Featured
What Is Sprint Football In College
Modified: August 21, 2023
Discover the exciting world of sprint football in college. Explore the sport's unique rules and traditions, teams to watch, and more. Featured on our site.
Introduction
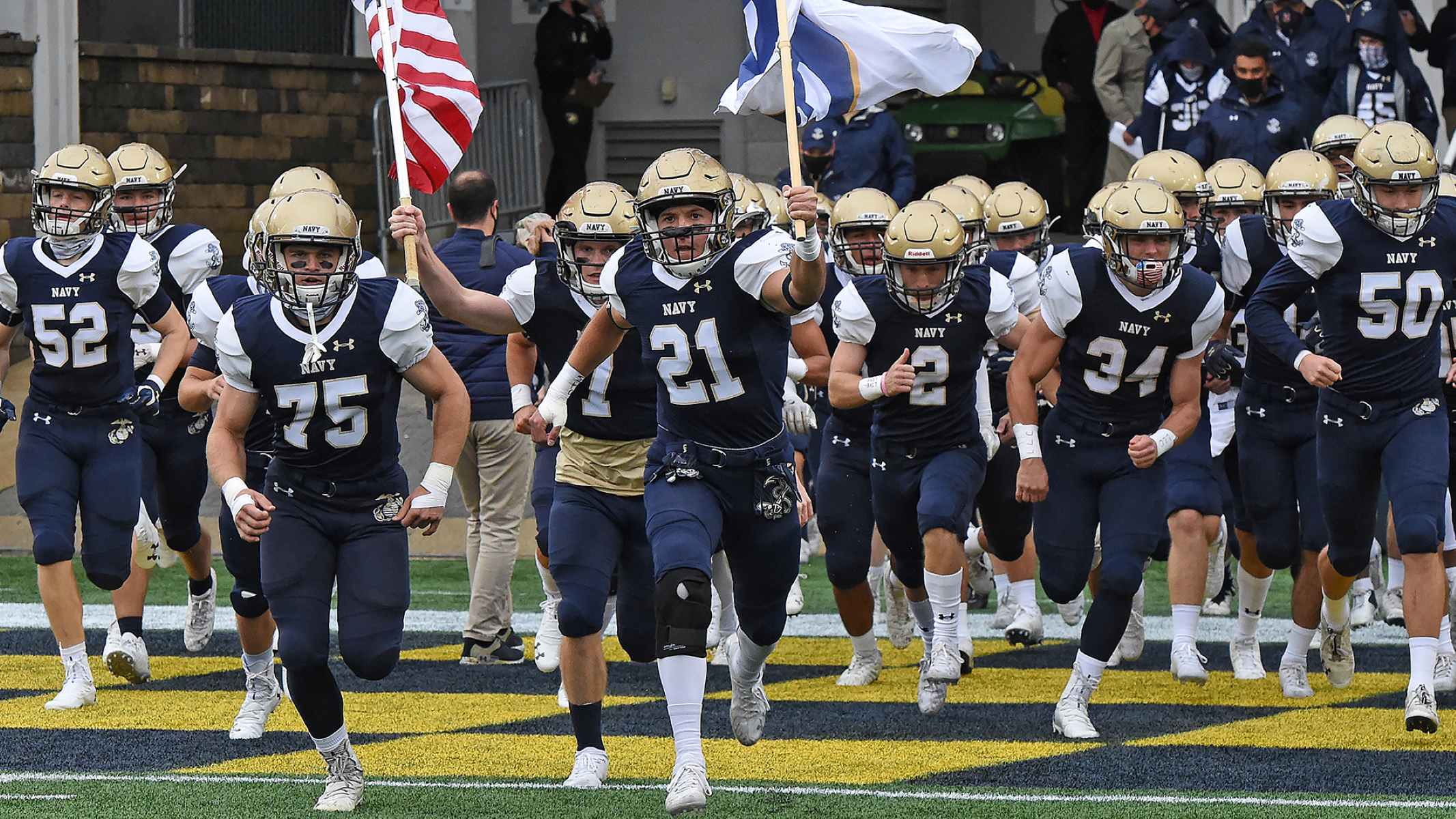
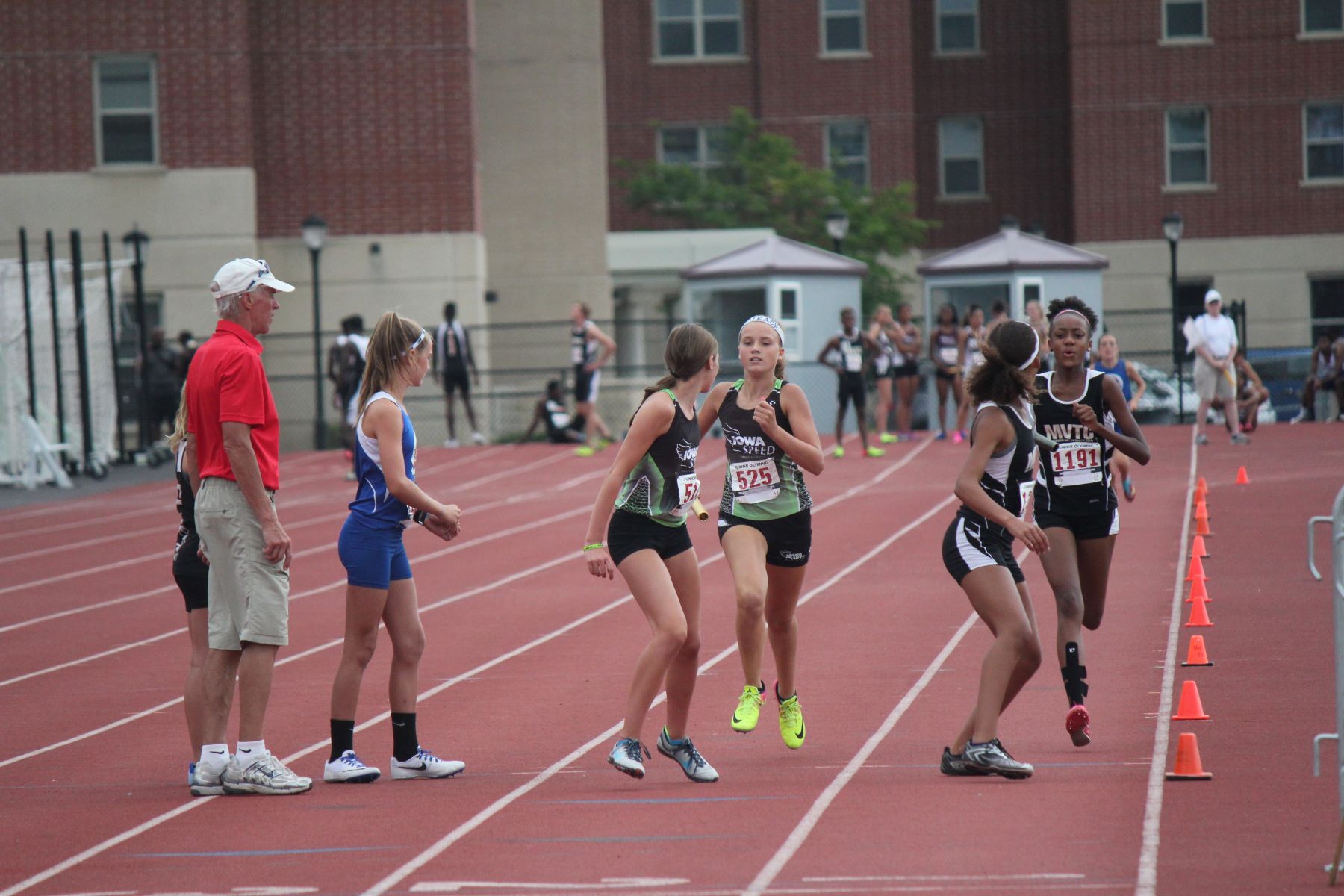
Sprint football, also known as lightweight football, is a unique and exciting sport that has gained popularity in college athletics. It offers a fast-paced and intense version of the traditional game, with some key differences that set it apart. In sprint football, players must meet a weight limit, typically 178 pounds, which makes it an inclusive sport where size and strength are not the sole determining factors of success on the field.
The origins of sprint football can be traced back to the early 20th century, when it was introduced as an alternative to regular football for smaller and lighter athletes. It was initially called “lightweight football” and was primarily played at the collegiate level. Over the years, the sport has evolved and gained recognition for its exciting gameplay and competitive nature.
