Featured
How To Measure Endurance
Modified: March 1, 2024
Learn the best strategies to measure endurance with our featured guide. Improve your fitness and track your progress accurately.
Introduction
Endurance is a critical component of physical fitness that plays a vital role in various aspects of daily life, sports performance, and overall health and well-being. It refers to the ability to sustain prolonged physical activity and resist fatigue. Whether you’re an athlete looking to improve your performance, a fitness enthusiast aiming to enhance your endurance levels, or an individual simply seeking to increase your stamina for daily tasks, measuring your endurance is an essential step towards achieving your goals.
Understanding your endurance capacity allows you to track your progress, set realistic goals, and design an effective training program tailored to your specific needs. By systematically assessing your endurance levels, you can identify areas for improvement, monitor your overall fitness level, and make necessary adjustments to optimize your performance.
In this article, we will delve into the significance of measuring endurance and explore different types of endurance tests to help you gauge your cardiovascular and muscular endurance. Additionally, we will discuss how endurance evaluation contributes to sports performance and share practical tips on how to keep track of your endurance progress.
Whether you’re an aspiring athlete, a fitness enthusiast, or someone looking to improve their overall fitness levels, measuring your endurance will provide you with valuable insights to guide your training and achieve your fitness goals. Join us as we embark on a journey to unravel the mysteries of endurance measurement and unlock your true potential.
Understanding Endurance
Endurance is a multifaceted concept that encompasses the body’s ability to sustain prolonged physical activity and resist fatigue. It is not limited to one specific area of fitness, but rather involves a combination of cardiovascular and muscular endurance. While cardiovascular endurance refers to the efficiency of the heart, lungs, and circulatory system in delivering oxygen to the working muscles, muscular endurance refers to the muscles’ ability to exert force repeatedly over an extended period of time.
Endurance is influenced by various factors, including genetics, training status, nutrition, and lifestyle habits. People with high levels of endurance often exhibit traits such as a high VO2 max (maximal oxygen consumption), efficient oxygen utilization by the muscles, and a high lactate threshold (the point at which lactate begins to accumulate in the blood).
Endurance activities can include aerobic exercise such as running, cycling, swimming, and rowing, as well as activities that require repetitive muscular contractions like weightlifting, calisthenics, and circuit training. These activities challenge the body’s ability to generate energy for extended periods and gradually increase the endurance capacity of the cardiovascular and musculoskeletal systems.
Building endurance requires a progressive and systematic approach. The body needs time to adapt to increasing demands, and gradual progression helps to minimize the risk of injury or overtraining. Incorporating a combination of low-intensity, long-duration workouts and high-intensity, shorter-duration workouts can help improve both cardiovascular and muscular endurance.
As you strive to understand endurance, keep in mind that it is a dynamic quality that can be improved through consistent training and proper recovery. It is important to listen to your body, provide adequate rest, and nourish it with a balanced diet to support your endurance goals.
Importance of Endurance Measurement
Measuring endurance is crucial for several reasons, providing valuable insights into your fitness level and helping you make informed decisions about your training and overall well-being. Here are some key reasons why endurance measurement is important:
- Baseline Assessment: Endurance measurement provides a baseline assessment of your current fitness level. By understanding your starting point, you can set realistic goals and track your progress over time. Additionally, it allows you to identify any weaknesses or areas for improvement.
- Goal Setting and Progress Tracking: Measuring endurance enables you to set specific and measurable goals. Whether you want to run a marathon, complete a challenging hike, or simply improve your stamina for daily activities, endurance measurement helps you establish achievable targets and track your progress towards them.
- Training Optimization: Endurance measurement helps design a training program tailored to your specific needs. By identifying your strengths and weaknesses, you can focus on areas that require improvement. Whether it’s adjusting the intensity, duration, or frequency of your workouts, having data on your endurance levels allows you to optimize your training for maximum results.
