Home>Misc>Featured>What Fitness Test Measures Cardiovascular Endurance


Featured
What Fitness Test Measures Cardiovascular Endurance
Modified: January 22, 2024
Improve your cardiovascular endurance with our featured fitness test. Measure your fitness level and enhance your stamina with this effective endurance assessment.
Introduction
Welcome to the world of fitness! When it comes to achieving optimal health and wellness, cardiovascular endurance plays a vital role. But what exactly is cardiovascular endurance? And why is it important to measure it? In this article, we will delve into the definition of cardiovascular endurance, explore the significance of measuring it, and discuss some common fitness tests that can help evaluate it.
Cardiovascular endurance, also known as cardiorespiratory endurance or aerobic endurance, refers to the ability of the heart, lungs, and blood vessels to efficiently supply oxygen-rich blood to the working muscles during prolonged periods of physical activity. In simpler terms, it is the capacity of your body to sustain aerobic activities for an extended period of time.
Measuring cardiovascular endurance is crucial for several reasons. Firstly, it provides valuable insights into your overall fitness level and helps you understand your body’s ability to endure and recover from physical exertion. Additionally, it is an essential component in assessing your risk for cardiovascular diseases such as heart attacks and strokes. Regularly monitoring your cardiovascular endurance can also track your progress and motivate you to improve.
There are various fitness tests available to measure cardiovascular endurance, each with its own unique approach. These tests challenge the body’s aerobic capabilities and provide quantitative data to evaluate cardiovascular fitness. We will explore some of the most common fitness tests in the next section to give you a better understanding of how they work and what they measure.
So, whether you are an athlete aiming to enhance your performance, a fitness enthusiast striving for better endurance, or simply someone looking to improve your overall health, understanding and measuring cardiovascular endurance is a crucial step towards achieving your goals. Let’s dive into the world of fitness tests and explore the different ways to assess and improve cardiovascular endurance.
What is Cardiovascular Endurance?
Cardiovascular endurance, also known as aerobic endurance, refers to the ability of the cardiovascular system to deliver oxygen-rich blood to the working muscles during prolonged periods of physical activity. It is a measure of how well your heart, lungs, and blood vessels work together to supply oxygen to the body and remove waste products.
During aerobic activities such as running, cycling, or swimming, the body’s demand for oxygen increases. To meet this demand, the heart pumps more blood, the lungs take in more oxygen, and the blood vessels transport oxygen to the working muscles. The efficiency of this process determines your cardiovascular endurance.
When you have good cardiovascular endurance, your body can sustain prolonged physical activity without fatigue. Your heart and lungs work efficiently, allowing you to maintain a steady pace and recover quickly. On the other hand, poor cardiovascular endurance can lead to fatigue, shortness of breath, and decreased performance in physical activities.
It is important to note that cardiovascular endurance is different from muscular endurance. While cardiovascular endurance focuses on the cardiovascular system’s ability to provide oxygen to the body, muscular endurance refers to the ability of specific muscles to repeatedly exert force over an extended period.
Several factors contribute to cardiovascular endurance, including genetics, age, sex, and lifestyle. Regular aerobic exercise, such as jogging, swimming, or cycling, helps improve cardiovascular endurance by strengthening the heart, increasing lung capacity, and improving blood circulation.
By measuring cardiovascular endurance, you can gain valuable insights into your overall fitness level and identify areas for improvement. Fitness tests specifically designed to evaluate cardiovascular endurance provide a quantifiable measure of your aerobic capacity and help track your progress over time.
In the next section, we will explore the importance of measuring cardiovascular endurance and how it can benefit your overall health and fitness journey.
Importance of Measuring Cardiovascular Endurance
Measuring cardiovascular endurance is of utmost importance in assessing your overall fitness level and tracking your progress in achieving optimal health. Here are some key reasons why it is essential to measure cardiovascular endurance:
- Evaluation of Fitness Level: Measuring cardiovascular endurance provides a quantitative measure of your aerobic capacity. It helps you understand how well your cardiovascular system is functioning and gives you an indication of your overall fitness level. By knowing your baseline endurance, you can set specific goals and work towards improving your fitness.
