Featured
What To Drink During A Workout
Modified: January 2, 2024
Discover the featured drinks you should have during your workout for optimal hydration and performance. Find out what to drink to fuel your exercise routine.
Introduction
When it comes to optimizing your workout, there are various factors to consider, such as exercise intensity, duration, and technique. However, one aspect that is often overlooked is proper hydration. Staying hydrated during a workout is crucial for maximizing performance, preventing fatigue, and promoting overall well-being.
During physical activity, our bodies lose water through sweat, and if this water is not replenished, it can lead to dehydration. Dehydration not only impairs physical performance but can also have negative effects on cognitive function and cardiovascular health.
While it may seem simple to quench your thirst with any beverage, not all drinks are created equal when it comes to fueling your workout. The choice of beverage can impact your energy levels, endurance, and even muscle recovery.
In this article, we will explore the different types of drinks that can enhance your workout performance. From the classic choice of water to electrolyte-rich sports drinks, protein shakes, and even infused water, we’ll uncover the benefits and optimal occasions for each.
Importance of Hydration During a Workout
Proper hydration is essential for maintaining physical performance and overall health during a workout. When you exercise, your body temperature rises, leading to sweating as a mechanism to cool down. This sweating causes a loss of fluids and electrolytes, which if not replenished, can result in dehydration.
Dehydration can have a significant impact on exercise performance. It can lead to decreased strength, endurance, and coordination, as well as increased fatigue and muscle cramps. Additionally, dehydration affects cognitive function, making it more difficult to concentrate and making you more prone to mistakes or accidents.
To prevent dehydration, it’s crucial to drink plenty of fluids before, during, and after your workout. The general recommendation is to consume around 17 to 20 ounces of water two to three hours before exercise. During exercise, aim to drink about 7 to 10 ounces of fluid every 10 to 20 minutes, depending on the intensity and duration of your workout.
Keep in mind that these recommendations may vary depending on factors such as body weight, sweat rate, and environmental conditions. It’s important to pay attention to your body’s cues and adjust your fluid intake accordingly.
Additionally, it’s not only water that needs to be replenished during exercise. When you sweat, you also lose important electrolytes such as sodium, potassium, and magnesium. These electrolytes play a crucial role in maintaining proper fluid balance, nerve function, and muscle contractions. Replenishing electrolytes is particularly important during more intense and prolonged workouts.