The rules and regulations of sprint football differ slightly from those of regular football. The most notable difference is the weight limit imposed on players. This limitation encourages athleticism, agility, and speed, as players must rely on their quickness and technique rather than sheer physicality. The smaller size of the players also leads to a faster and more dynamic game, with plays unfolding rapidly and requiring quick decision-making.
Sprint football offers several advantages and benefits, both for the players and the fans. It provides a platform for athletes who may not fit the prototypical football player mold to showcase their skills and compete at a high level. The sport emphasizes strategy, agility, and teamwork, allowing players to develop these traits and gain valuable experience on the field.
In recent years, sprint football has gained traction among colleges and universities across the United States. Several college sprint football leagues have been established, providing opportunities for teams to compete and showcase their talent. These leagues closely follow the rules and regulations set forth by the Collegiate Sprint Football League (CSFL) and the National Collegiate Sprint Football Championship (NCSFC).
Throughout its history, sprint football has produced some notable players who have gone on to achieve success in the sport. These athletes have proven that size is not the only determining factor in football, and they have excelled on the field with their speed, agility, and skills.
Looking ahead, sprint football faces various challenges in terms of expanding its reach and attracting more athletes. The sport requires continued promotion and support to ensure its longevity and growth. However, with its exciting gameplay and unique characteristics, sprint football has the potential to become even more popular in the world of college athletics.
History of Sprint Football
The origins of sprint football can be traced back to the early 20th century when it emerged as an alternative to regular football for athletes of smaller build. The sport was initially known as “lightweight football” and gained popularity in colleges and universities across the United States.
In 1934, the Collegiate Sprint Football League (CSFL) was formed to oversee and organize lightweight football competitions. The league set a weight limit of 165 pounds for players, with the intention of creating a more inclusive sport where athletes of various sizes could participate.
Over the years, lightweight football continued to evolve, and in 1998, the CSFL renamed the sport “sprint football” to better reflect its fast-paced nature and emphasize the importance of speed and agility on the field.
The CSFL has played a pivotal role in the growth and development of sprint football. It has expanded to include teams from prestigious Ivy League institutions such as Army, Navy, Cornell, Penn, and Princeton, among others. The league has attracted a dedicated following of fans and garnered attention for its exciting gameplay and competitive atmosphere.
The National Collegiate Sprint Football Championship (NCSFC) was established in 2011 to provide a platform for teams to compete for the title of national champion. The NCSFC is a culmination of the CSFL season and features a playoff format, adding to the intensity and excitement of the sport.
Sprint football has gained recognition for its unique characteristics and the opportunities it provides for athletes who may not fit the traditional football player mold. The weight limit ensures that size and strength are not the sole determining factors of success on the field, allowing athletes with speed, agility, and skill to showcase their abilities.
While sprint football initially gained popularity in the college setting, there have been efforts to establish the sport at the high school level as well. Some schools have introduced lightweight programs, providing younger athletes with a chance to experience the thrill of sprint football and develop their skills.
As sprint football continues to evolve and grow, there is potential for further expansion and recognition. The sport offers a unique and exciting alternative to regular football, catering to athletes of various sizes and showcasing the importance of agility and speed in a fast-paced game. With dedicated leagues, competitive championships, and passionate players and fans, sprint football has carved out its own space in the world of collegiate athletics.
Rules and Regulations
Sprint football follows a set of rules and regulations that differentiate it from regular football. These rules are designed to ensure fair play, promote safety, and create a level playing field for all athletes involved.
The most significant distinction in sprint football is the weight limit imposed on players. In the Collegiate Sprint Football League (CSFL), the weight limit is typically set at 178 pounds. This limitation aims to create a balance between athletes of different sizes and levels of physicality, emphasizing skill, speed, and agility over sheer strength.
With a smaller player roster, sprint football teams consist of nine players on the field for each side, as opposed to the traditional eleven. This adjustment allows for greater freedom of movement and creates a more fast-paced and dynamic playing experience.
The field dimensions in sprint football are also altered. The playing field measures 100 yards in length and 40 yards in width, making it narrower than a regular football field. This adjustment further enhances the fast-paced nature of the game, as plays unfold quickly, and players have less space to cover.
