
Featured
What Vitamin Is Good For Brain Health
Published: September 10, 2023
Discover the power of featured vitamins for brain health and enhance your cognitive function. Find out which essential nutrient is essential for optimal brain performance.
Introduction
When it comes to overall health and well-being, one area that often gets overlooked is brain health. Our brain is a complex organ that requires proper nutrition to function optimally. Just like any other organ in our body, the brain needs specific vitamins and nutrients to maintain its health and cognitive function.
From memory and focus to mood and decision-making, the brain is responsible for a wide range of functions that play a vital role in our daily lives. That’s why it is crucial to prioritize brain health and provide it with the necessary nutrients it needs to thrive.
In this article, we will explore the importance of vitamins for brain health and delve into specific vitamins that are known to have a positive impact on cognitive function. By understanding the role of these essential vitamins, you can make informed choices to support your brain health and overall well-being.
So, let’s dive into the fascinating world of brain health and discover the vitamins that can help boost cognitive function and support optimal brain performance.
Understanding Brain Health
Before we delve into the specific vitamins that promote brain health, it’s important to have a basic understanding of what brain health entails. Brain health refers to the overall well-being and optimal functioning of the brain, encompassing cognitive abilities, emotional stability, and neurological processes.
As we age, it’s natural for cognitive function to decline gradually. However, certain lifestyle factors, such as poor nutrition, lack of exercise, chronic stress, and inadequate sleep, can accelerate this decline and increase the risk of developing cognitive disorders like dementia and Alzheimer’s disease.
Fortunately, there are steps we can take to support and enhance our brain health. Proper nutrition plays a critical role in this process, as the brain relies on a constant supply of nutrients to perform its various functions. By nourishing your brain with the right vitamins and minerals, you can help preserve cognitive function, improve memory, and promote overall brain health.
In addition to proper nutrition, engaging in regular mental stimulation, getting sufficient sleep, managing stress, and maintaining an active lifestyle are all important factors in supporting brain health. By adopting a holistic approach that addresses these various aspects, you can optimize your brain’s performance and reduce the risk of cognitive decline.
Now that we have a foundation for understanding brain health, let’s explore the specific vitamins that are known to play a vital role in supporting cognitive function and overall brain health.
Importance of Vitamins for Brain Health
Vitamins are essential micronutrients that our bodies need to function properly. They play a crucial role in various bodily processes, including brain health. Certain vitamins have been specifically linked to cognitive function and can help support the overall health of our brains.
One of the key reasons vitamins are important for brain health is their role in energy production. The brain is one of the most energy-demanding organs in our body, and it requires a constant supply of energy to function optimally. B vitamins, in particular, are crucial for converting the food we eat into energy that the brain can utilize effectively.
In addition to energy production, vitamins also play a role in the production of neurotransmitters, which are chemicals that facilitate communication between brain cells. Neurotransmitters are involved in a wide range of brain functions, including mood regulation, memory formation, and cognitive processes. Certain vitamins, such as vitamin B6 and vitamin C, are involved in the synthesis of neurotransmitters, thereby supporting optimal brain function.
Furthermore, vitamins act as antioxidants in the body, helping to protect our brain cells from oxidative stress and damage. Oxidative stress occurs when there is an imbalance between the production of harmful free radicals and the body’s ability to neutralize them. This process has been linked to various neurodegenerative disorders, such as Alzheimer’s disease. Vitamins C and E, as well as other antioxidants, help combat oxidative stress and protect the brain against damage.
Moreover, vitamins contribute to the formation and maintenance of the myelin sheath, a protective covering around nerve cells that facilitates efficient and rapid communication between different parts of the brain. Vitamin D, in particular, is crucial for the development and maintenance of a healthy myelin sheath.
Overall, ensuring an adequate intake of vitamins is essential for supporting brain health and cognitive function. By providing the brain with the necessary vitamins, we can enhance energy production, support neurotransmitter synthesis, protect against oxidative stress, and promote optimal communication between brain cells.
Now, let’s explore some specific vitamins that have been shown to have a positive impact on brain health.
Vitamin B Complex
The B vitamins, collectively known as the vitamin B complex, are a group of water-soluble vitamins that play a crucial role in brain health. This group includes vitamins B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B7, B9, and B12, each with its own unique functions and benefits.
Vitamin B1, also known as thiamine, helps support cognitive function and aids in the production of neurotransmitters. It is involved in converting glucose into energy that the brain can use effectively. A deficiency in thiamine has been linked to memory loss and other cognitive impairments.