The bottom line is that staying hydrated during a workout is essential for optimal performance and overall well-being. Proper hydration helps maintain energy levels, prevent muscle cramps, and enhance cognitive function. By paying attention to your fluid intake and replenishing both water and electrolytes, you can ensure that you get the most out of your exercise routine.
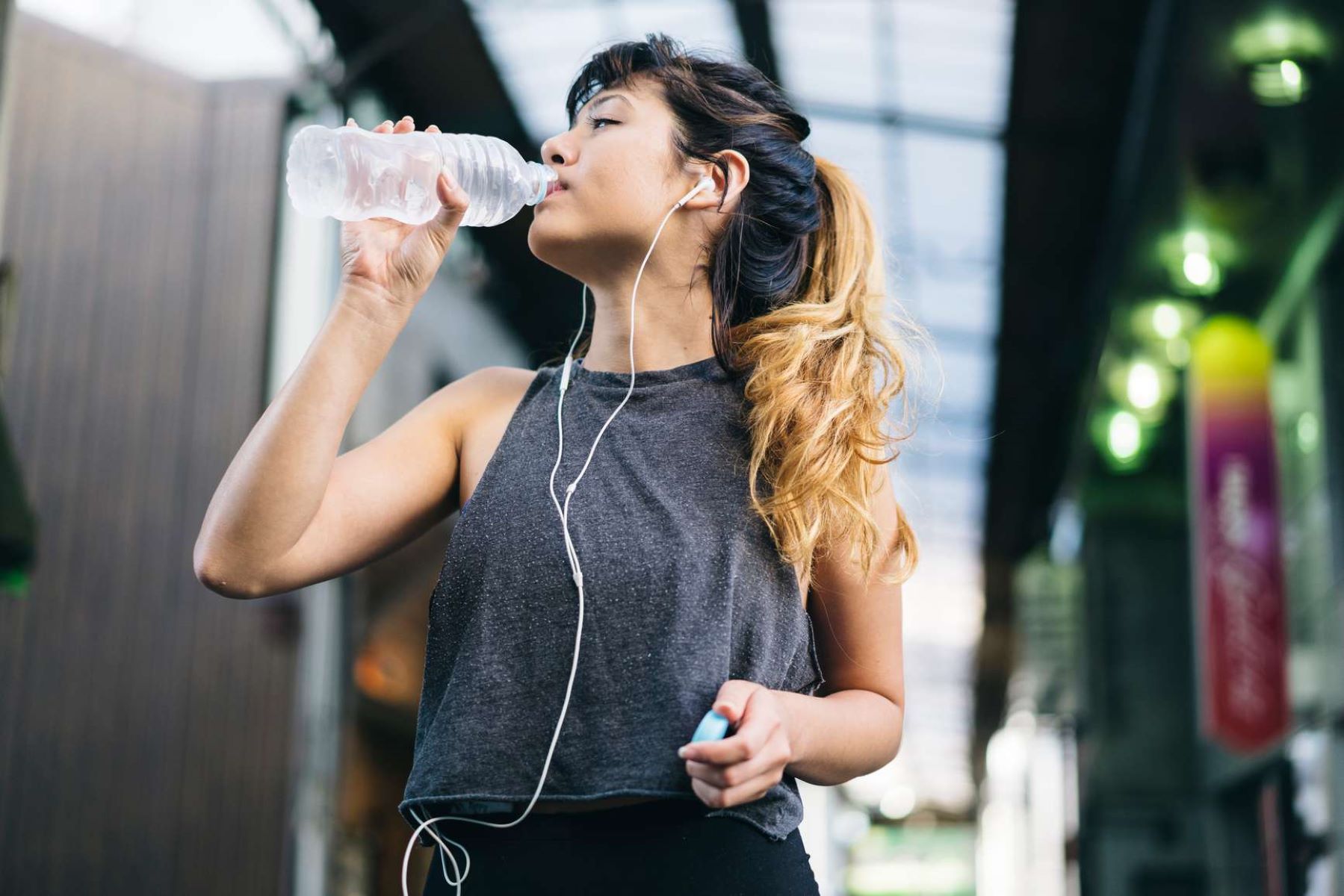
Water: The Ultimate Hydration Source
When it comes to hydration, water is the go-to choice for many. It is readily available, affordable, and most importantly, essential for our overall health and well-being. Water makes up a significant portion of our body composition and is involved in numerous bodily functions, including temperature regulation, nutrient transportation, and waste removal.
Drinking water before, during, and after a workout is crucial to maintain proper hydration levels. It helps to replenish the fluids lost through sweating and supports optimal physical performance. For shorter and less intense workouts, water alone is generally sufficient to meet your hydration needs.
It’s important to note that everyone’s water needs differ based on factors such as body weight, activity level, and environmental conditions. As a general guideline, aim to drink at least 8 cups (64 ounces) of water per day, and increase your intake during periods of increased physical activity.
To make drinking water more convenient and enjoyable during a workout, consider investing in a reusable water bottle that you can easily carry with you. Opt for bottles with measurements to track your hydration progress throughout the day.
If you find plain water to be bland or boring, you can infuse it with fruits, herbs, or even a splash of citrus juice to add some flavor. Experiment with combinations like lemon and mint, strawberries and basil, or cucumber and lime to create your own personalized hydration concoctions.
Remember, staying properly hydrated is not only important during your workout but also throughout the day. Whenever you reach for a beverage, consider grabbing a glass of water to keep your hydration levels in check. It’s a simple and effective way to ensure that you’re meeting your body’s hydration needs.
Sports Drinks: The Optimal Choice for Intense Workouts
For individuals engaging in intense and prolonged workouts, sports drinks can be a game-changer. These beverages are specifically formulated to replenish electrolytes and provide a quick source of energy to fuel your muscles.
Sports drinks typically contain a combination of carbohydrates, electrolytes, and sometimes even protein. The carbohydrates provide a readily available source of energy, while the electrolytes help maintain proper fluid balance and support muscle function.
During high-intensity exercise, our bodies rely heavily on carbohydrates as a fuel source. When we deplete our glycogen stores, which are our stored carbohydrates, our energy levels can drop, and our performance can suffer. Consuming a sports drink during these workouts can help replenish glycogen levels and provide an immediate boost of energy.