Other rules in sprint football mirror those of regular football, such as the scoring system, penalties, and timing. Teams aim to score touchdowns, field goals, and extra points, while following the rules and regulations set by the CSFL and the NCSFC. Penalties may be enforced for various infractions, and games are divided into four quarters, each lasting 12 minutes.
For safety reasons, sprint football requires players to wear full pads, including helmets, shoulder pads, hip and tailbone pads, and knee and thigh pads. This equipment helps protect players from potential injuries while ensuring a level of physicality in the game.
Officials, including referees and judges, are responsible for enforcing the rules and ensuring fair play during sprint football games. They monitor the field, assess penalties, and oversee the flow of the game to maintain a safe and competitive environment.
The rules and regulations of sprint football are continually reviewed and updated to enhance the sport and adapt to the changing needs of the players and teams involved. These rules contribute to the unique nature of sprint football, fostering a fast-paced and exciting game where athletes of varying sizes can excel.
Differences between Sprint Football and Regular Football
Sprint football and regular football may share similarities, but there are key differences that set them apart. These differences impact the gameplay, strategies, and physical requirements for the athletes involved.
The most significant difference between sprint football and regular football is the weight limit imposed on players. In sprint football, players must meet a weight limit of around 178 pounds, whereas in regular football, there are no weight restrictions. This limitation in sprint football ensures a more level playing field, allowing athletes of smaller build to compete against opponents of similar size rather than being at a disadvantage against larger opponents.
Due to the weight restrictions, the size of the teams also differs between sprint football and regular football. In sprint football, teams consist of nine players on the field, while regular football teams have eleven players on the field. Smaller team sizes in sprint football lead to a faster-paced game, with more open space and increased opportunities for explosive plays.
The field dimensions in sprint football are also modified compared to regular football. The length of the field remains the same at 100 yards, but the width is reduced to 40 yards in sprint football, making it narrower than a regular football field. The smaller field size in sprint football intensifies the game, with players having less space to cover and making each play more impactful.
Another significant difference lies in the physical requirements and playing style of the athletes. In sprint football, where size and brute strength are not the determining factors of success, speed, agility, and skill play a more vital role. Players in sprint football need to rely on their quickness, technique, and football IQ to navigate the field effectively. Regular football, on the other hand, often places a larger emphasis on size, strength, and power.
Equipment is also a point of difference between sprint football and regular football. While both sports require athletes to wear helmets, shoulder pads, and other protective gear, the equipment used in sprint football is typically lighter to accommodate the weight restrictions. This modification allows for a greater range of movement and agility, aligning with the nature of the sport.
Moreover, the rules and regulations of the games may have some variations, particularly in terms of penalties and play clock management. These differences are in place to suit the specific needs and dynamics of each sport, ensuring fair play and maintaining the pace of the game.
Overall, while both sprint football and regular football share the same objective of scoring touchdowns and showcasing athletic prowess, the weight limit, team size, field dimensions, physical requirements, and playing style set them apart. These differences contribute to the uniqueness and excitement of the sprint football experience.
Benefits and Advantages of Sprint Football
Sprint football offers numerous benefits and advantages, both for the players involved and the overall college athletics landscape.
One of the key advantages of sprint football is its inclusive nature. By imposing a weight limit, the sport ensures that athletes of various sizes and builds have the opportunity to participate and excel. This promotes diversity and creates a level playing field where skill, speed, and agility are emphasized over sheer physicality.
Sprint football also provides a platform for athletes who may not fit the traditional football player mold to showcase their talents. The sport values quickness, technique, and strategic thinking, allowing individuals with these attributes to thrive. It opens up opportunities for athletes who may have been overlooked in traditional football programs to compete at a high level and gain recognition.
The sport’s emphasis on speed, agility, and skill development has several benefits for the players involved. Sprint football helps athletes improve their cardiovascular fitness, endurance, and overall athleticism. The fast-paced and dynamic nature of the game encourages quick decision-making, reflexes, and coordination. These skills translate well to other sports and can contribute to the overall development of the athletes’ athletic abilities.
Moreover, sprint football fosters teamwork and camaraderie among players. Teams must work together to execute strategies, communicate effectively, and support one another on the field. The shared experiences and shared goals in sprint football create a strong team dynamic and build lasting connections among teammates.
