Home>Misc>Featured>How Does Blood Pressure Meds Affect Athletic Performance

Featured
How Does Blood Pressure Meds Affect Athletic Performance
Modified: January 2, 2024
Discover how blood pressure medications can impact athletic performance and find out how to manage your performance while on these medications. Featured article.
Introduction
High blood pressure, also known as hypertension, is a common health condition that affects millions of people around the world. While there are various lifestyle modifications and medications available to manage blood pressure, athletes and individuals engaged in rigorous physical activities often have concerns about the potential effects of blood pressure medications on their athletic performance.
In this article, we will explore how blood pressure medications can impact athletic performance. We will discuss different types of blood pressure medications, their mechanisms of action, and how they may affect athletes’ abilities to perform at their best. Additionally, we will delve into the potential side effects of these medications and provide insights on managing blood pressure while maintaining optimal athletic performance.
It is important to note that this article is intended for informational purposes only and should not replace professional medical advice. If you have any concerns or questions about your blood pressure medications and athletic performance, it is always recommended to consult with a healthcare provider.
Now, let’s dive into the world of blood pressure medications and their impact on athletic performance.
Understanding Blood Pressure Medications
Blood pressure medications, also known as antihypertensive drugs, are prescribed to individuals with high blood pressure to help lower and control their blood pressure levels. There are several different classes of blood pressure medications, each with its own unique mechanism of action that targets specific areas of the cardiovascular system.
One common class of blood pressure medications is beta-blockers. These medications work by blocking the effects of adrenaline, a hormone that increases heart rate and constricts blood vessels. By reducing the heart’s workload and relaxing blood vessels, beta-blockers help lower blood pressure. Some examples of beta-blockers include metoprolol and propranolol.
Another class of blood pressure medications is calcium channel blockers. These medications work by blocking the entry of calcium into muscle cells in the walls of arteries, leading to relaxation of the blood vessels and a decrease in blood pressure. Examples of calcium channel blockers include amlodipine and verapamil.
ACE inhibitors (angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors) are another commonly prescribed class of blood pressure medications. ACE inhibitors work by blocking the production of angiotensin II, a hormone that causes blood vessels to constrict. By blocking the effects of this hormone, ACE inhibitors help relax blood vessels and lower blood pressure. Some examples of ACE inhibitors include lisinopril and enalapril.
Angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs) are similar to ACE inhibitors in their mechanism of action. However, instead of blocking the production of angiotensin II, ARBs block the effects of this hormone by binding to specific receptors. This results in relaxation of blood vessels and a reduction in blood pressure. Common examples of ARBs include losartan and valsartan.
Diuretics, also known as water pills, are another class of blood pressure medications. These medications work by increasing the excretion of sodium and water from the body, reducing the volume of blood and thus lowering blood pressure. Diuretics may include thiazide diuretics, such as hydrochlorothiazide, or loop diuretics, such as furosemide.
Understanding the different classes of blood pressure medications is important in assessing how they may impact an athlete’s performance. The mechanisms of action of these medications can have implications for cardiovascular function, endurance, and overall athletic performance. In the following sections, we will explore the effects of these medications on athletic performance in more detail.