Furthermore, the electrolytes in sports drinks, such as sodium, potassium, and magnesium, help replace the minerals lost through sweat. This is particularly important for individuals who tend to sweat heavily during their workouts, as excessive sweating can lead to imbalances and muscle cramps.
It’s important to note that sports drinks are not necessary for every workout. If you’re engaging in a shorter, low-intensity workout, water should be sufficient to meet your hydration needs. Sports drinks are best reserved for intense workouts lasting longer than 60 minutes or in hot and humid environments where you may be sweating excessively.
When choosing a sports drink, be sure to check the label for the carbohydrate and electrolyte content. Different brands and varieties may have varying levels, so choose one that aligns with your specific needs. Additionally, be mindful of the calorie content, as some sports drinks can be high in sugar and calories.
Remember, sports drinks should complement a well-balanced diet and should not be used as a substitute for regular meals. It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional or sports nutritionist to determine the best approach for incorporating sports drinks into your workout routine.
Electrolyte-rich Beverages: Enhancing Performance and Replenishing Nutrients
When it comes to maximizing performance and replenishing nutrients during a workout, electrolyte-rich beverages can be a valuable addition to your hydration routine. These beverages are specially formulated to provide a balance of electrolytes that are crucial for optimal muscle function and hydration.
Electrolytes are minerals that carry an electric charge and help regulate important bodily functions, including nerve signaling, muscle contractions, and fluid balance. The most common electrolytes found in these beverages are sodium, potassium, calcium, and magnesium.
During intense workouts or prolonged physical activity, our bodies lose electrolytes through sweat. Replenishing these electrolytes is essential to prevent dehydration, maintain muscle function, and support overall performance.
Electrolyte-rich beverages can come in various forms, including powders, tablets, and ready-to-drink options. They are typically low in calories and may have added flavors to make them more palatable. Some popular choices include electrolyte water, coconut water, and specialized sports drinks.
Electrolyte water is a great option for those looking for a zero-calorie, no-sugar alternative. It contains essential electrolytes without any additional carbohydrates or artificial sweeteners. Coconut water, on the other hand, is a natural source of electrolytes and also provides natural sugars and hydration benefits.
Specialized sports drinks that focus on replenishing electrolytes are also available. These drinks often contain a combination of electrolytes and carbohydrates to provide both hydration and energy during and after intense workouts. They can be particularly beneficial for endurance athletes or individuals engaging in high-intensity activities.
When choosing an electrolyte-rich beverage, consider your individual needs and the duration and intensity of your workout. If you are engaging in light to moderate exercise, water with added electrolytes may be sufficient. However, for longer or more intense workouts, you may benefit from a specialized electrolyte beverage to optimize performance and prevent electrolyte imbalances.
As with any drink, it’s important to read the labels and be aware of any added sugars or artificial ingredients. Choose beverages that align with your nutritional goals and preferences.
Remember, electrolyte-rich beverages should be viewed as a complement to a well-rounded diet and should not replace whole foods or other hydration sources. It’s essential to listen to your body and choose the right hydration strategy that works best for you.
Protein Shakes: Boosting Muscle Recovery and Growth
Protein shakes have gained popularity among athletes and fitness enthusiasts as a convenient and effective way to support muscle recovery and growth. These beverages provide a concentrated source of protein, which is essential for repairing and building muscle tissue.
During a workout, our muscles undergo microscopic damage, and protein is necessary to repair and rebuild these tissues. Consuming protein shortly after exercise can enhance the recovery process and promote muscle growth.
Protein shakes are a convenient option as they can be quickly consumed and absorbed by the body. They come in various forms, including whey, casein, and plant-based options such as pea or soy protein. These protein powders can be blended with water, milk, or other liquids and often include additional nutrients like vitamins, minerals, and amino acids.
Whey protein, derived from milk, is one of the most popular choices due to its complete amino acid profile, fast absorption rate, and ability to promote muscle protein synthesis. Casein, on the other hand, is a slower-digesting protein that provides a sustained release of amino acids, making it an ideal choice for nighttime recovery.
For individuals following a plant-based or lactose-free diet, there are a variety of protein powders available that are derived from sources like soy, pea, hemp, or rice. These plant-based protein options can provide similar benefits to animal-based proteins and are suitable for those with specific dietary preferences or restrictions.
