Home>Misc>Featured>Relative Vs. Vo2 Max Which Is A Better Indicator Of Cardiovascular Fitness

Featured
Relative Vs. Vo2 Max Which Is A Better Indicator Of Cardiovascular Fitness
Modified: August 21, 2023
Discover the featured article exploring the comparison between relative and Vo2 max as indicators of cardiovascular fitness, helping you determine which is more effective for assessing your health and performance.
Introduction
When it comes to assessing cardiovascular fitness, two important indicators often come into play: relative fitness and VO2 max. Understanding these concepts and their significance is crucial for anyone seeking to improve their cardiovascular health and overall fitness level. Both relative fitness and VO2 max provide valuable insights into an individual’s cardiovascular capacity, but they approach the assessment from different angles.
Relative fitness is a measurement that takes into account an individual’s cardiovascular capacity in relation to their body weight and composition. It provides a more personalized view of cardiovascular fitness by considering an individual’s specific physiological factors. On the other hand, VO2 max, also referred to as maximal oxygen uptake, measures the maximum amount of oxygen that an individual can utilize during intense physical activity. It is often used as a benchmark to evaluate cardiovascular endurance and performance.
Understanding the differences and similarities between these two indicators is essential in determining which one is a better reflection of an individual’s cardiovascular fitness. By exploring the intricacies of relative fitness and VO2 max, we can gain a deeper understanding of their significance and how they can be used to assess and improve one’s cardiovascular health.
In this article, we will delve into the definitions, importance, factors influencing relative fitness and VO2 max, as well as the pros and cons of using each as an indicator of cardiovascular fitness. By the end, you will have a clearer understanding of which indicator aligns better with your fitness goals and how you can use that knowledge to optimize your cardiovascular fitness.
Definition of Relative Fitness
Relative fitness, also known as specific aerobic power, is a measure of an individual’s cardiovascular capacity in relation to their body weight and composition. It takes into account factors such as height, weight, muscle mass, and body fat percentage to provide a more comprehensive understanding of an individual’s fitness level.
Unlike absolute fitness, which solely focuses on an individual’s aerobic power without considering these physiological factors, relative fitness provides a more personalized and accurate assessment. By taking into account an individual’s body composition, relative fitness allows for a fair comparison across individuals of different sizes and weights.
One common way to measure relative fitness is by calculating the maximum oxygen consumption per kilogram of body weight, also known as VO2 max/kg. This value indicates how efficiently the body is able to utilize oxygen during physical activity. A higher value signifies a greater cardiovascular capacity relative to body weight, indicating better overall fitness.
Relative fitness is an essential measurement in assessing cardiovascular health, as it provides a more accurate reflection of an individual’s true fitness level. In addition, it can be useful in tracking progress over time during fitness regimens or weight loss journeys. By focusing on improving relative fitness, individuals can make significant improvements to their cardiovascular health and overall well-being.
It is important to note that relative fitness is not solely determined by body weight or composition. Factors such as cardiovascular endurance, muscular strength, and overall health also play a role in determining an individual’s relative fitness. Therefore, it is crucial to adopt a well-rounded approach to fitness that includes cardiovascular exercise, strength training, and a balanced diet to achieve optimal results.
Definition of VO2 Max
VO2 max, or maximal oxygen uptake, is a measure of the maximum amount of oxygen that an individual can consume and utilize during intense physical activity. It is widely considered as one of the most reliable indicators of cardiovascular endurance and aerobic fitness.
VO2 max is typically expressed in milliliters of oxygen per kilogram of body weight per minute (ml/kg/min). The measurement reflects the efficiency of the cardiovascular system in delivering oxygen to the muscles and the muscles’ ability to use that oxygen to produce energy.