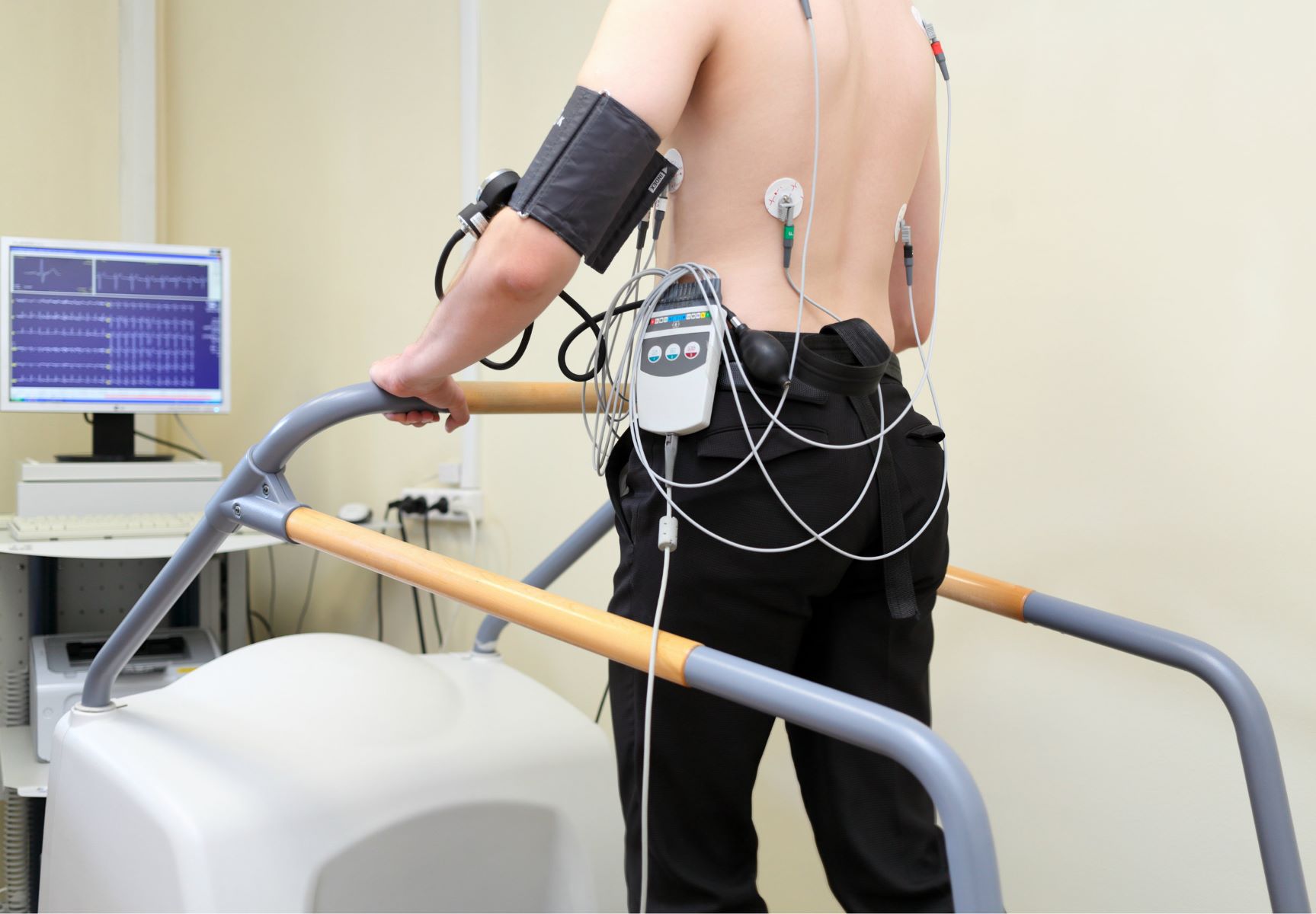
Effects of Blood Pressure Medications on Athletic Performance
Blood pressure medications can have both direct and indirect effects on athletic performance. While these medications are crucial for managing high blood pressure, athletes may need to be aware of how they might affect their performance in certain sports or physical activities.
One potential effect of blood pressure medications is a decrease in heart rate. Beta-blockers, for example, can lower heart rate by blocking the effects of adrenaline on the heart. While this may be beneficial for individuals with high blood pressure, it can affect athletic performance, particularly in sports that require high levels of cardiovascular endurance. A lower heart rate can lead to decreased exercise capacity and reduced ability to sustain high-intensity activities. Athletes engaging in endurance sports, such as long-distance running or cycling, may need to adjust their training and performance expectations when taking beta-blockers.