While protein shakes can be a convenient and effective way to support muscle recovery, it’s important to note that whole foods should still be a primary source of protein in a well-balanced diet. Foods like lean meats, poultry, fish, eggs, dairy products, legumes, and nuts should be incorporated to ensure a variety of nutrients and dietary fiber.
When incorporating protein shakes into your workout routine, it’s important to consider your specific goals, activity level, and nutritional needs. It’s recommended to consume a protein shake within 30 minutes to an hour after exercise to optimize muscle recovery. The amount of protein needed can vary depending on factors such as body weight, training intensity, and goals, but a general guideline is around 20-30 grams per serving.
Keep in mind that protein shakes should not replace a balanced meal but rather be used as a supplement to support your overall nutrition and fitness goals. It’s always best to consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian to determine the best approach for incorporating protein shakes into your individual routine.
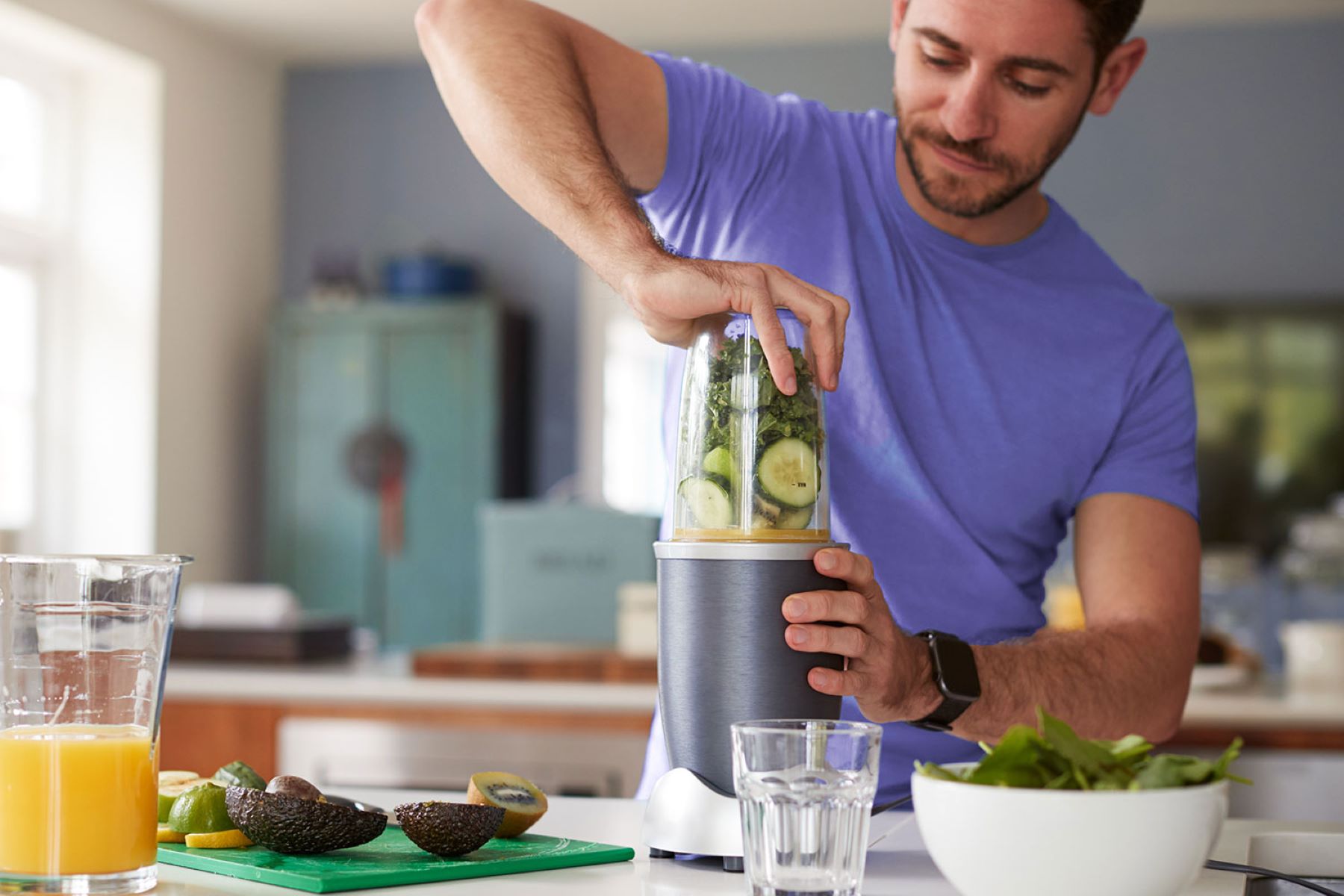
Smoothies: A Nutrient-Packed Pre or Post-Workout Option
Smoothies are a versatile and nutrient-packed beverage option that can be enjoyed as a pre or post-workout drink. These blended concoctions offer a convenient way to consume a variety of nutrients, including carbohydrates, protein, healthy fats, vitamins, and minerals, all in one glass.
