Featured
How Is Exercise Intensity Measured
Published: September 30, 2023
Discover how exercise intensity is measured and learn about featured techniques in this informative guide.
Introduction
Measuring exercise intensity is an essential component of any fitness program. It helps individuals track their progress, set appropriate goals, and optimize their workouts for maximum effectiveness. But how exactly is exercise intensity measured?
There are various methods and tools available to gauge exercise intensity, each offering unique insights into the body’s exertion level. From heart rate monitoring to subjective ratings of perceived exertion, these techniques provide valuable information that can guide individuals in tailoring their workouts to their specific fitness goals and abilities.
In this article, we will explore several common methods used to measure exercise intensity, including heart rate monitoring, rating of perceived exertion (RPE), the talk test, metabolic equivalents (METs), power output, and oxygen consumption (VO2).
By understanding these different approaches, you will be empowered to make informed decisions about your workout routine and ensure that you are getting the most out of your physical activity.
Heart Rate Monitoring
Heart rate monitoring is one of the most common and widely used methods to measure exercise intensity. It involves tracking and analyzing the number of times your heart beats per minute during physical activity. It provides a reliable indicator of the body’s physiological response to exercise.
To monitor your heart rate, you will need a heart rate monitor or a wearable fitness device equipped with a built-in heart rate sensor. These devices typically use a chest strap, wrist-based optical sensors, or finger sensors to detect your heart rate.
During a workout, your heart rate should increase in accordance with the intensity of the exercise. The American Heart Association recommends aiming for a target heart rate zone of 50-85% of your maximum heart rate, which can be calculated by subtracting your age from 220.
Heart rate monitoring allows you to gauge the intensity of your workout in real-time. You can adjust your effort accordingly to stay within your target heart rate zone for optimal benefits. For example, if your goal is to improve cardiovascular fitness, you might aim for the higher end of your target heart rate zone. If you’re focusing on fat burning or recovery, you might aim for the lower end.
It’s important to note that individual factors, such as fitness level, age, and medications, can influence heart rate responses. Therefore, it’s crucial to listen to your body and consult with a healthcare professional if you have any concerns or underlying health conditions.
Heart rate monitoring is an accessible and practical method to measure exercise intensity. By understanding your heart rate and its relationship to different exercise intensities, you can optimize your workouts and achieve your fitness goals more effectively.
Rating of Perceived Exertion (RPE)
The Rating of Perceived Exertion (RPE) is a subjective method used to gauge exercise intensity based on your perception of how hard you are working. It provides a simple and accessible way to monitor and adjust your workout intensity without relying on external devices or measurements.
The RPE scale typically ranges from 0 to 10, with 0 being no exertion at all (such as sitting or lying down) and 10 being the highest level of exertion imaginable. It allows individuals to rate their perceived effort during exercise based on a combination of physical sensations, such as heart rate, breathing rate, muscle fatigue, and overall discomfort.
Using the RPE scale, you can assess how hard you feel you are working and adjust your exercise intensity accordingly. For example, if you aim to work at a moderate intensity, you might aim for an RPE of around 5-6, where you feel you are working but can still maintain a conversation. If you want to push yourself to a higher intensity, you might aim for an RPE of 7-8, where you are breathing heavily and finding it challenging to talk.
The RPE method is flexible and can be applied to various types of exercise, including cardiovascular workouts, strength training, and even group fitness classes. It allows you to adapt your intensity based on your current fitness level, fatigue, and other individual factors. It’s important to remember that everyone’s perception of effort is unique, so what feels challenging for one person may feel different for another.
By incorporating the RPE method into your workouts, you can develop a better understanding of how your body responds to different levels of exercise intensity. It also enables you to make adjustments based on your goals, whether it’s improving endurance, building strength, or simply maintaining overall fitness.
Talk Test
The Talk Test is a simple and practical method to measure exercise intensity based on one’s ability to carry on a conversation during physical activity. It provides a convenient way to assess if you are working at an appropriate intensity level without the need for complicated measurements or devices.
The concept behind the Talk Test is straightforward: if you can comfortably hold a conversation while exercising, you are likely working at a moderate intensity. This level of intensity is generally recommended for general fitness and cardiovascular health benefits.
Conversely, if you find it difficult to speak in full sentences or have to catch your breath while talking, it indicates a higher intensity level. This may be suitable for more intense workouts aimed at improving aerobic capacity or endurance.
The Talk Test is particularly useful for individuals who may not have access to heart rate monitors or other equipment to measure exercise intensity. It provides an intuitive and reliable method to gauge effort and adjust workout intensity accordingly.
It’s important to note that the Talk Test may not be as accurate for highly fit individuals who may have a high level of cardiovascular fitness. In such cases, they might be able to carry on a conversation even at a higher exercise intensity. However, for most people, the Talk Test offers a valuable guide to finding an appropriate level of exertion.
Keep in mind that the Talk Test is subjective and can vary depending on factors such as age, fitness level, and the type of activity you are engaged in. It is a general guideline rather than a precise measurement. Listening to your body’s signals and adjusting your workout intensity accordingly is key to optimizing your exercise experience and meeting your fitness goals.