Calcium channel blockers and ACE inhibitors may have less impact on heart rate compared to beta-blockers. However, these medications can still affect athletic performance indirectly. By reducing blood pressure and relaxing blood vessels, they may alter blood flow to muscles during exercise. This can lead to a decrease in oxygen and nutrient delivery to the muscles, potentially impacting overall performance, especially in activities that require bursts of intense effort or quick recovery. It is important for athletes taking these medications to work closely with their healthcare team to monitor their blood pressure levels and optimize their training and performance strategies.
Diuretics, on the other hand, can have distinct effects on athletic performance. These medications increase urine production and promote fluid loss, which can lead to dehydration if not managed properly. Dehydration can cause a decrease in blood volume, impairing cardiovascular function and reducing physical performance. Athletes taking diuretics should closely monitor their hydration status and develop appropriate strategies to maintain optimal fluid balance.
It is important to note that the effects of blood pressure medications on athletic performance can vary among individuals. Factors such as dosage, individual response to medication, and the specific demands of the sport or activity should all be taken into consideration. It is recommended that athletes discuss their use of blood pressure medications with their healthcare provider, who can provide personalized guidance and recommendations based on their unique needs and circumstances.
In the next section, we will discuss the potential side effects of blood pressure medications on athletic performance.
Beta-Blockers
Beta-blockers are a class of blood pressure medications commonly prescribed to manage hypertension. They work by blocking the effects of adrenaline on the heart, resulting in a decrease in heart rate and blood pressure. While beta-blockers are effective in controlling high blood pressure, they can also have implications for athletic performance.
One of the primary effects of beta-blockers is a reduction in heart rate. By blocking the effects of adrenaline, beta-blockers slow down the heart’s rhythm, resulting in a lower resting heart rate. In some cases, this can lead to a decrease in exercise capacity, as the heart may not be able to pump blood at a rate necessary to meet the demands of intense physical activity. Athletes taking beta-blockers may experience decreased endurance, reduced ability to sustain high-intensity efforts, and slower recovery times.
Additionally, beta-blockers can affect the body’s physiological response to exercise. Adrenaline, also known as epinephrine, plays a crucial role in the body’s “fight or flight” response, increasing heart rate and blood flow to the muscles. By blocking the effects of adrenaline, beta-blockers can dampen this response, potentially affecting an athlete’s ability to perform at peak levels during competitive events or intense training sessions.
Despite the potential drawbacks for athletic performance, beta-blockers may have some benefits in specific sports or activities. They can help reduce anxiety and tremors, which may be advantageous for athletes participating in sports that require precision, such as archery or shooting. Beta-blockers have been included in the list of prohibited substances by certain sports organizations, such as the International Olympic Committee, due to their potential to enhance performance. Athletes should be aware of the rules and regulations of their respective sport governing the use of beta-blockers.
It is important for athletes considering or currently taking beta-blockers to work closely with their healthcare provider and sports medicine team. Adjustments to training routines, performance expectations, and medication dosage may be necessary to strike a balance between managing blood pressure and maintaining optimal athletic performance.
In the following sections, we will explore the effects of other classes of blood pressure medications on athletic performance.
Calcium Channel Blockers
Calcium channel blockers are a class of blood pressure medications that work by blocking the entry of calcium into muscle cells in the walls of arteries. By doing so, they help relax blood vessels and decrease blood pressure. While calcium channel blockers are effective in managing hypertension, it’s important to consider their potential impact on athletic performance.
One of the effects of calcium channel blockers is their ability to dilate blood vessels, improving blood flow and reducing the workload on the heart. This can be beneficial for individuals with high blood pressure; however, it may influence athletic performance indirectly. By dilating blood vessels, calcium channel blockers can alter blood flow distribution, potentially affecting the delivery of oxygen and nutrients to the muscles during exercise.
This alteration in blood flow can have implications for endurance and performance, particularly in activities that require sustained aerobic effort. Athletes participating in endurance sports, such as long-distance running or cycling, may find that their performance is affected by the decreased oxygen and nutrient supply to the muscles. It is important for athletes taking calcium channel blockers to monitor their energy levels, endurance, and recovery, and work closely with their healthcare team to optimize their training and performance strategies.