As a pre-workout option, smoothies can provide the necessary fuel to increase energy levels and sustain stamina during exercise. By combining carbohydrates from fruits, such as bananas or berries, with a source of protein, like Greek yogurt or protein powder, smoothies can help in promoting muscle glycogen stores and preventing muscle breakdown.
The carbohydrates in the smoothie provide a quick source of energy while the protein helps with muscle repair and growth. Adding healthy fats, such as nut butters or avocados, can further enhance the nutritional profile and provide sustained energy throughout the workout.
For post-workout recovery, smoothies can be an excellent option to replenish nutrients and support muscle repair. By including a combination of protein and carbohydrates, smoothies can help restore glycogen levels and initiate the recovery process.
Including ingredients such as a high-quality protein powder, Greek yogurt, or milk, along with fruits and vegetables, can help provide the necessary amino acids, antioxidants, and vitamins needed for muscle recovery and growth.
Smoothies also allow for customization based on personal preferences and dietary needs. They can be easily tailored to be vegan, gluten-free, or dairy-free by using plant-based milk alternatives, protein powders, and a variety of fruits and vegetables.
It’s important to note that the nutritional content of a smoothie can vary depending on the ingredients and portion sizes used. Be mindful of added sugars and consider using whole fruits instead of juices or sweetened syrups to keep the sugar content in check.
To make a smoothie even more beneficial, consider adding additional nutrient-dense ingredients such as spinach, kale, chia seeds, flaxseeds, or nut butters. These ingredients can not only boost the nutritional value of the smoothie but also provide additional fiber, antioxidants, and healthy fats.
Experimenting with different combinations of fruits, vegetables, proteins, and healthy fats can help you find the perfect smoothie recipe that suits your taste buds and supports your fitness goals.
Remember, smoothies should not replace whole foods in your diet, but rather serve as a convenient and nutrient-dense option to support your pre or post-workout nutrition.
Coffee and Tea: Providing an Energy Boost and Endurance
When it comes to getting an energy boost and enhancing endurance, coffee and tea have long been popular choices. These caffeinated beverages are known for their stimulating effects on the central nervous system and can provide an extra kick during your workout.
Coffee, in particular, is a widely consumed beverage due to its high caffeine content. Caffeine acts as a stimulant, reducing fatigue and improving alertness and focus. Consuming a cup of coffee before your workout can help increase your energy levels, allowing you to push harder and perform better.
Caffeine has been shown to enhance endurance performance by reducing perceived exertion and delaying fatigue. It can also help increase fat oxidation, making it a potential aid for those looking to improve their body composition.
Tea, on the other hand, may have a milder caffeine content compared to coffee but still provides a gentle energy boost. Green tea, in particular, contains a compound called catechins, which have been associated with increased fat oxidation and improved exercise performance.
In addition to caffeine, tea also contains other beneficial compounds such as antioxidants and polyphenols, which have been linked to various health benefits. These compounds can help reduce inflammation, improve cardiovascular health, and boost immunity.
It’s important to note that the effects of caffeine can vary depending on the individual’s tolerance and sensitivity. It’s recommended to start with a moderate amount and assess your tolerance before consuming larger quantities. Additionally, it’s essential to listen to your body and avoid excessive caffeine consumption, which can lead to jitters, increased heart rate, and disrupted sleep patterns.