- Risk Assessment: Cardiovascular endurance is closely linked to cardiovascular health. By measuring your endurance capacity, you can assess your risk for heart diseases such as heart attacks and strokes. Individuals with poor cardiovascular endurance may be at a higher risk, highlighting the importance of improving endurance levels to protect heart health.
- Progress Tracking: Regularly measuring cardiovascular endurance allows you to track your progress over time. As you engage in aerobic exercise and training, you can monitor how your endurance levels improve. This provides motivation and helps you stay committed to your fitness goals.
- Performance Enhancement: For athletes and individuals involved in sports or physical activities, measuring cardiovascular endurance is crucial for enhancing performance. By knowing your endurance capacity, you can tailor your training programs to focus on improving endurance specific to your sport or activity. This can lead to better stamina, increased energy levels, and improved overall performance.
Measuring cardiovascular endurance also helps in identifying any limitations or areas of weakness that need to be addressed. By pinpointing these areas, you can design targeted exercise and training routines to improve your endurance levels and overcome any barriers to achieving your goals.
In addition to the above benefits, measuring cardiovascular endurance can also provide a sense of achievement and satisfaction as you witness your endurance levels improving. It encourages a positive mindset, boosts self-confidence, and instills a sense of discipline and dedication to maintaining a healthy and active lifestyle.
Now that we understand the importance of measuring cardiovascular endurance, let’s explore some common fitness tests that can assess your aerobic capacity and endurance in the next section.
Common Fitness Tests for Cardiovascular Endurance
There are several fitness tests available that can help assess and measure cardiovascular endurance. These tests are designed to challenge the aerobic capacity of the body and provide valuable insights into your endurance levels. Let’s take a closer look at some of the most commonly used fitness tests:
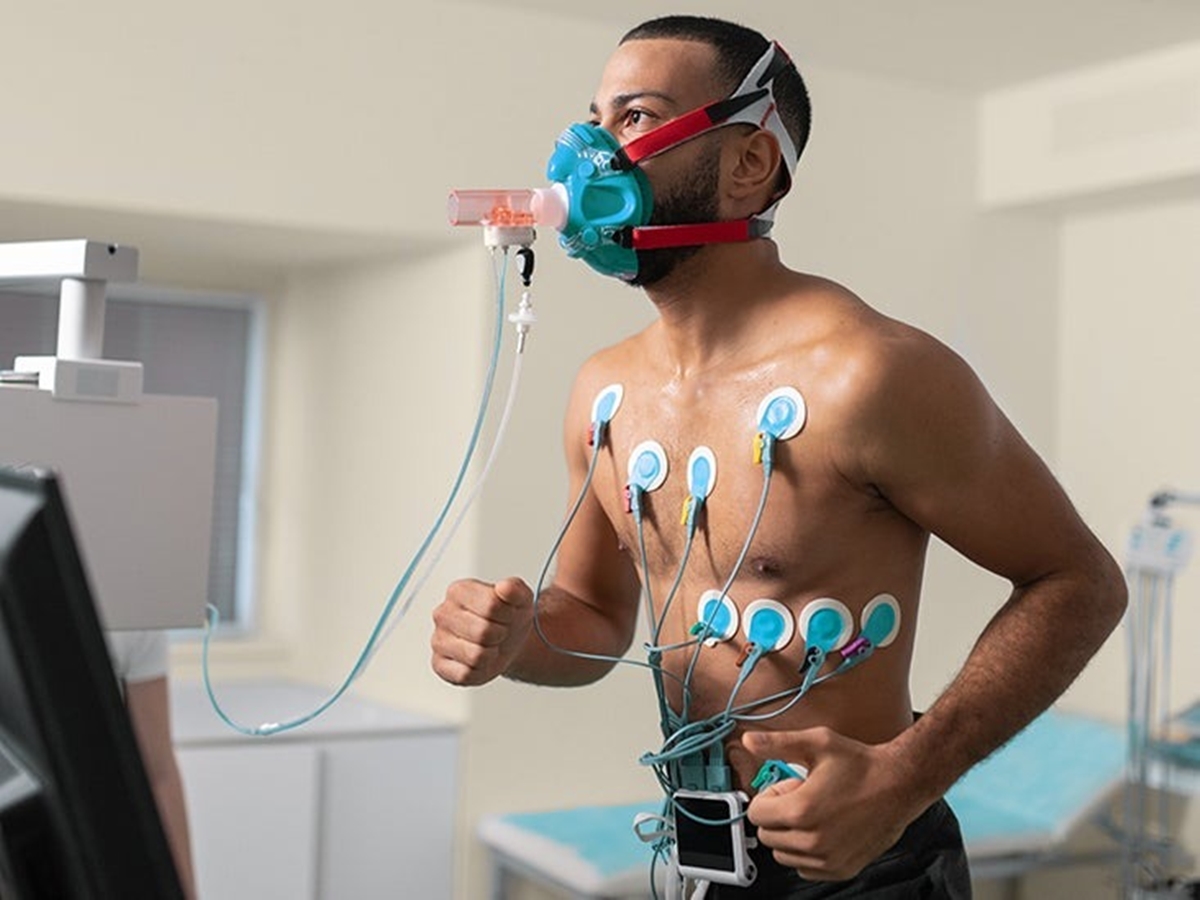
- Maximum Oxygen Consumption Test: Also known as the VO2 max test, this is considered the gold standard for measuring cardiovascular endurance. It determines the maximum amount of oxygen your body can utilize during intense exercise. The test involves running on a treadmill or cycling on an ergometer while wearing a mask that measures oxygen uptake and carbon dioxide output.