For colleges and universities, sprint football offers several advantages as well. It provides an additional avenue for student-athletes to pursue their passion for football and compete at the collegiate level. This expands the range of options available to athletes and can contribute to a stronger and more diverse athletic program.
Sprint football can also help colleges and universities attract a wider range of students. By offering a sport that embraces athletes of various sizes and builds, institutions can showcase their commitment to inclusivity and provide opportunities for student-athletes who may not have considered participating in traditional football.
Furthermore, the unique characteristics of sprint football, such as its fast-paced gameplay and emphasis on skill, can generate excitement and interest among fans. The sport offers an entertaining and thrilling spectator experience, attracting a dedicated fan base and further enhancing the overall college athletics atmosphere.
In summary, sprint football offers numerous benefits and advantages for both the players and the colleges and universities involved. Its inclusive nature, focus on skill and speed, and promotion of teamwork contribute to the development and growth of athletes while expanding the opportunities available in college athletics.
College Sprint Football Leagues
Sprint football has gained significant recognition and popularity in college athletics, leading to the establishment of dedicated leagues that oversee and organize competitions. These leagues provide a platform for teams to showcase their skills, compete for championships, and promote the growth of the sport.
One of the most prominent sprint football leagues is the Collegiate Sprint Football League (CSFL). Founded in 1934, the CSFL is composed of teams from prestigious colleges and universities across the United States. Some of the notable institutions that participate in the CSFL include Army, Navy, Cornell, Penn, Princeton, and Franklin Pierce University.
The CSFL sets the standards for weight limits, field dimensions, rules, and other aspects of sprint football. It ensures fair play, safety, and uniformity throughout the league. Through its governance and support, the CSFL has played a crucial role in the development and growth of sprint football as a collegiate sport.
Within the CSFL, teams compete throughout the season in regular-season games to secure a spot in the playoffs. The top teams then face off in the CSFL Championship game, vying for the title of conference champion. The championship game is highly competitive and garners significant attention from fans and supporters of sprint football.
In addition to the CSFL, other college sprint football leagues have been established to provide opportunities for teams from different regions to compete. These leagues include the Eastern Sprint Football League (ESFL) and the Midwest Sprint Football League (MSFL), among others.
The Eastern Sprint Football League (ESFL) consists of teams primarily from schools in the East Coast region. It provides a platform for these teams to participate in regular-season games, ultimately leading to the ESFL Championship game. The ESFL operates under the same weight limit and rules as set forth by the CSFL.
The Midwest Sprint Football League (MSFL) features teams from colleges and universities in the Midwest region. It offers athletes and teams the opportunity to compete against each other in sprint football, following the same weight limit and rules as the CSFL and other affiliated leagues.
These college sprint football leagues, such as the CSFL, ESFL, and MSFL, create a sense of community, healthy competition, and camaraderie among teams and athletes. They provide a platform for athletes to showcase their skills and represent their respective institutions on a competitive stage.
Through these leagues, college sprint football continues to grow and gain recognition across the country. The dedication and commitment of the participating schools, players, coaches, and fans contribute to the development and success of sprint football as an established collegiate sport.
Famous Sprint Football Players
Sprint football has produced some notable players who have gone on to achieve success both within the sport and beyond. These athletes have proven that size and weight limitations are not barriers to excelling in football and have shown that speed, agility, and skill are equally valuable on the field.
One such famous sprint football player is Joe Dunn, who played for the Army Black Knights in the Collegiate Sprint Football League (CSFL). Dunn was a standout player known for his exceptional speed and agility. After his sprint football career, he continued to pursue football at the professional level, signing with the Philadelphia Eagles as a wide receiver. Dunn’s success in sprint football and subsequent transition to professional football demonstrated the level of talent and skill present in the sport.
Kevin Bonner is another notable sprint football player who made a name for himself in the sport. Bonner was a standout player for the Cornell Big Red, earning multiple All-CSFL selections during his career. His speed, quickness, and ability to make explosive plays on the field set him apart. Bonner’s success in sprint football led him to earn a spot on the Army football coaching staff, where he continues to make a significant impact in the sport.