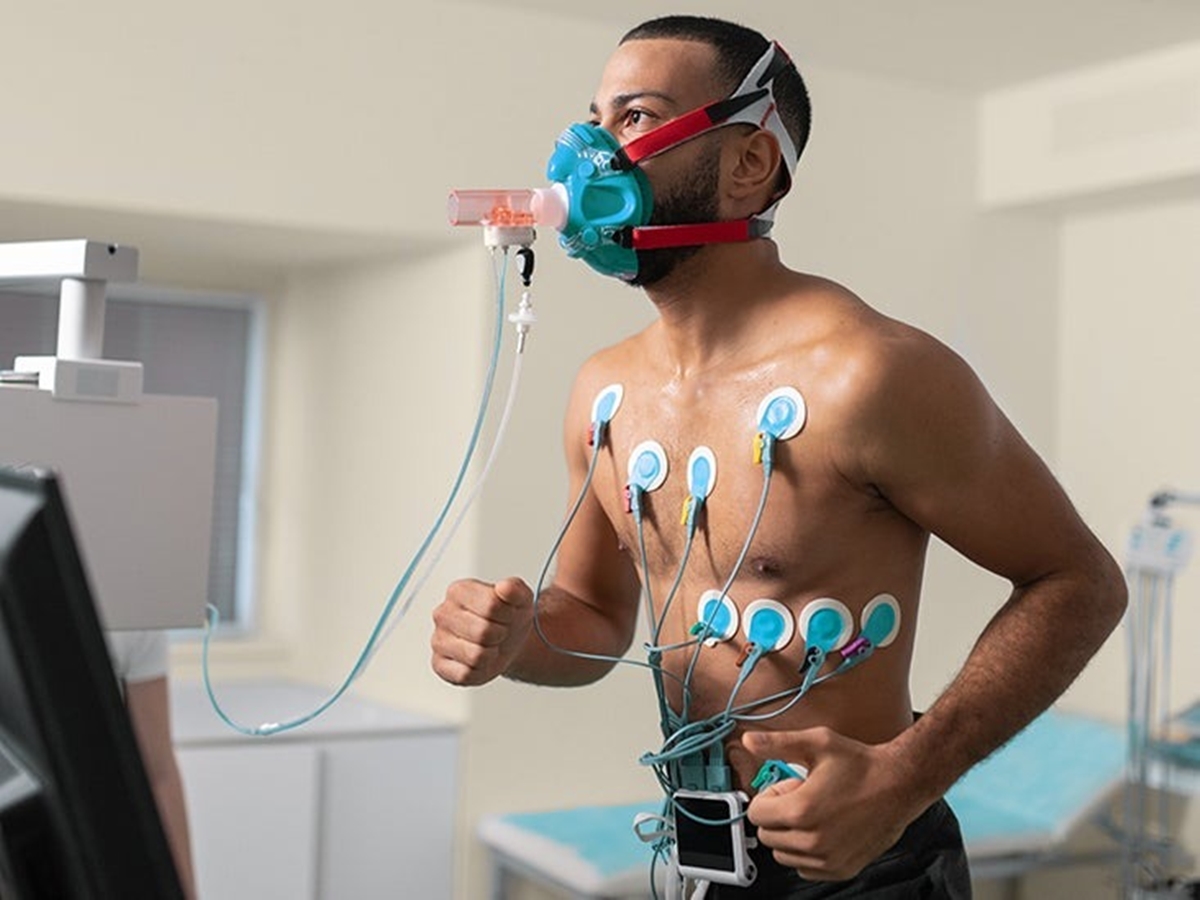
Measuring VO2 max typically involves a laboratory test, such as a graded exercise test on a treadmill or a cycle ergometer. During the test, the individual undergoes progressively more challenging levels of exercise while their oxygen consumption and heart rate are monitored. The point at which oxygen consumption plateaus despite an increase in workload indicates the individual’s VO2 max.
A higher VO2 max value indicates better cardiovascular fitness and endurance. It signifies that an individual has a greater capacity to sustain high-intensity exercise for extended periods. Athletes, particularly those involved in endurance sports such as long-distance running or cycling, often undergo VO2 max testing to gauge their fitness level and set training targets.
It is important to note that VO2 max is influenced by various physiological factors such as age, sex, and genetics. Furthermore, it can also be improved through proper training and exercise. Regular aerobic exercise, such as running, cycling, or swimming, can enhance cardiovascular function and increase VO2 max over time.
While VO2 max is a valuable indicator of cardiovascular fitness, it focuses solely on an individual’s aerobic capacity and does not take into account other factors such as body weight or composition. To get a holistic view of cardiovascular health, it is beneficial to consider VO2 max alongside other indicators like relative fitness or strength measures.