- Preventing Plateaus and Overtraining: Regularly measuring your endurance helps prevent plateaus and overtraining. By monitoring your progress, you can make necessary adjustments to your training regime, ensuring that you continue to challenge yourself while avoiding burnout or injuries.
- Health Monitoring: Endurance measurement provides insights into your overall health and well-being. Endurance capacity is closely linked to cardiovascular health, and improvements in endurance often indicate improvements in heart and lung function. Monitoring your endurance levels can serve as an early indicator of potential health issues or indicate the effectiveness of a prescribed training or rehabilitation program.
- Motivation and Accountability: Measuring endurance and seeing progress can be incredibly motivating. It provides a sense of accomplishment and encourages you to stay committed to your fitness journey. Additionally, sharing your progress with others or participating in events that require endurance can create a sense of accountability and further drive your efforts.
In summary, endurance measurement plays a vital role in understanding your current fitness level, setting goals, optimizing your training, and tracking your progress. Whether you’re an athlete, fitness enthusiast, or simply someone looking to improve overall health, regularly measuring your endurance can help you reach new heights and unlock your full potential.
Types of Endurance Tests
There are various types of endurance tests that can assess different aspects of your endurance capacity. These tests help measure both cardiovascular endurance and muscular endurance. Here are some commonly used endurance tests:
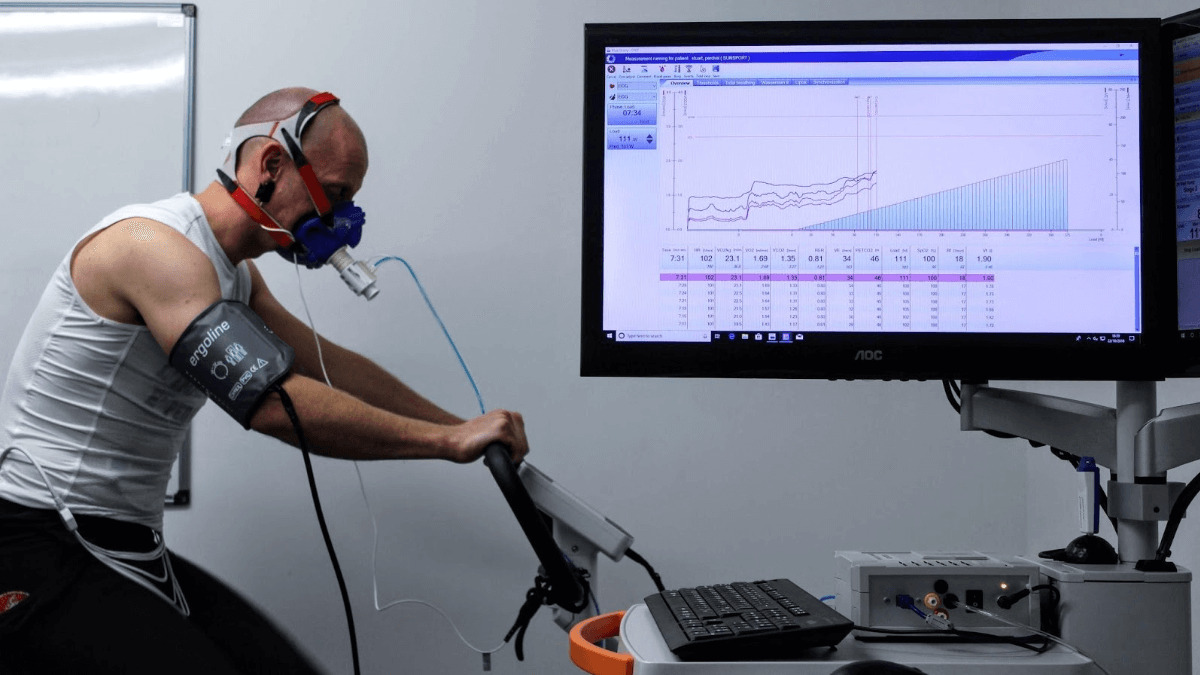
- VO2 Max Test: The VO2 max test is considered the gold standard for measuring cardiovascular endurance. It measures the maximum amount of oxygen your body can utilize during intense exercise. This test typically involves running on a treadmill or cycling while wearing a breathing mask. It provides valuable information about your aerobic capacity and is often used by athletes to evaluate their cardiovascular fitness levels.