By incorporating the Talk Test into your exercise routine, you can maintain a safe and effective workout intensity level, ensuring that you are challenging your body without overexerting yourself.
METs (Metabolic Equivalents)
METs, or Metabolic Equivalents, are a unit of measurement used to express the energy expenditure or intensity of physical activities. It allows for a standardized way to compare the energy cost of different activities regardless of an individual’s body weight or fitness level.
To put it simply, 1 MET represents the energy expenditure at rest, which is equivalent to sitting quietly and doing nothing. Any physical activity performed above this level will have a higher MET value.
For example, moderate-intensity activities such as brisk walking, cycling at a moderate pace, or swimming have MET values between 3-6. This means that these activities require 3-6 times more energy expenditure compared to rest.
The MET value of an activity is determined through scientific measurement and analysis. It takes into account factors such as oxygen consumption, heart rate, and energy expenditure during the activity. These values are then used to create tables or charts that individuals can reference to determine the intensity of their chosen activity.
METs provide a useful tool for individuals who want to monitor and control their exercise intensity. By knowing the MET value of an activity, you can make informed decisions about the appropriateness and intensity of your workout routine.
It’s important to note that individual variations and fitness levels can impact the energy expended during an activity. However, METs provide a general guideline for understanding relative exercise intensities. For example, an activity with a higher MET value will generally be more intense than one with a lower MET value.
When planning your workouts, you can use MET values to ensure a balanced routine. Combining activities with different MET values can help you vary the intensity of your exercise and target different muscle groups.
Keep in mind that METs are just one tool to consider when measuring exercise intensity. Other factors such as heart rate, perceived exertion, and individual fitness goals should also be taken into account. Understanding the concept of METs can help you make informed choices about your physical activities and design a well-rounded fitness program.
Power Output
Power output is a measurement of the rate at which work is performed during physical activity. It quantifies the intensity of exercise by taking into account both the force exerted and the speed at which the work is done. Power output is commonly used in activities that involve explosive movements or high levels of strength and speed.
In the context of exercise, power is typically measured in watts. It represents the amount of energy expended per unit of time. The higher the power output, the greater the intensity of the exercise.
To measure power output, specialized equipment such as power meters or ergometers may be used. These devices provide real-time feedback on the amount of power generated during an activity. For example, in cycling, a power meter mounted on the bike can measure the force applied to the pedals and calculate the corresponding power output.
Power output is particularly relevant in sports and activities that require explosive movements or short bursts of maximum effort, such as sprinting or weightlifting. It allows athletes and fitness enthusiasts to track their performance, set goals, and monitor improvements in strength and power.
It’s important to note that power output is influenced by factors such as technique, muscle strength, coordination, and fatigue. Proper form and technique play a critical role in optimizing power output and reducing the risk of injury.
While power output is not as commonly used by recreational exercisers as methods like heart rate monitoring or perceived exertion, it can be a valuable tool for individuals seeking to push their physical limits, improve athletic performance, or engage in specific training programs.
Understanding power output can be beneficial for those involved in sports that require explosive movements, such as track and field, basketball, or hockey. Additionally, it can help enthusiasts who are looking to challenge themselves and achieve new levels of fitness.
However, it’s important to remember that power output is just one aspect of exercise intensity measurement. Combining multiple methods and considering other factors like heart rate, perceived exertion, and individual goals will provide a more comprehensive understanding of exercise intensity.