Among the famous sprint football players, we also find players who have excelled in other sports. One such example is Jake Stebbins who played sprint football for the Army Black Knights. Stebbins, known for his elite speed and agility, transitioned from sprint football to lacrosse and went on to become a standout player at the collegiate level, earning numerous accolades for his performance on the field.
These success stories highlight the potential for achievement and recognition in sprint football. They demonstrate that talented and dedicated athletes can thrive in the sport, using their speed, agility, and football skills to excel on the field.
Furthermore, it’s important to note that every sprint football team possesses a roster of talented players who contribute to the success of the team. While some players may reach fame and recognition at a higher level, the collective efforts of the team are what lead to victories.
As sprint football continues to grow in popularity, it is likely that we will see the emergence of more famous sprint football players who will further elevate the profile of the sport and inspire future generations of athletes.
Challenges and Future of Sprint Football
While sprint football has made significant strides in recent years, it still faces several challenges as it looks toward the future. Addressing these challenges is crucial for the continued growth and success of the sport.
One of the primary challenges is increasing awareness and visibility of sprint football. Many people are still unaware of the sport and its unique characteristics. Efforts must be made to promote sprint football at the high school and youth levels to generate interest and attract young athletes. Increased media coverage and marketing can help raise the profile of the sport and attract a broader fanbase.
Another challenge is recruiting and retaining talented athletes. Many high school athletes may not be aware of the opportunities available in sprint football or may be hesitant to pursue the sport due to its weight restrictions. Educating athletes and their families about the benefits and opportunities of sprint football can help overcome this challenge and attract more talented players to the sport.
Financial support is also a significant challenge for sprint football programs. As a less recognized and established sport compared to mainstream football, securing sufficient funding for equipment, facilities, and coaching staff can be difficult. Additional investment and support, both from colleges and universities and potential sponsors, are crucial for the sustainability and growth of sprint football programs.
Expanding the reach of sprint football is another challenge. Currently, the sport is primarily concentrated in the United States, with most competitions and leagues centered around American colleges and universities. Exploring opportunities for international competition and collaboration can broaden the horizons of sprint football and increase its global recognition.
Looking ahead, the future of sprint football appears promising. The sport offers an alternative for athletes who may not fit the traditional football player mold and provides an exciting and fast-paced game for both players and fans. The ongoing efforts of dedicated leagues, such as the Collegiate Sprint Football League (CSFL), to promote and organize sprint football competitions contribute to its future success.
Additionally, the advancements in technology and media have made it easier to promote and access sports content. Online streaming platforms and social media can be utilized to share sprint football games and highlights, reaching a wider audience and generating more interest in the sport.
With continued efforts to address the challenges it faces and opportunities for growth, sprint football has the potential to expand its reach, attract more talented athletes, and garner widespread recognition. By promoting the sport’s unique qualities, engaging in strategic partnerships, and investing in its development, the future of sprint football looks promising.
Conclusion
Sprint football, with its weight restrictions and fast-paced gameplay, offers a unique and inclusive experience within the realm of college athletics. It provides a platform for athletes of varying sizes and builds to excel on the field, emphasizing skill, speed, and agility over sheer physicality.
Throughout its history, sprint football has faced challenges, such as increasing awareness, recruiting talented athletes, securing financial support, and expanding its reach. However, with the dedication and passion of leagues like the Collegiate Sprint Football League (CSFL) and other affiliated organizations, the sport has made significant strides.
The benefits and advantages of participating in sprint football are numerous. It fosters an inclusive and diverse environment where athletes of varying sizes can showcase their skills and compete at a high level. The sport promotes teamwork, camaraderie, and individual development, both on and off the field.
The future of sprint football holds great potential. By continuing to raise awareness, recruit talented athletes, secure necessary funding, and expand its reach, sprint football can attract a broader audience and elevate its profile within the college athletics landscape.
Efforts to promote sprint football at the high school and youth levels, as well as exploring opportunities for international competition, can contribute to the long-term growth and success of the sport.
In conclusion, sprint football offers an exciting and engaging alternative to traditional football, providing opportunities for athletes to showcase their skills, compete at a high level, and foster inclusivity within the sport. With ongoing efforts to address challenges and invest in its future, sprint football has the potential to thrive and become an increasingly popular sport within the college athletics community.