It is worth noting that the impact of calcium channel blockers on performance may vary among individuals. The dose, duration of medication use, and specific demands of the sport or activity should all be considered when assessing the potential effects on athletic performance. Athletes should engage in open communication with their healthcare provider to discuss any concerns or adjustments that may be necessary to optimize both blood pressure management and athletic performance.
In the upcoming sections, we will explore the effects of other classes of blood pressure medications on athletic performance.
ACE Inhibitors
ACE inhibitors, short for angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, are a class of blood pressure medications commonly prescribed to individuals with hypertension. These medications work by blocking the production of angiotensin II, a hormone that causes blood vessels to constrict. While ACE inhibitors are effective in lowering blood pressure, athletes may wonder about their potential effects on athletic performance.
One of the primary effects of ACE inhibitors is their ability to relax and widen blood vessels. By doing so, these medications help improve blood flow and reduce blood pressure. However, the dilation of blood vessels caused by ACE inhibitors can influence the body’s physiological response to exercise. The altered blood flow distribution may impact the delivery of oxygen and nutrients to the muscles, potentially affecting an athlete’s performance, particularly during activities that require bursts of intense effort or quick recovery.
It is important to note that the extent of these effects may vary among individuals. Factors such as dosage, individual response to medication, and the specific demands of the sport or activity should be considered when assessing the potential impact on athletic performance. Athletes taking ACE inhibitors should work closely with their healthcare provider and sports medicine team to monitor their blood pressure levels and adjust their training and performance strategies as needed.
Another consideration with ACE inhibitors is their potential to increase potassium levels in the blood. While this is generally well-tolerated, athletes participating in sports that place a high demand on potassium balance, such as endurance events or endurance training, should be aware of the potential for hyperkalemia (excess potassium levels). Regular monitoring of potassium levels and coordination with healthcare providers is essential to manage this potential side effect.
Lastly, it’s worth noting that some athletes may experience a dry cough as a side effect of ACE inhibitors. This cough can be bothersome and disruptive to training or performance. In such cases, athletes should communicate with their healthcare provider to explore alternative medications or strategies to manage their blood pressure while minimizing the impact on athletic performance.
Overall, athletes taking ACE inhibitors should engage in open communication with their healthcare providers to discuss any concerns, potential adjustments to medication or dosages, and strategies to optimize both blood pressure management and athletic performance.
In the upcoming sections, we will explore the effects of other classes of blood pressure medications on athletic performance.
Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers
Angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs) are a class of blood pressure medications prescribed to manage hypertension. These medications work by blocking the effects of angiotensin II, a hormone that causes blood vessels to constrict. While ARBs are effective in lowering blood pressure, athletes may have concerns about how they can impact their athletic performance.
Similar to ACE inhibitors, ARBs help relax blood vessels, improve blood flow, and reduce blood pressure. The relaxation of blood vessels caused by ARBs can affect the body’s response to exercise and blood flow distribution. This alteration in blood flow can impact the delivery of oxygen and nutrients to the muscles, potentially influencing an athlete’s performance, particularly in activities that require bursts of intense effort or quick recovery.
It is important to note that the extent of these effects may vary among individuals. Factors such as dosage, individual response to medication, and the demands of the sport or activity should be considered when assessing the potential impact on athletic performance. Athletes taking ARBs should work closely with their healthcare provider and sports medicine team to monitor their blood pressure levels and make necessary adjustments to their training and performance strategies.
One advantage of ARBs over ACE inhibitors is that they are less likely to cause a dry cough, a common side effect associated with ACE inhibitors. This can be beneficial for athletes who may experience disruptions in training or performance due to the cough. However, athletes should be aware of other potential side effects of ARBs, such as dizziness, lightheadedness, or electrolyte imbalances, and communicate any concerns with their healthcare provider.
As with any blood pressure medication, consistency in taking ARBs as prescribed is crucial for effective management of blood pressure. Athletes should be compliant with their medication regimen and maintain regular communication with their healthcare provider to ensure their blood pressure and athletic performance are optimized.