- Cooper Test: The Cooper test is a simple and popular test for measuring cardiovascular endurance. It involves running as far as possible in 12 minutes. The distance covered is used as an indicator of your aerobic fitness level. The farther you run, the higher your cardiovascular endurance.
- Beep Test: The beep test, also known as the multi-stage fitness test or shuttle run test, is a progressive test that assesses cardiovascular endurance. It involves running back and forth between two points at an increasing pace, with each level becoming progressively more challenging. The test measures the point at which you can no longer keep up with the pace, indicating your cardiovascular endurance level.
- Push-Up Test: The push-up test is a common test used to measure upper body muscular endurance. It involves performing as many push-ups as possible until exhaustion. This test primarily assesses the endurance of the chest, shoulder, and triceps muscles.
- Sit-Up Test: The sit-up test is used to measure abdominal muscle endurance. It involves performing as many sit-ups as possible within a specific time limit. This test evaluates the endurance and strength of the abdominal muscles.
- Plank Test: The plank test is a static exercise that assesses both core muscle endurance and overall body strength. It involves holding a proper plank position for as long as possible. The longer you can hold the plank, the better your muscular endurance.
These endurance tests provide quantitative data that can be compared over time to track improvements or identify areas for further training. While these tests are widely used, it’s important to consult with a fitness professional to ensure proper technique and to determine which test is most appropriate for your specific fitness goals and capabilities.
Assessing Cardiovascular Endurance
Cardiovascular endurance, also known as aerobic endurance, refers to the ability of the cardiovascular system to efficiently deliver oxygen to the muscles during prolonged physical activity. Assessing cardiovascular endurance is essential for understanding your overall fitness level and determining the effectiveness of your training program. Here are some methods commonly used to assess cardiovascular endurance:
- VO2 Max Test: The VO2 max test is considered the most accurate and reliable method for assessing cardiovascular endurance. It measures the maximum amount of oxygen your body can utilize during intense exercise. This test typically involves running on a treadmill or cycling while wearing a breathing mask that measures the amount of oxygen consumed and carbon dioxide produced. The results are expressed as milliliters of oxygen per kilogram of body weight per minute (ml/kg/min). A higher VO2 max indicates better cardiovascular endurance.
- Field Tests: Field tests are practical and convenient methods to assess cardiovascular endurance outside a laboratory setting. Some commonly used field tests include the Cooper Test and the Beep Test. The Cooper Test involves running as far as possible in 12 minutes, while the Beep Test involves running back and forth between two points at an increasing pace. These tests provide an estimate of your aerobic fitness level.
- Heart Rate Monitoring: Monitoring your heart rate during exercise can provide insights into your cardiovascular endurance. By tracking your heart rate while performing activities at different intensities, you can determine your heart rate zones and assess your ability to sustain exercise at higher levels of intensity. The longer you can maintain an elevated heart rate during exercise, the greater your cardiovascular endurance.
- Rating of Perceived Exertion (RPE): RPE is a subjective method of assessing cardiovascular endurance. It involves rating your perceived level of exertion during exercise on a scale from 1 to 10. A higher RPE indicates higher intensity and potentially better cardiovascular endurance. This method can be useful for individuals who do not have access to specialized equipment or prefer a self-assessment approach.