Vitamin B2, also called riboflavin, is important for brain cell maintenance and function. It acts as an antioxidant, helping to protect brain cells from oxidative stress. Riboflavin also plays a role in energy production and the metabolism of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats.
Vitamin B3, or niacin, is involved in energy metabolism and the production of ATP, the energy currency of cells. Niacin has been shown to support memory and cognitive function. It also helps promote healthy blood flow to the brain, ensuring an adequate supply of nutrients and oxygen.
Vitamin B5, or pantothenic acid, is essential for the synthesis of coenzyme A, a molecule involved in the production of energy from carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. Pantothenic acid also helps support the formation of neurotransmitters, contributing to optimal brain function.
Vitamin B6, or pyridoxine, plays a vital role in neurotransmitter synthesis, including serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine. These neurotransmitters are involved in regulating mood, sleep, and cognitive functions. Vitamin B6 also helps support brain development in infants and children.
Vitamin B7, commonly known as biotin, is essential for maintaining healthy brain function. It supports the production of neurotransmitters and aids in the metabolism of fats and carbohydrates. Biotin deficiency can lead to neurological symptoms, such as depression and cognitive impairments.
Vitamin B9, also known as folate or folic acid, is crucial for brain development and the production of DNA and RNA, the genetic building blocks. It is particularly important during pregnancy, as adequate folate intake helps prevent neural tube defects and supports healthy brain development in the fetus.
Vitamin B12, or cobalamin, is necessary for the proper functioning of the nervous system. It is involved in the synthesis of myelin, the protective covering around nerve cells, and supports overall brain health. Vitamin B12 deficiency is associated with cognitive decline and neurological disorders.
To ensure you are getting an adequate intake of the vitamin B complex, incorporate foods such as whole grains, legumes, leafy green vegetables, eggs, meat, and dairy products into your diet. Alternatively, you can consider taking a B-complex supplement to meet your daily requirements.
Incorporating the vitamin B complex into your diet can help support brain health, enhance cognitive function, and maintain overall well-being.
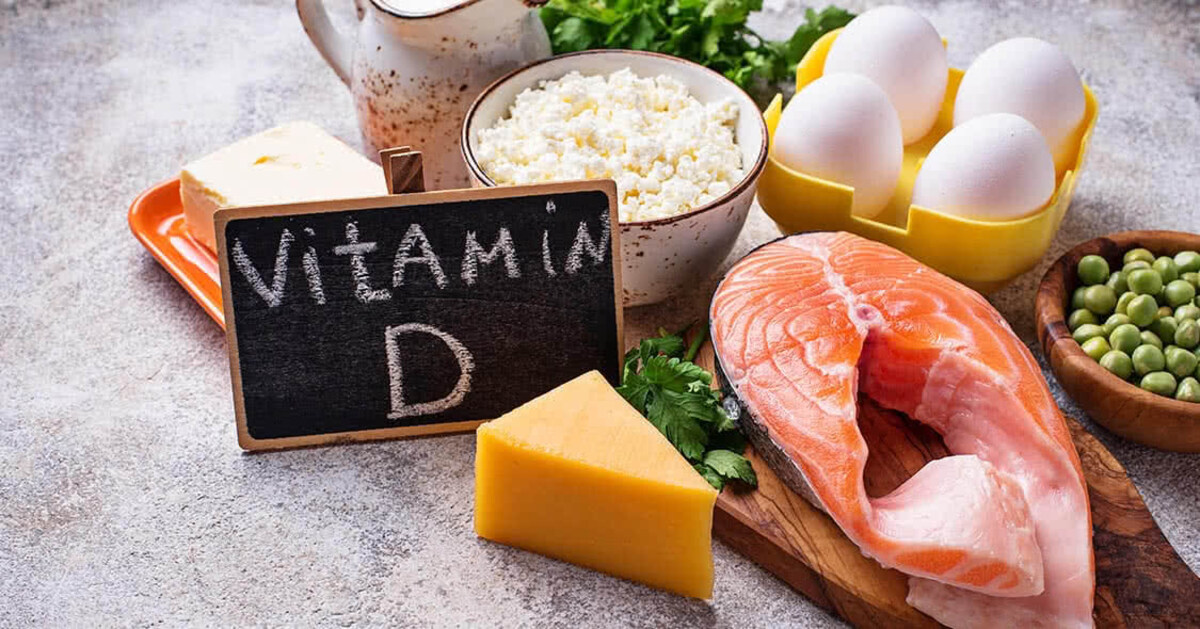
Vitamin D
Vitamin D, often referred to as the “sunshine vitamin,” is crucial for overall health, including brain health. While it is primarily known for its role in maintaining strong bones and supporting immune function, emerging research suggests that vitamin D also plays a vital role in cognitive function and mental well-being.