Importance of Cardiovascular Fitness
Cardiovascular fitness, also known as cardiorespiratory fitness, refers to the ability of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems to supply oxygen-rich blood to the muscles during physical activity. It plays a crucial role in maintaining overall health and well-being. Here are some key reasons why cardiovascular fitness is important:
1. Improved Heart Health: Regular cardiovascular exercise strengthens the heart muscle, improves blood circulation, and lowers blood pressure. This reduces the risk of heart disease, stroke, and other cardiovascular conditions.
2. Increased Energy Levels: Cardiovascular fitness improves the body’s efficiency in producing and delivering oxygen to the muscles. This leads to increased energy levels and reduced feelings of fatigue during daily activities.
3. Weight Management: Engaging in cardiovascular exercise helps burn calories, which can aid in weight loss and weight management. It also helps maintain a healthy body weight, reducing the risk of obesity-related conditions.
4. Enhanced Mental Health: Regular cardio workouts release endorphins, which are known as “feel-good” hormones. This can alleviate stress, anxiety, and depression, promoting overall mental well-being.
5. Increased Stamina and Endurance: Cardiovascular fitness improves the body’s ability to perform sustained physical activity without fatigue. This is particularly beneficial for athletes and individuals involved in high-intensity sports or activities.
6. Reduced Risk of Chronic Diseases: Regular cardiovascular exercise has been associated with a decreased risk of chronic conditions such as type 2 diabetes, certain types of cancer, and metabolic syndrome.
7. Improved Brain Function: Cardiovascular fitness promotes better blood flow to the brain, which enhances cognitive function, memory, and overall brain health.
Incorporating cardiovascular exercise into your fitness routine is essential for maintaining and improving cardiovascular fitness. Some examples of effective cardiovascular exercises include running, swimming, cycling, brisk walking, and dancing. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic activity per week to reap the benefits of cardiovascular fitness.
Comparison between Relative Fitness and VO2 Max
Relative fitness and VO2 max are two distinct indicators used to assess cardiovascular fitness. While they provide valuable insights into an individual’s aerobic capacity, there are key differences between the two. Here, we compare and contrast relative fitness and VO2 max:
1. Measurement Focus: Relative fitness takes into account an individual’s cardiovascular capacity in relation to their body weight and composition. It provides a personalized view of fitness, considering factors such as height, weight, and muscle mass. On the other hand, VO2 max measures the maximum amount of oxygen an individual can consume and utilize during intense physical activity. It solely focuses on aerobic capacity and does not consider body weight or composition.
2. Personalization: Relative fitness allows for a fair comparison across individuals of different sizes and weights. By considering body composition, it presents a more accurate reflection of an individual’s fitness level. In contrast, VO2 max is less personalized, as it does not account for individual variations in body weight or composition. It is primarily used to compare individuals of similar body types and assess their aerobic endurance.
3. Testing Methods: While both relative fitness and VO2 max can be measured, they utilize different testing methods. Relative fitness is typically measured using the maximum oxygen consumption per kilogram of body weight (VO2 max/kg) calculation. It can be determined through laboratory tests or equations that take into account factors such as heart rate and workload. VO2 max, on the other hand, requires a direct measurement of oxygen consumption during a graded exercise test.
4. Usability: Relative fitness is a valuable indicator for individuals seeking to assess their overall fitness level, especially in terms of body weight and composition. It can be particularly useful for individuals aiming to lose weight or improve muscular strength. VO2 max, on the other hand, is commonly used in sports and athletic training to evaluate the aerobic fitness and endurance capacity of athletes. It helps coaches and trainers determine appropriate training intensities and set specific performance goals.
5. Comprehensive View: Relative fitness provides a more holistic view of an individual’s cardiovascular fitness by considering multiple physiological factors. It looks beyond aerobic capacity and takes into account elements such as body weight, composition, and overall muscle strength. VO2 max, in contrast, focuses solely on aerobic capacity and does not consider other factors.
Both relative fitness and VO2 max offer valuable insights into an individual’s cardiovascular capacity. Depending on the specific goals and objectives of an individual, one indicator may be more applicable than the other. It is important to remember that neither indicator should be viewed in isolation. To obtain a comprehensive assessment of cardiovascular fitness, it is beneficial to consider multiple indicators and consult with a healthcare professional or fitness expert.