- Cooper’s 12-Minute Run Test: This test is a simple and practical way to assess cardiovascular endurance. It requires you to run as far as you can in 12 minutes. The distance covered is used as an indicator of your endurance capacity.
- 1.5-Mile Run Test: Similar to the Cooper’s test, the 1.5-mile run test involves running a specific distance within a set time frame. This test is commonly used in military and law enforcement fitness assessments to evaluate cardiovascular endurance.
- Beep Test: Also known as the multi-stage fitness test or the shuttle run test, the beep test is a progressive and challenging fitness assessment. It involves running back and forth between two points, keeping up with a series of beeps that increase in speed and intensity. The test measures the maximum volume of oxygen you can consume, reflecting your cardiovascular endurance.
- Treadmill Stress Test: This test is usually conducted under the supervision of a medical professional. It involves running on a treadmill while your heart rate, blood pressure, and breathing are monitored. The test measures how well your cardiovascular system functions under stress.
These fitness tests provide objective measures of cardiovascular endurance and can help tailor exercise programs to focus on specific areas of improvement. It is important to note that these tests should be conducted under professional supervision and in a controlled environment to ensure safety and accuracy of the results.
By undergoing these fitness tests, you can gain valuable insights into your aerobic capacity and identify areas for improvement. The results can serve as a baseline for setting realistic goals and tracking progress over time. It is important to remember that cardiovascular endurance is not fixed and can be improved with regular aerobic exercise and training.
In the next section, we will explore the factors that can affect cardiovascular endurance and provide tips on how to improve it.
Maximum Oxygen Consumption Test
The Maximum Oxygen Consumption test, commonly referred to as the VO2 max test, is considered the gold standard for measuring cardiovascular endurance. This test provides a comprehensive assessment of your body’s ability to utilize oxygen during intense exercise.
The VO2 max test involves running on a treadmill or cycling on an ergometer while wearing a mask that measures oxygen uptake and carbon dioxide output. The intensity of the exercise gradually increases, pushing your cardiovascular system to its maximum capacity. The test continues until you reach your maximum effort or show signs of exhaustion.