One of the key functions of vitamin D is its involvement in the regulation of calcium levels. Calcium is essential for proper neurotransmitter function and communication between brain cells. Vitamin D helps ensure that calcium is properly absorbed and utilized in the body, contributing to optimal brain function.
Moreover, vitamin D has been linked to neuroprotective properties. It has been found to promote the production of neurotrophic factors, which are proteins that support the growth, survival, and function of neurons. These factors help protect brain cells from degeneration and play a critical role in maintaining cognitive function.
Low levels of vitamin D have been associated with an increased risk of cognitive decline and neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer’s disease and dementia. In fact, studies have shown that individuals with higher vitamin D levels have better cognitive function and a reduced risk of these disorders.
In addition to its direct effects on brain health, vitamin D also plays a role in regulating mood and preventing depressive symptoms. Research has found an association between low vitamin D levels and an increased risk of depression. It is believed that this connection may be due to vitamin D’s impact on neurotransmitter function and its ability to modulate inflammation in the brain.
While our bodies can produce vitamin D when exposed to sunlight, many people do not get enough sunlight exposure due to various factors like indoor lifestyles and limited sun exposure during certain seasons or geographic locations. Consequently, it is essential to obtain vitamin D through other sources.
Dietary sources of vitamin D include fatty fish (such as salmon and mackerel), fortified dairy products, egg yolks, and mushrooms. However, it may be challenging to get sufficient vitamin D through diet alone, especially for individuals with limited sun exposure or specific dietary restrictions.
Supplementation is a common approach to ensure adequate vitamin D levels. It is recommended to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the appropriate dosage for your specific needs and to monitor your vitamin D levels regularly.
By maintaining sufficient levels of vitamin D, you can support brain health, promote cognitive function, and potentially reduce the risk of cognitive decline and mood disorders.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3 fatty acids are a type of polyunsaturated fat that is renowned for its numerous health benefits, particularly for brain health. Two essential omega-3 fatty acids that have been extensively studied are eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA).
These fatty acids are integral components of the cell membranes in the brain and play a critical role in maintaining the structure and function of brain cells. They are involved in the transmission of signals between brain cells and contribute to the overall health and integrity of the brain.
Omega-3 fatty acids are known for their anti-inflammatory properties. Inflammation in the brain has been linked to various neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s. By reducing inflammation, omega-3 fatty acids may help protect the brain against damage and the onset of cognitive decline.
Furthermore, omega-3 fatty acids have been shown to support the production of neurotransmitters, including serotonin and dopamine, which are essential for regulating mood, sleep, and cognitive function. Adequate levels of these neurotransmitters are crucial for optimal brain performance and mental well-being.
Research has also indicated that omega-3 fatty acids may have a positive impact on memory and cognition. Studies have shown that individuals with higher levels of omega-3 fatty acids in their blood have better memory and cognitive function compared to those with lower levels.
In addition to their direct effects on the brain, omega-3 fatty acids also have cardiovascular benefits. They can help reduce the risk of heart disease and stroke by promoting heart health and reducing cholesterol levels.
Sources of omega-3 fatty acids include fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines. Plant-based sources include flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts. However, it may be challenging to obtain sufficient omega-3 fatty acids through diet alone, especially for individuals who do not consume fish or have specific dietary restrictions.
Supplementation is a popular option to ensure an adequate intake of omega-3 fatty acids. Fish oil supplements, derived from fish or algae, are readily available and can provide a concentrated dose of EPA and DHA. It’s important to choose high-quality supplements and follow the recommended dosage as advised by a healthcare professional.
By incorporating omega-3 fatty acids into your diet or supplement routine, you can support brain health, enhance cognitive function, and potentially reduce the risk of neurodegenerative diseases.
Vitamin E
Vitamin E is a powerful antioxidant that plays a crucial role in maintaining brain health. It protects the brain cells from oxidative stress, which occurs when there is an imbalance between the production of harmful free radicals and the body’s ability to neutralize them.
Oxidative stress can lead to cellular damage and has been implicated in the development of various neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease. Vitamin E acts as a shield, neutralizing free radicals and reducing the risk of brain cell damage.
In addition to its antioxidant properties, vitamin E has been studied for its potential role in memory and cognitive function. It has been suggested that vitamin E may help improve memory and delay cognitive decline associated with aging. However, more research is needed to fully understand the extent of its cognitive benefits.