In the following sections, we will explore the effects of other classes of blood pressure medications on athletic performance.
Diuretics
Diuretics, commonly referred to as “water pills,” are a class of blood pressure medications prescribed to manage hypertension. These medications work by increasing urine production and promoting fluid loss, which helps reduce blood volume and lower blood pressure. While diuretics are effective in managing high blood pressure, it’s important for athletes to understand their potential impact on athletic performance.
One of the primary effects of diuretics is the promotion of fluid loss from the body. Diuretics increase the excretion of sodium and water, leading to a decrease in blood volume. While this can be beneficial for individuals with high blood pressure, it can also lead to dehydration if not managed properly. Dehydration can have a significant impact on athletic performance, as it can impair cardiovascular function and reduce physical stamina.
Athletes taking diuretics should closely monitor their hydration status and develop strategies to maintain optimal fluid balance. This includes ensuring adequate fluid intake before, during, and after exercise, particularly in hot or humid conditions. It may also be necessary to work with a healthcare provider or sports nutritionist to determine the appropriate amount of fluid and electrolytes needed for effective hydration.
It is also worth noting that diuretics can have additional side effects that may impact athletic performance. These include electrolyte imbalances, such as decreased levels of potassium, sodium, and magnesium, which can affect muscle function. Fatigue, muscle weakness, and cramps can occur as a result. Athletes should be aware of these potential side effects and work with their healthcare provider to address any imbalances and maintain optimal electrolyte levels.
Furthermore, some diuretics, such as thiazide diuretics, can affect the body’s ability to regulate blood sugar levels. This can potentially impact energy levels and athletic performance, particularly in endurance events or activities that rely heavily on glucose metabolism. Athletes taking diuretics should monitor their blood sugar levels and work with a healthcare provider to manage any fluctuations and optimize performance.
While diuretics can present challenges for athletes, it is worth noting that individual responses may vary. Athletes should engage in open communication with their healthcare provider and sports medicine team to discuss their specific needs and develop strategies to optimize both blood pressure management and athletic performance.
In the upcoming sections, we will explore the effects of other classes of blood pressure medications on athletic performance.
Potential Side Effects of Blood Pressure Medications on Athletic Performance
While blood pressure medications are essential for managing hypertension, athletes should be aware of the potential side effects that these medications can have on athletic performance. Understanding these side effects can help athletes make informed decisions and work closely with their healthcare providers to optimize both their blood pressure management and their athletic endeavors.
One of the common side effects of blood pressure medications is a decrease in heart rate. Medications such as beta-blockers can lower heart rate by blocking the effects of adrenaline. While this can be beneficial for individuals with high blood pressure, it may impact athletic performance, particularly in sports that require high levels of cardiovascular endurance. A lower heart rate can lead to decreased exercise capacity and reduced ability to sustain high-intensity activities.
Another potential side effect is the alteration of blood flow. Medications like calcium channel blockers and ACE inhibitors can relax blood vessels, which may affect the distribution of blood to the muscles. This can impact oxygen and nutrient delivery to the muscles during exercise, potentially affecting overall performance, especially in activities that require bursts of intense effort or quick recovery.
Furthermore, diuretics can cause fluid loss and increase the risk of dehydration if not managed properly. Dehydration can impair cardiovascular function, reduce physical stamina, and negatively impact athletic performance. It is important for athletes taking diuretics to closely monitor their hydration status and implement strategies to maintain optimal fluid balance.
Electrolyte imbalances are another potential side effect of blood pressure medications. Diuretics, in particular, can lead to decreased levels of potassium, sodium, and magnesium. These imbalances can affect muscle function, leading to fatigue, muscle weakness, and cramps. Athletes should be aware of these potential electrolyte imbalances and work with their healthcare provider to address any deficiencies and optimize performance.
Some blood pressure medications may also have specific side effects that can impact athletic performance. For example, beta-blockers can cause dizziness, insomnia, or fatigue, while ACE inhibitors can sometimes cause a dry cough. It is important for athletes to communicate any side effects they experience with their healthcare provider to explore potential alternative solutions or adjustments to medication regimens.