The primary measurement derived from the VO2 max test is your VO2 max value, which represents the maximum amount of oxygen your body can consume and utilize during exercise. It is typically measured in milliliters of oxygen per kilogram of body weight per minute (ml/kg/min).
VO2 max is influenced by various factors, including genetics, age, sex, and training status. A higher VO2 max value indicates a superior cardiovascular endurance capacity, as your body can efficiently deliver oxygen to the working muscles and remove waste products.
The VO2 max test provides valuable insights into your aerobic fitness level and can be used to assess and monitor your progress over time. It helps determine your baseline endurance capacity, identify potential areas for improvement, and track the effectiveness of your training programs.
It is important to note that the VO2 max test should be conducted under the supervision of professionals in a controlled environment to ensure accuracy and safety. The test can be physically demanding and requires a high level of effort and motivation from the participant.
Improving your VO2 max value can lead to enhanced cardiovascular endurance and overall fitness. Regular aerobic exercise, such as running, swimming, or cycling, is key to improving VO2 max. High-intensity interval training (HIIT), which alternates intense bursts of exercise with periods of active recovery, has been shown to be particularly effective in boosting VO2 max.
Additionally, incorporating a variety of aerobic activities into your training routine, gradually increasing the intensity and duration of your workouts, and practicing good nutrition and hydration can all contribute to improving your VO2 max and cardiovascular endurance.
Incorporating the Maximum Oxygen Consumption test into your fitness assessments can provide valuable information about your endurance capacity and guide your training efforts for optimal results.
Cooper’s 12-Minute Run Test
Cooper’s 12-minute run test is a simple and practical fitness test widely used to assess cardiovascular endurance. It requires you to run as far as you can within a 12-minute time frame. This test provides a measure of your aerobic capacity and endurance.
To perform the Cooper’s 12-minute run test, find a flat track or a measured running route. Start running at a comfortable pace, aiming to maintain a steady rhythm throughout the 12 minutes. The goal is to cover as much distance as possible within the given time.
After completing the run, record the distance covered in meters or laps around the track. This distance serves as an indicator of your endurance capacity. The further you run, the better your cardiovascular endurance.
Cooper’s test is suitable for individuals of different fitness levels, from beginners to elite athletes. It is a versatile test that can be conducted in various settings, making it accessible to many people.
The test results can be used to assess your current aerobic fitness level, track your progress over time, and set specific goals for improvement. It provides tangible data that can help you tailor your training programs and monitor your endurance gains.
To improve your performance in the Cooper’s 12-minute run test and enhance your cardiovascular endurance, it is important to incorporate regular aerobic exercise into your routine. This can include activities such as running, swimming, cycling, or dancing.
Gradually increasing the duration and intensity of your workouts can help improve your endurance. Implementing interval training, which involves alternating between periods of high-intensity exercise and recovery, can also be effective in boosting cardiovascular fitness.
In addition to cardiovascular exercise, it is important to focus on proper nutrition, hydration, and rest to support optimal endurance performance. Eating a well-balanced diet, staying hydrated, and getting adequate rest and recovery are all essential elements of maintaining and improving cardiovascular endurance.
By regularly incorporating the Coopers 12-minute run test into your fitness assessments and using the results as a benchmark, you can monitor your progress, stay motivated, and work towards achieving your endurance goals.
1.5-Mile Run Test
The 1.5-mile run test is a commonly used fitness test to assess cardiovascular endurance and aerobic capacity. It involves running a specific distance, typically 1.5 miles or 2.4 kilometers, within a set time frame. This test is often used in military and law enforcement fitness assessments to evaluate an individual’s endurance level.
To perform the 1.5-mile run test, find a flat and measured running route or track. Start running at a steady pace, aiming to complete the distance as quickly as possible. Make sure to pace yourself and maintain a consistent effort throughout the run.