Factors Affecting Relative Fitness and VO2 Max
Several factors can impact an individual’s relative fitness and VO2 max. Understanding these factors is crucial in assessing and improving cardiovascular fitness. Here are some key factors that can influence relative fitness and VO2 max:
1. Body Composition: Body composition, including muscle mass, body fat percentage, and overall weight, can impact relative fitness. Individuals with a higher muscle mass and lower body fat percentage generally have a higher relative fitness level, as muscles require more oxygen during physical activity.
2. Age: Age plays a role in both relative fitness and VO2 max. As we age, there is a natural decline in aerobic capacity and muscle mass, which can lower both relative fitness and VO2 max. Regular exercise and a healthy lifestyle can help slow down this decline.
3. Training and Exercise Habits: Regular aerobic activity and exercise can significantly improve both relative fitness and VO2 max. Engaging in cardiovascular exercises that challenge the aerobic system, such as running, cycling, or swimming, can lead to adaptations and improvements in both indicators. The frequency, intensity, and duration of exercise play a role in determining the extent of these improvements.
4. Genetics: Genetic factors can influence an individual’s baseline level of relative fitness and VO2 max. Some individuals may have a higher genetic predisposition for greater aerobic capacity and relative fitness, while others may have a more limited potential. However, it is important to note that genetic factors do not determine an individual’s potential to improve their relative fitness and VO2 max through training and exercise.
5. Environmental Factors: Environmental conditions, such as altitude and temperature, can impact both relative fitness and VO2 max. High-altitude environments can reduce oxygen availability, thus affecting an individual’s aerobic capacity. Similarly, extreme temperatures can impose additional cardiovascular strain, affecting both indicators.
6. Health Conditions and Medications: Certain health conditions, such as cardiovascular diseases or respiratory disorders, can affect both relative fitness and VO2 max. Medications used to manage these conditions may also impact cardiovascular function. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional to understand the influence of specific health conditions and medications on these fitness indicators.
7. Overall Lifestyle Factors: Lifestyle factors such as diet, sleep, stress levels, and habits like smoking and alcohol consumption can affect both relative fitness and VO2 max. A well-balanced diet with adequate macro and micronutrients and sufficient restful sleep can support cardiovascular health and improve fitness indicators.
By recognizing these factors, individuals can identify areas for improvement and make targeted changes to enhance their cardiovascular fitness. Regular physical activity, a healthy lifestyle, and consistent effort to improve these factors can lead to significant progress in both relative fitness and VO2 max.
Pros and Cons of Relative Fitness as an Indicator
Relative fitness is a valuable indicator of cardiovascular fitness, but like any assessment tool, it has its pros and cons. Let’s examine some of the advantages and disadvantages of using relative fitness as an indicator:
Pros:
- Personalized Assessment: Relative fitness takes into account an individual’s body weight and composition, providing a more personalized assessment of cardiovascular fitness. It allows for fair comparisons across individuals of different sizes and weights.
- Accuracy: By considering physiological factors such as height, weight, and muscle mass, relative fitness provides a more accurate reflection of an individual’s true fitness level. It gives a comprehensive assessment beyond just aerobic capacity.
- Tracking Progress: Relative fitness is a useful tool for tracking progress over time. Individuals can monitor changes in their fitness level as they engage in exercise and weight management programs. It provides a tangible measure of improvement.
- Applicable to Weight Loss: Relative fitness is particularly relevant for individuals looking to lose weight or improve body composition. It helps assess the impact of weight loss efforts on cardiovascular fitness, providing motivation and guidance for achieving fitness goals.
Cons:
- Incomplete Assessment: While relative fitness provides a more comprehensive view of cardiovascular fitness, it does not solely focus on aerobic capacity, which may be important in certain contexts such as sports or performance training.
- Genetic Variations: Relative fitness can be influenced by genetic factors, which may limit an individual’s potential to reach a certain level of fitness. However, it is important to note that genetic factors do not determine an individual’s ability to improve their relative fitness through training and exercise.
- Subjectivity: The calculation of relative fitness may vary based on the specific equations or methods used. Different formulas and approaches can yield slightly different results, introducing a level of subjectivity to the assessment.
- Impact of Muscle Mass: Relative fitness considers muscle mass in its calculation, which can be advantageous for individuals with higher muscle mass. However, this may disadvantage individuals who focus primarily on cardiovascular fitness and have lower muscle mass.