It’s crucial for athletes to remember that the impact of blood pressure medications on athletic performance can vary among individuals. Factors such as dosage, individual response to medication, and the specific demands of the sport or activity should all be considered. Athletes should engage in open communication with their healthcare providers to discuss any concerns, monitor their blood pressure levels, and make necessary adjustments to training and performance strategies.
By being aware of the potential side effects of blood pressure medications, athletes can actively manage their health while striving to achieve their athletic goals.
Managing Blood Pressure and Athletic Performance
Successfully managing blood pressure while maintaining optimal athletic performance requires a multi-faceted approach. Athletes should work closely with their healthcare providers and sports medicine team to develop a comprehensive plan tailored to their individual needs and goals.
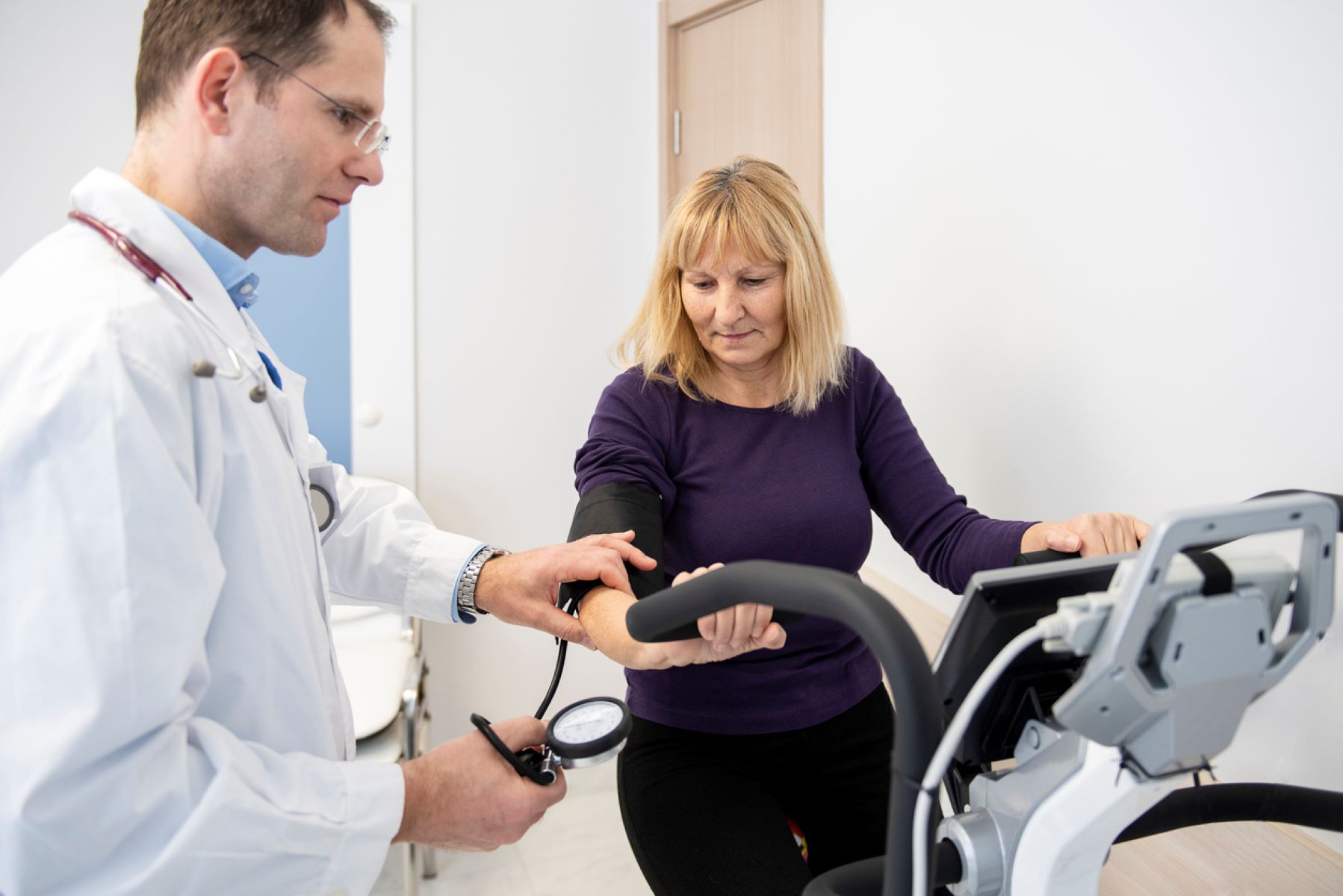
Regular monitoring of blood pressure is crucial for athletes, as it helps assess the effectiveness of medications and guides treatment adjustments. By keeping track of blood pressure readings, athletes and healthcare professionals can make informed decisions about medication dosages and monitor the impact on athletic performance.
