult with a healthcare professional or a certified exercise specialist for personalized recommendations.
In addition to exercise, maintaining a nutritious diet is crucial for optimal bone health. Ensure you are getting enough calcium, vitamin D, and other essential nutrients through a balanced diet or supplements if necessary.
Remember to listen to your body and progress gradually. Start with exercises that you are comfortable with and gradually increase the intensity or duration as your fitness level improves.
Consistency is key when it comes to exercise for bone health. Aim for regular physical activity, allowing for rest days to promote recovery and avoid overtraining.
By following these exercise recommendations and maintaining a healthy lifestyle, you can promote bone density, strength, and overall bone health throughout your life.
Now that we have explored exercise recommendations for bone health, let’s conclude our discussion on the impact of exercise on bones.
Conclusion
Exercise plays a crucial role in maintaining and improving bone health. By engaging in regular physical activity, we can enhance bone density, strength, and overall bone mineral content. Weight-bearing exercises, resistance training, impact exercises, and balance and coordination exercises are particularly effective in promoting optimal bone health.
Exercise stimulates bone remodeling, with osteoblasts depositing more minerals and collagen to strengthen and densify the bones. This helps prevent bone loss and reduces the risk of conditions like osteoporosis. Additionally, exercise improves balance, stability, and coordination, reducing the likelihood of falls and fractures, especially in older adults.
It is important to note that the impact of exercise on bone health is influenced by factors such as exercise intensity, duration, frequency, as well as age, sex, genetics, and overall health. Therefore, it is crucial to tailor your exercise routine to your individual needs and abilities.
In addition to exercise, maintaining a balanced diet rich in calcium, vitamin D, and other essential nutrients is crucial for optimal bone health. Proper nutrition provides the necessary building blocks for bone formation and supports the effects of exercise on bone density and strength.
By incorporating a variety of weight-bearing exercises, resistance training, impact exercises, and balance and coordination exercises, along with proper nutrition, you can effectively maintain and improve your bone health throughout your life.
So, don’t overlook the importance of exercise when it comes to your bones. Make physical activity a priority in your daily routine, and you will reap the numerous benefits of strong, healthy bones that support you in all aspects of life.