Timing is crucial in the 1.5-mile run test. Keep track of the time it takes you to complete the distance, and record your finishing time in minutes and seconds. This time serves as an indicator of your cardiovascular endurance, with faster completion times indicating better endurance capacity.
The 1.5-mile run test is a practical and accessible way to evaluate your aerobic fitness level. It provides a standardized and objective measure of your endurance, making it easy to compare your results over time and set realistic goals for improvement.
To improve your performance in the 1.5-mile run test and enhance your cardiovascular endurance, incorporate a combination of aerobic training and interval workouts into your routine. Regular running, jogging, or other cardio exercises can help build your endurance base.
Interval training, which alternates between high-intensity and lower-intensity periods, can be particularly beneficial for improving aerobic capacity. For example, you can incorporate speed intervals during your runs by alternating between faster-paced running and recovery periods.
In addition to training, it is important to maintain a balanced diet, stay hydrated, and get adequate rest and recovery. Proper nutrition and hydration support your energy levels and overall performance, while rest and recovery allow your body to repair and adapt to the training stimulus.
By regularly incorporating the 1.5-mile run test into your fitness assessments and monitoring your progress, you can track your improvement in cardiovascular endurance. Remember to approach the test with the right mindset and give your best effort, but also listen to your body and avoid overexertion to prevent injury.
The 1.5-mile run test offers a practical and effective way to measure cardiovascular endurance and can be an excellent tool to motivate and challenge yourself to improve your overall fitness.
Beep Test
The beep test, also known as the multi-stage fitness test or the shuttle run test, is a popular fitness assessment used to measure cardiovascular endurance and aerobic capacity. This test involves running back and forth between two points, keeping up with a series of beeps that increase in speed and intensity.
To perform the beep test, set up two markers approximately 20 meters apart. Start running at a comfortable pace, timed with the beeps. As the test progresses, the time between beeps decreases, requiring you to maintain a faster pace. The test is divided into stages, with each stage representing an increase in speed.
The beep test continues until you are unable to keep up with the required pace and cannot reach the marker before the next beep. The level and distance you reach before stopping are used to determine your fitness level and cardiovascular endurance.
The beep test is a challenging and dynamic way to assess aerobic fitness as it incorporates progressive increases in intensity. It measures your body’s ability to efficiently use oxygen and deliver it to working muscles during high-intensity exercise.
By performing the beep test regularly, you can track your progress and endurance gains over time. This test provides tangible data that allows you to set specific goals and tailor your training programs to improve your cardiovascular endurance.
To improve your performance in the beep test, it is important to incorporate regular aerobic training into your routine. Running, cycling, swimming, and other forms of cardio exercises can help enhance your endurance and prepare you for the demands of the test.
Incorporating interval training can be particularly effective for improving cardiovascular endurance for the beep test. Structuring your workouts to include periods of higher intensity followed by active recovery can help improve your ability to withstand the increasing pace and intensity of the test.
Additionally, focusing on proper nutrition, hydration, and adequate rest and recovery are essential for optimizing your performance. Fueling your body with nutrient-rich foods, staying hydrated, and allowing enough time for rest and recovery are all important components of maintaining and enhancing cardiovascular endurance.
The beep test offers a challenging and dynamic way to assess and improve your cardiovascular endurance. By incorporating it into your fitness routine and striving to improve your performance, you can enhance your overall fitness and exceed your endurance goals.
Treadmill Stress Test
The treadmill stress test is a comprehensive fitness assessment commonly used to evaluate cardiovascular endurance and assess the performance of the cardiovascular system under stress. This test is typically conducted under the supervision of healthcare professionals in a controlled environment.
The test involves running on a treadmill while your heart rate, blood pressure, and breathing are closely monitored. The intensity and speed of the treadmill increase gradually, simulating the stress and demands placed on the cardiovascular system during physical exertion.