Despite the limitations, relative fitness remains a valuable indicator of cardiovascular fitness, especially for individuals aiming to improve body composition and overall health. It is important to consider relative fitness alongside other fitness assessments to obtain a holistic view of cardiovascular health and wellness.
Pros and Cons of VO2 Max as an Indicator
VO2 max is a widely accepted and reliable indicator of cardiovascular fitness, but it is important to understand the pros and cons associated with its use as an assessment tool. Let’s examine some of the advantages and disadvantages of using VO2 max as an indicator:
Pros:
- Objective Measurement: VO2 max provides an objective measurement of an individual’s aerobic capacity. It directly assesses the maximum amount of oxygen that can be consumed and utilized during intense physical activity, providing a quantitative value.
- Standardized Benchmark: VO2 max serves as a standardized benchmark for evaluating aerobic fitness and endurance. It allows for comparisons across individuals of similar body types and helps identify strengths and weaknesses in cardiovascular capacity.
- Performance Evaluation: VO2 max testing is commonly used in sports and athletic training to evaluate an individual’s aerobic fitness and endurance capacity. It can help coaches and trainers assess an athlete’s potential and set specific performance goals.
- Training Intensity Guidance: By knowing an individual’s VO2 max, trainers and coaches can determine appropriate training intensities and develop effective training programs to improve cardiovascular fitness.
Cons:
- Limited to Aerobic Capacity: VO2 max solely focuses on aerobic capacity and does not take into account other aspects of cardiovascular fitness, such as body composition or strength. This limited scope may not provide a comprehensive view of overall fitness.
- Testing Requirements: Accurate measurement of VO2 max requires specialized laboratory testing equipment and expertise. This can make it less accessible and more time-consuming compared to other fitness assessment methods.
- Genetic Influences: Similar to other fitness indicators, genetic factors can impact an individual’s baseline level of VO2 max. Some individuals may have a higher genetic potential for greater aerobic capacity, while others may have a natural limitation.
- Expensive and Invasive Testing: Traditional VO2 max testing methods, such as graded exercise tests in a laboratory setting, can be expensive and require participants to perform physically demanding activities. This may not be feasible or practical for everyone.
Despite its limitations, VO2 max remains a valuable and widely accepted indicator of cardiovascular fitness, particularly in the context of sports and athletic performance. It provides valuable insights into an individual’s aerobic capacity and endurance potential.
When using VO2 max as an indicator, it is important to consider it alongside other fitness assessments and individual goals. Integrating a well-rounded approach to training and considering factors like body composition, strength, and overall health will contribute to a more comprehensive evaluation of cardiovascular fitness and overall well-being.
Conclusion
Relative fitness and VO2 max are both valuable indicators of cardiovascular fitness, providing insights into an individual’s aerobic capacity and overall health. However, they approach the assessment from different angles and have their own set of advantages and disadvantages.
Relative fitness offers a more personalized assessment by considering an individual’s body weight and composition. It provides a comprehensive view of cardiovascular fitness, allowing for fair comparisons across individuals of different sizes and weights. It is particularly relevant for individuals aiming to improve body composition and overall health.
On the other hand, VO2 max is a standardized benchmark for evaluating aerobic fitness and endurance. It directly measures the maximum amount of oxygen an individual can consume and utilize during intense physical activity. It is commonly used in sports and athletic training to assess an athlete’s cardiorespiratory fitness and set performance goals.
Both indicators have their pros and cons. Relative fitness takes into account multiple physiological factors, providing a more accurate reflection of an individual’s true fitness level. However, it may not solely focus on aerobic capacity, which may be important in certain contexts. VO2 max offers an objective measurement of aerobic fitness but does not consider other aspects of cardiovascular fitness.
To obtain a holistic view of cardiovascular health, it is beneficial to consider multiple fitness indicators alongside relative fitness and VO2 max. Factors such as body composition, strength, genetics, and overall lifestyle play a role in determining an individual’s overall cardiovascular fitness.
Individuals should consult with healthcare professionals or fitness experts to determine which indicators align best with their goals and needs. By focusing on improving cardiovascular fitness and adopting a well-rounded approach to training, individuals can optimize their cardiovascular health and enhance their overall well-being.