While coffee and tea can provide an energy boost and enhance workout performance, it’s important to consider other factors such as hydration. Caffeine can have diuretic effects, so be sure to balance your caffeine intake with sufficient water or other hydrating beverages to maintain proper fluid balance.
Lastly, be mindful of the additional ingredients added to your coffee or tea. Sweeteners, creamers, syrups, and whipped toppings can significantly increase the calorie and sugar content of these beverages. Consider opting for healthier alternatives such as using natural sweeteners or consuming your coffee or tea black.
Incorporating coffee or tea into your pre-workout routine can provide that extra boost of energy and mental focus for a successful workout. However, it’s important to use these beverages in moderation and consider your personal tolerance and overall hydration needs.
Infused Water: Adding Flavor and Essential Nutrients
Infused water has gained popularity as a refreshing and flavorful alternative to plain water. This beverage involves adding fruits, vegetables, herbs, or spices to water, allowing their natural flavors and nutrients to infuse into the liquid.
Not only does infused water provide a subtle and refreshing taste, but it also adds essential nutrients and antioxidants to your hydration routine. The infusion process allows the water to extract the vitamins, minerals, and other beneficial compounds from the ingredients, enhancing both the flavor and nutritional content.
One of the main benefits of infused water is the variety it offers. You can get creative with the ingredients, combining different flavors and colors to create a vibrant and flavorful beverage. Some popular combinations include lemon and cucumber, strawberry and basil, or orange and mint.
In addition to providing a burst of flavor, infused water can also support hydration and overall health. Fruits and vegetables used in infused water are rich in vitamins and minerals, adding an extra nutritional boost to your drink. For example, citrus fruits like lemons and oranges are high in vitamin C, which can boost immunity and aid in collagen production.
Herbs and spices can also be added to infused water, offering their own unique health benefits. Mint leaves or ginger slices can aid in digestion, while basil or rosemary can provide antioxidants and reduce inflammation.
Not only does infused water promote hydration and nutrient intake, but it can also be a healthier alternative to sugary beverages. By infusing water with natural flavors, you can enjoy a satisfying and refreshing drink without any added sugars or artificial ingredients.
Infused water is easy to make at home. Simply add your choice of fruits, vegetables, herbs, or spices to a pitcher or water bottle, and let it sit for a few hours to allow the flavors to infuse. You can create larger batches and keep them refrigerated for several days.
It’s important to note that while infused water can enhance the taste and nutritional value of water, it should not replace plain water altogether. Plain water is still essential for hydration and maintaining overall body functions.
Next time you reach for a glass of water, consider adding a twist with infused water. It’s a simple and enjoyable way to stay hydrated while adding flavor and essential nutrients to your daily routine.
Conclusion
Choosing the right beverage during a workout can greatly impact your performance, endurance, and recovery. Hydration plays a vital role in supporting your overall well-being and optimizing exercise outcomes.
Water is the ultimate hydration source, providing essential fluid replenishment without any added calories or artificial ingredients. It should be the go-to choice for shorter and less intense workouts.
For intense and prolonged workouts, sports drinks can be the optimal choice. These beverages contain a combination of carbohydrates and electrolytes to fuel your muscles and replenish essential nutrients.
Electrolyte-rich beverages are particularly beneficial for individuals engaging in high-intensity activities or those who tend to sweat heavily. These drinks help restore electrolyte imbalances and enhance overall hydration.
Protein shakes can play a valuable role in muscle recovery and growth. They provide a concentrated source of protein to support muscle repair and replenish energy stores after exercise.
Smoothies offer a convenient and nutrient-packed option for pre or post-workout nutrition. They can be customized with a variety of ingredients to provide a balanced mix of carbohydrates, protein, healthy fats, vitamins, and minerals.
Coffee and tea can provide an energy boost and enhance endurance, thanks to their caffeine content. However, it’s important to consume them in moderation and consider their effects on hydration.
Finally, infused water offers a flavorful and nourishing option to stay hydrated while enjoying the natural goodness of fruits, vegetables, herbs, and spices.
Remember, everyone’s hydration needs may vary, so it’s essential to listen to your body and adjust your fluid intake accordingly. Additionally, consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian to personalize your hydration strategy based on your individual goals and needs.
By selecting the right beverage for your workout, you can optimize your performance, promote muscle recovery, and maintain overall hydration for a successful exercise routine.