The purpose of the treadmill stress test is to determine how well your cardiovascular system functions under stress and to identify any potential abnormalities or limitations. The test provides valuable information about your heart’s response to exercise, your endurance capacity, and your overall cardiovascular health.
During the test, the healthcare professional will monitor your heart rate, blood pressure, and electrical activity of the heart (through an electrocardiogram or ECG). The test can also include blood tests to evaluate how well your heart is functioning and to assess your risk for cardiovascular diseases.
The data collected during the treadmill stress test, such as heart rate response, blood pressure changes, and ECG readings, are analyzed to assess your cardiovascular endurance and diagnose any underlying conditions or abnormalities.
The treadmill stress test is used for various purposes, including evaluating exercise capacity, identifying any signs of heart disease, determining optimal exercise intensity levels, and guiding treatment plans for individuals with existing cardiovascular conditions.
While the treadmill stress test is typically performed for diagnostic purposes, it can also be used to monitor and track improvements in cardiovascular endurance over time. By periodically repeating the test, you can assess the effectiveness of your training programs and make adjustments as needed.
To prepare for a treadmill stress test, it is best to consult with your healthcare provider. They will provide specific instructions tailored to your needs, which may include avoiding certain medications, fasting before the test, and wearing suitable workout attire.
It is important to remember that the treadmill stress test should be conducted under the supervision of healthcare professionals to ensure safety and accuracy of the results. They will closely monitor your vital signs and ensure that you are properly equipped to handle the physical demands of the test.
The treadmill stress test offers valuable insights into your cardiovascular endurance and can provide important information about your overall heart health. By undergoing this test, you can better understand your endurance capacity, evaluate your cardiovascular fitness level, and take proactive steps to improve your cardiovascular health.
Factors Affecting Cardiovascular Endurance
Cardiovascular endurance is influenced by various factors, both intrinsic and extrinsic, that can impact its level and performance. By understanding these factors, you can gain insight into why your cardiovascular endurance may vary and identify areas for improvement. Here are some key factors that affect cardiovascular endurance:
- Genetics: Genetic factors can play a role in determining your baseline cardiovascular endurance. Some individuals may be genetically predisposed to having higher or lower endurance levels. However, it is important to note that genetics are not the sole determining factor and that cardiovascular endurance can still be improved through training and lifestyle modifications.
- Age: As we age, our cardiovascular endurance naturally declines. This is due to physiological changes such as a decrease in aerobic capacity, muscle mass, and lung function. However, regular exercise and physical activity can help slow down this decline and maintain cardiovascular endurance as we age.
- Sex: In general, males tend to have higher cardiovascular endurance compared to females. This is primarily attributed to differences in body composition, hormones, and muscle mass. However, it is important to note that individual variations exist, and both males and females can improve their cardiovascular endurance through training.
- Training Level: The level of physical activity and training you engage in significantly influences cardiovascular endurance. Regular aerobic exercise, such as running, swimming, or cycling, can improve endurance by strengthening the heart, increasing lung capacity, and improving overall cardiovascular function.
- Diet and Nutrition: Proper nutrition plays a crucial role in fueling your body for optimal cardiovascular endurance. Consuming a balanced diet that includes complex carbohydrates, lean proteins, and essential fats provides the energy and nutrients necessary for endurance activities. Hydration is also essential to support cardiovascular function.
- Body Composition: Body composition, specifically the ratio of lean muscle mass to fat mass, can affect cardiovascular endurance. Higher levels of lean muscle mass are associated with better endurance performance as muscles are responsible for oxygen utilization and energy production during exercise.
- Mental Stamina: Mental stamina and motivation also play a role in cardiovascular endurance. Mental resilience, determination, and the ability to push through discomfort can impact your endurance capacity. Developing mental strategies and staying focused during challenging workouts can help improve endurance performance.
These factors interact with one another, and their impact on cardiovascular endurance varies from person to person. While some factors like genetics and age are beyond our control, many can be influenced and improved through lifestyle modifications and training.