Developing and implementing a well-rounded lifestyle plan is essential for managing blood pressure. This plan should include regular exercise, a balanced diet, stress management techniques, and maintaining a healthy body weight. Regular exercise, in particular, plays a vital role in lowering blood pressure and improving overall cardiovascular health. Athletes should engage in a combination of aerobic exercise, strength training, and flexibility exercises to enhance their physical fitness and support blood pressure management.
Communication and collaboration with healthcare providers are crucial in managing blood pressure and athletic performance. Athletes should discuss their athletic goals, training routines, and competition schedules to ensure that their medications are adjusted accordingly. Healthcare providers can also provide guidance on potential adjustments to training intensities, recovery strategies, and finding the right balance between blood pressure management and performance optimization.
Additionally, athletes should be vigilant in monitoring and maintaining optimal hydration levels. Proper hydration is vital for overall health and athletic performance. Drinking adequate amounts of fluid before, during, and after training sessions or competitions can help prevent dehydration and the associated negative impact on cardiovascular function and physical performance.
Regular check-ups and follow-up appointments with healthcare providers are essential for athletes taking blood pressure medications. It allows for ongoing monitoring of blood pressure levels, assessment of medication effectiveness, and adjustment of treatment plans. Open and honest communication regarding any side effects or concerns is crucial for optimizing both blood pressure management and athletic performance.
Achieving a balance between blood pressure management and athletic performance requires a personalized approach. The support and expertise of healthcare providers, sports medicine professionals, and coaches are invaluable in navigating this journey. By working collaboratively and proactively managing blood pressure, athletes can strive to reach their full athletic potential while maintaining their cardiovascular health.
Conclusion
Managing blood pressure while maintaining optimal athletic performance is a delicate balance that requires careful consideration and collaboration between athletes, healthcare providers, and sports medicine professionals. Understanding the potential effects of blood pressure medications on athletic performance is crucial for athletes to make informed decisions and optimize their training and competition outcomes.
Blood pressure medications, such as beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers, ACE inhibitors, angiotensin II receptor blockers, and diuretics, can have both direct and indirect effects on athletic performance. These medications can impact heart rate, blood flow distribution, fluid balance, and electrolyte levels, all of which can influence an athlete’s endurance, stamina, and overall performance.
Athletes should work closely with healthcare providers to determine the most appropriate medication regimen, dosage, and adjustments needed to manage blood pressure effectively while minimizing potential negative impacts on athletic performance. Regular blood pressure monitoring, lifestyle modifications including exercise and a balanced diet, and prudent hydration practices are essential components of blood pressure management for athletes.
Open communication, ongoing monitoring, and collaboration between athletes and healthcare providers are key to finding the right balance between blood pressure management and athletic performance. It is essential for athletes to discuss their goals, concerns, and any potential side effects they may experience with their healthcare providers in order to make educated decisions regarding medication and training programs.
Ultimately, with proper guidance and proactive management, athletes can successfully navigate the challenges of managing blood pressure while striving to achieve their athletic goals. Prioritizing cardiovascular health alongside athletic performance will contribute to athletes’ overall well-being and longevity in their pursuit of excellence.