Assessing cardiovascular endurance provides valuable information about your aerobic fitness level, helps set appropriate exercise intensities, and allows you to track progress over time. It is important to note that cardiovascular endurance can be improved through regular aerobic exercise such as running, swimming, cycling, and other activities that elevate and sustain your heart rate for an extended period. Consulting with a fitness professional can help you choose the most appropriate method for assessing cardiovascular endurance and guide you in developing an effective training plan.
Measuring Muscular Endurance
Muscular endurance is a crucial component of overall fitness, especially for activities that require repetitive muscle contractions over an extended period. Assessing muscular endurance helps identify the strength and stamina of specific muscle groups and provides insights into the effectiveness of your training program. Here are some common methods for measuring muscular endurance:
- Repetition Maximum (RM) Test: The repetition maximum test involves performing as many repetitions as possible of a specific exercise with a predetermined weight. For example, in a push-up RM test, you would perform as many push-ups as you can with proper form. This test helps determine your muscle endurance capacity and identifies any muscular imbalances or weaknesses.
- Timed Exercises: Timed exercises are another way to measure muscular endurance. This method involves performing a specific exercise for a set amount of time, such as a plank hold, wall sit, or bodyweight squats. The goal is to perform the exercise for as long as possible without compromising form. Tracking the duration of the exercise provides a measure of muscular endurance.
- Muscular Endurance Tests: Various specific tests target different muscle groups to measure their endurance. Examples include the push-up test for upper body endurance, the sit-up test for core endurance, and the squat test for lower body endurance. These tests typically involve performing as many repetitions as possible with good form within a specific time frame.
- Circuit Training: Circuit training is a form of exercise that combines aerobic and strength-training exercises in a continuous cycle. It challenges both cardiovascular endurance and muscular endurance. The number of repetitions of each exercise within a circuit and the total number of circuits completed can serve as an indirect measure of muscular endurance.
Measuring muscular endurance allows you to track progress, focus on specific muscle groups, and design targeted training programs. It is important to note that improving muscular endurance requires consistent resistance training, gradually increasing the resistance or number of repetitions, and providing adequate rest and recovery. Consulting with a fitness professional can ensure proper form, technique, and exercise selection for accurate measurement and effective improvement of muscular endurance.
Evaluating Endurance in Sports Performance
Endurance plays a crucial role in sports performance, as it directly impacts an athlete’s ability to sustain physical activity and perform at a high level for an extended period. Evaluating endurance in sports performance involves assessing the specific endurance elements required for a particular sport and determining an athlete’s capacity to meet those demands. Here are some key factors to consider when evaluating endurance in sports:
- Sport-Specific Demands: Each sport has unique endurance requirements. Understanding the specific demands of a sport, such as running long distances in soccer or maintaining a high work rate in basketball, is essential in evaluating an athlete’s endurance capabilities.
- Endurance Testing: Utilizing sport-specific endurance tests can provide valuable insights into an athlete’s ability to meet the demands of their sport. These tests may include timed drills, simulated game scenarios, or sport-specific endurance challenges. Evaluating an athlete’s performance in these tests can help identify areas of strength and areas for improvement.
- Game Analysis: Analyzing an athlete’s performance during competitive games can offer valuable information about their endurance. Observing how an athlete maintains intensity, sustains effort throughout the game, and recovers quickly between plays can provide insights into their endurance levels and potential areas for improvement.
- Heart Rate Monitoring: Monitoring an athlete’s heart rate during training and competition can provide quantitative data on their cardiovascular endurance. Measuring heart rate in different situations, such as during intense bursts of activity or during recovery periods, can help assess an athlete’s ability to maintain performance and recover quickly between efforts.
- Training Volume and Intensity: Evaluating an athlete’s training volume and intensity can provide a snapshot of their endurance capacity. Monitoring the duration and intensity of training sessions, as well as the frequency of workouts, can help determine whether an athlete is adequately training to improve their endurance for their specific sport.