It is important to approach improving cardiovascular endurance holistically by considering all of these factors. By incorporating regular cardiovascular exercise, maintaining a nutritious diet, and focusing on mental stamina, you can optimize your cardiovascular endurance and achieve your fitness goals.
Tips for Improving Cardiovascular Endurance
Improving cardiovascular endurance is achievable through consistent effort and a focused approach to training. By following these tips, you can enhance your endurance capacity and boost your overall cardiovascular fitness:
- Incorporate Regular Aerobic Exercise: Engage in regular aerobic activities such as running, swimming, cycling, or dancing. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity exercise per week.
- Interval Training: Include interval training in your workouts. Alternate between periods of higher intensity and active recovery to challenge your cardiovascular system and improve your endurance. For example, try alternating between sprints and jogging during a run.
- Progressive Overload: Gradually increase the intensity, duration, and frequency of your workouts to continually challenge your cardiovascular system and adapt to higher levels of endurance. This principle of progressive overload helps prevent plateaus and stimulates further improvements.
- Variety in Training: Incorporate a variety of aerobic exercises in your training routine. Cross-training with different activities such as swimming, cycling, or rowing can target different muscle groups and prevent overuse injuries while improving overall cardiovascular endurance.
- Strength Training: Include strength training exercises to improve muscular endurance, which complements cardiovascular endurance. Focus on compound exercises that involve multiple muscle groups, like squats, lunges, push-ups, and rows.
- Proper Nutrition: Maintain a balanced diet rich in whole grains, lean proteins, fruits, and vegetables. These provide the necessary nutrients and energy to fuel your workouts and support optimal cardiovascular function.
- Hydration: Stay hydrated before, during, and after your workouts. Dehydration can impair cardiovascular function and hinder endurance performance. Drink water regularly and consider sports drinks during prolonged or intense workouts.
- Consistency: Stick to a regular exercise routine, aiming for at least three to five workouts per week. Consistency is key in improving cardiovascular endurance and maintaining progress over time.
- Rest and Recovery: Allow for adequate rest and recovery days to allow your body to repair and adapt to the training stimulus. Recovery is just as important as training and is crucial for preventing overtraining and injuries.
- Gradual Progression: Avoid pushing yourself too hard too quickly. Gradually increase the intensity and duration of your workouts to minimize the risk of injury. Listen to your body and adjust your training accordingly.
Remember, improving cardiovascular endurance takes time and dedication. Be patient with your progress, celebrate small victories, and make adjustments to your training as needed. By incorporating these tips into your routine, you can steadily improve your cardiovascular endurance and reach your fitness goals.
Conclusion
Cardiovascular endurance is a crucial component of overall fitness and plays a significant role in maintaining optimal health. Measuring and improving cardiovascular endurance can have numerous benefits, including assessing your fitness level, tracking progress, and reducing the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
By understanding the factors that influence cardiovascular endurance and incorporating effective strategies, you can enhance your aerobic capacity and improve your overall fitness. Fitness tests such as the maximum oxygen consumption test, Coopers 12-minute run test, 1.5-mile run test, beep test, and treadmill stress test provide valuable insights into your endurance level and can guide your training efforts.
To improve cardiovascular endurance, incorporate regular aerobic exercise, interval training, and strength training into your routine. Consistency, progressive overload, proper nutrition, hydration, and rest are key to optimizing your endurance gains. It is important to consider individual factors such as genetics, age, sex, and training level while setting realistic goals and monitoring progress.
Remember, improving cardiovascular endurance is a journey that requires commitment, patience, and dedication. Listen to your body, consult with professionals when necessary, and strive for gradual improvements. Prioritizing cardiovascular fitness will not only enhance your performance in physical activities but also contribute to your overall well-being.
So, lace up your shoes, get moving, and take the exciting challenge of improving your cardiovascular endurance. Your hard work and commitment will pay off as you achieve new levels of fitness and embrace a healthier, more active lifestyle.