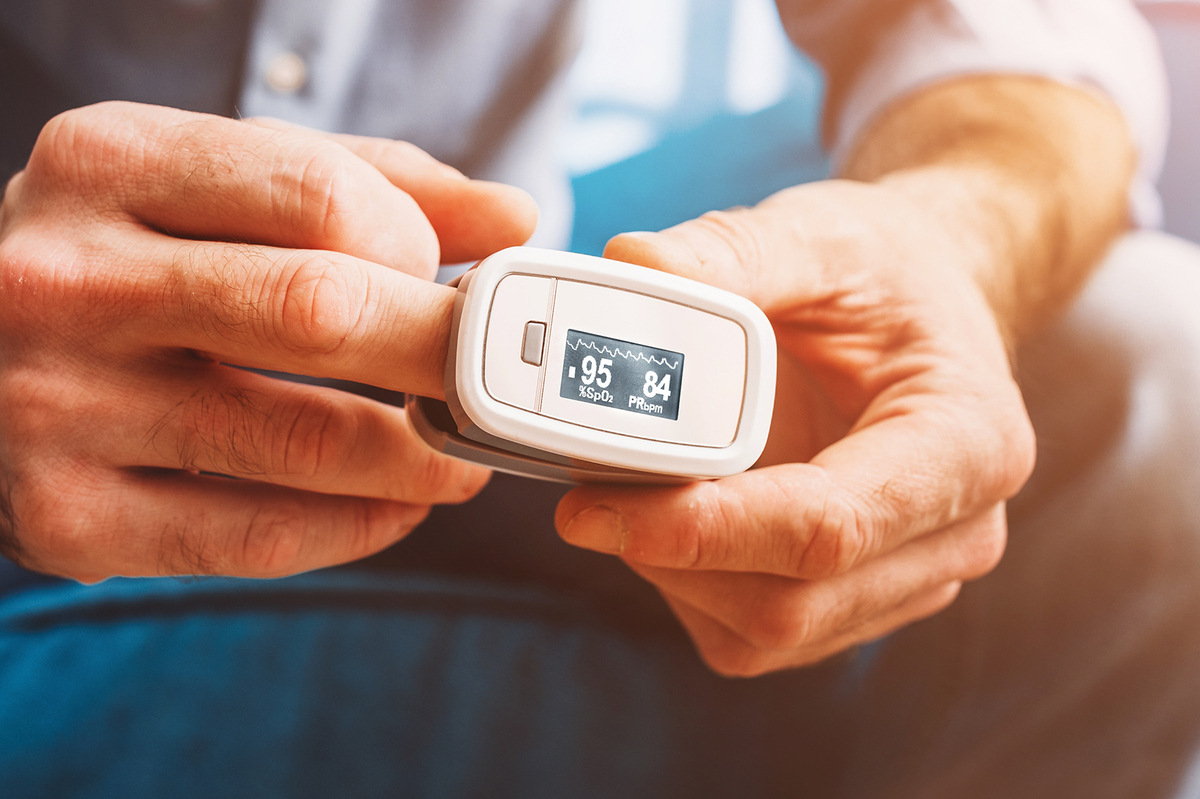
Oxygen Consumption (VO2)
Oxygen Consumption, often referred to as VO2 (volume of oxygen consumed), is a direct measure of the amount of oxygen utilized by the body during exercise. It is considered one of the most accurate indicators of exercise intensity and aerobic fitness.
During physical activity, the muscles require oxygen to produce energy. The body’s ability to take in, transport, and utilize oxygen is a crucial factor in determining exercise intensity and endurance capacity. VO2 reflects the efficiency of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems in delivering oxygen to the working muscles.
VO2 can be measured through laboratory-based tests that involve wearing a face mask or mouthpiece connected to specialized equipment. These tests measure the volume of oxygen consumed and the amount of carbon dioxide produced during exercise.
VO2max, specifically, is the maximum amount of oxygen the body can utilize during intense exercise. It is a strong indicator of aerobic capacity and can be used to assess one’s overall fitness level. The higher the VO2max, the more efficient the body is at extracting oxygen and delivering it to the muscles.
VO2 can also be estimated using equations that take into account factors such as age, weight, gender, and exercise intensity. While these estimations are not as accurate as laboratory measurements, they provide a useful approximation of oxygen consumption during exercise.
Knowing your VO2max or estimated VO2 can help you set appropriate exercise intensities, track improvements in cardiovascular fitness, and design training programs tailored to your specific goals and abilities.
Incorporating activities that challenge your aerobic system, such as running, cycling, swimming, or rowing, can improve your VO2max over time. By consistently working at intensities that elevate your heart rate and increase your breathing rate, you can train your body to become more efficient at using oxygen.
It’s important to note that VO2 testing is more commonly used in athletic and clinical settings and may not be easily accessible or necessary for the average individual. However, understanding the concept of oxygen consumption and its relationship to exercise intensity can help you make informed choices about the types of activities and training methods that will contribute to your overall fitness and performance.
Conclusion
Measuring exercise intensity is crucial for designing effective and personalized workout routines that align with your fitness goals. By understanding the different methods used to measure exercise intensity, you can make informed decisions about the appropriate level of effort and adjust your workouts accordingly.
Heart rate monitoring provides real-time feedback on your cardiovascular response to exercise, allowing you to stay within your target heart rate zone. The Rating of Perceived Exertion (RPE) offers a subjective assessment of how hard you feel you are working, while the Talk Test provides a practical way to determine if you are exercising at a moderate intensity.
Metabolic Equivalents (METs) provide a standardized measurement of energy expenditure during physical activities, helping you compare and select exercises of different intensities. Power output measures the rate at which work is performed, particularly relevant for explosive movements and strength-focused activities.
Oxygen Consumption (VO2) reflects the body’s efficiency in utilizing oxygen during exercise, and it is considered a reliable indicator of aerobic fitness. Understanding your VO2max or estimating your VO2 can guide you in setting appropriate exercise intensities.
Combining these methods and considering individual factors such as fitness level, goals, and preferences can help you create a well-rounded and effective exercise regimen.
Remember, exercise intensity is not a one-size-fits-all concept. It is important to listen to your body and adjust your intensity level based on your own comfort, fitness level, and health status. Consulting with a healthcare professional or certified fitness expert can provide further guidance on measuring exercise intensity and tailoring your workouts to your specific needs.
So, next time you lace up your running shoes, hop on a bike, or step into the gym, consider incorporating some of these methods to ensure that you are making the most out of your workouts and maximizing your fitness journey.