Evaluating endurance in sports performance is a dynamic process that requires ongoing assessment and adjustment. By understanding the sport-specific demands and utilizing various evaluation methods, coaches and athletes can identify strengths, weaknesses, and potential areas for improvement in order to optimize performance on the field.
Tracking Endurance Progress
Tracking your endurance progress is essential for monitoring improvements, staying motivated, and making informed decisions about your training. By regularly assessing and recording your endurance levels, you can objectively measure your progress and adjust your workouts accordingly. Here are some effective ways to track endurance progress:
- Keep a Training Journal: Maintaining a training journal allows you to record and review your workouts, including the duration, intensity, and type of exercise performed. You can document how you felt during the workout, any challenges encountered, and any notable achievements. Regularly reviewing your journal helps you identify patterns and trends in your endurance progress.
- Monitor Performance Metrics: Tracking performance metrics, such as the distance covered, time taken, or repetitions completed, in specific endurance tests or workouts can provide concrete data on your progress. By comparing your performance over time, you can gauge improvements in your endurance capacity.
- Heart Rate Monitoring: Monitoring your heart rate during exercise can provide valuable insights into your cardiovascular fitness. By tracking your heart rate during similar workouts, you can assess improvements in your heart’s efficiency and better endurance. Over time, you may notice that your heart rate decreases for a given level of exertion, indicating enhanced cardiovascular endurance.
- Regular Fitness Assessments: Periodically assessing your endurance using standardized tests, such as the Cooper Test or VO2 max test, can offer a comprehensive evaluation of your fitness level. By comparing your results from previous assessments, you can track improvements in your endurance performance.
- Subjective Assessment: In addition to objective measurements, it is important to listen to your body and assess how you feel during and after workouts. Notice any improvements in your perceived exertion levels, breathing efficiency, and recovery time. Subjective assessments can provide valuable insights into your overall endurance progress.
- Use Technology: Various fitness tracking devices, smartphone apps, and wearable technology can help track and analyze your endurance progress. These tools provide real-time tracking of metrics such as distance, pace, heart rate, and calories burned. They can also offer visual representations of your progress over time, motivating you to strive for further improvements.
By implementing these tracking methods consistently, you can gain a clearer understanding of your endurance progress and make data-driven decisions to optimize your training. Remember that progress may not always be linear, and it’s important to celebrate the small victories along the way. Stay consistent, stay motivated, and enjoy the journey towards improving your endurance.
Conclusion
Measuring and tracking endurance is crucial for individuals looking to improve their fitness levels, athletes aiming to enhance their performance, or anyone seeking to enhance their overall well-being. Endurance measurement provides valuable insights into cardiovascular and muscular endurance, helping set realistic goals, design effective training programs, and track progress over time.
Understanding endurance involves recognizing its components, including cardiovascular endurance and muscular endurance. Cardiovascular endurance refers to the efficiency of the heart, lungs, and circulatory system, while muscular endurance relates to the ability of muscles to exert force repeatedly over an extended period. Both types of endurance play significant roles in daily life activities and sports performance.
Various tests and methods can be used to assess endurance levels. The VO2 max test is considered the gold standard for measuring cardiovascular endurance, while repetition maximum tests, timed exercises, and muscular endurance tests can evaluate muscular endurance. Additionally, sport-specific endurance evaluation, heart rate monitoring, and tracking training volume and intensity contribute to a comprehensive assessment of endurance.
Tracking endurance progress is vital for monitoring improvements, staying motivated, and making informed decisions about training. Keeping a training journal, monitoring performance metrics, using technology, and conducting regular fitness assessments are effective ways to measure progress objectively. It’s also important to listen to your body and assess subjective experiences during workouts.
By regularly measuring and tracking your endurance, you can identify areas for improvement, set realistic goals, and optimize your training. Whether you’re an athlete, fitness enthusiast, or someone looking to enhance your overall fitness levels, understanding and measuring endurance will guide you towards reaching your full potential and living a healthier, more active lifestyle.