Furthermore, vitamin E is involved in the maintenance of healthy blood vessels, including those that supply the brain. It helps promote adequate blood flow to the brain, ensuring that essential nutrients and oxygen reach the brain cells, which is vital for optimal cognitive function.
Dietary sources of vitamin E include nuts (such as almonds and sunflower seeds), seeds, vegetable oils (such as olive oil and sunflower oil), spinach, and avocados. Incorporating these foods into your diet can help increase your intake of vitamin E.
However, it may be challenging to obtain sufficient vitamin E through diet alone, especially for individuals with dietary restrictions or those who have difficulty absorbing fat, as vitamin E is a fat-soluble vitamin.
If dietary sources are not sufficient, supplementation can be considered. Vitamin E supplements are available in various forms, such as alpha-tocopherol. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the appropriate dosage and discuss any potential interactions with medications.
By including vitamin E in your diet or supplement routine, you can support brain health, protect against oxidative stress, and potentially enhance memory and cognitive function.
Antioxidants
Antioxidants are crucial for brain health as they help protect brain cells from oxidative stress. Oxidative stress occurs when there is an imbalance between the production of harmful free radicals and the body’s ability to neutralize them. It has been implicated in the development of neurodegenerative diseases and cognitive decline.
Antioxidants work by neutralizing free radicals, which are unstable molecules that can damage cells and DNA. By neutralizing these free radicals, antioxidants help prevent or minimize cell damage and inflammation, thereby promoting brain health.
Several vitamins, such as vitamin C, vitamin E, and certain B vitamins, act as potent antioxidants. Vitamin C, for example, is a water-soluble antioxidant that can readily penetrate the blood-brain barrier and protect brain cells from oxidative damage. It works in conjunction with other antioxidants, including vitamin E, to provide comprehensive protection.
Vitamin E, as mentioned earlier, is a fat-soluble antioxidant that helps protect brain cells from oxidative stress. It is especially beneficial for the membranes of brain cells, as it can halt the chain reaction of free radical damage.
Other antioxidants, such as flavonoids and polyphenols found in fruits and vegetables, have also shown promising effects on brain health. These compounds have anti-inflammatory properties and can help reduce the risk of neurodegenerative diseases. Additionally, certain plant compounds, like resveratrol found in grapes and berries, have been associated with cognitive benefits and may help improve memory and learning abilities.
The best way to incorporate antioxidants into your diet is by consuming a variety of colorful fruits and vegetables. Berries, dark leafy greens, citrus fruits, tomatoes, and bell peppers are excellent sources of antioxidants. Additionally, herbs and spices like turmeric, ginger, and cinnamon also boast antioxidant properties.
It’s worth noting that the total antioxidant capacity of a food is not solely determined by the presence of individual antioxidants. The combination of different antioxidants in a food can have a synergistic effect, enhancing their overall antioxidant activity. Therefore, it is important to consume a diverse range of antioxidant-rich foods to reap the full benefits.
While a balanced diet rich in antioxidants is ideal, certain circumstances may require additional supplementation. It is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional to determine if antioxidant supplements are necessary and to discuss the appropriate dosage for your specific needs.
By incorporating a variety of antioxidant-rich foods into your diet and considering supplementation when appropriate, you can support brain health, protect against oxidative stress, and reduce the risk of cognitive decline.
Vitamin C
Vitamin C, also known as ascorbic acid, is a water-soluble vitamin that has numerous health benefits, including its role in supporting brain health. It is a powerful antioxidant that helps protect brain cells from oxidative stress and damage caused by free radicals.
The brain is particularly susceptible to oxidative stress due to its high metabolic rate and the abundance of fatty acids. Vitamin C helps neutralize the harmful effects of free radicals, reducing the risk of brain cell damage and inflammation.
In addition to its antioxidant properties, vitamin C is involved in the synthesis of neurotransmitters, such as dopamine and norepinephrine, which play a crucial role in regulating mood, attention, and cognitive function. Adequate levels of vitamin C are necessary for the production and balance of these neurotransmitters.
Vitamin C also aids in the production of collagen, a protein that is essential for maintaining the structure and function of blood vessels. Proper blood flow to the brain is vital for delivering oxygen and nutrients, supporting optimal cognitive function. By promoting healthy blood vessels, vitamin C indirectly supports brain health.
Furthermore, vitamin C has been shown to enhance the absorption of iron from plant-based sources. Iron is essential for oxygen transport to the brain, and a deficiency in iron can lead to cognitive impairments. Consuming vitamin C-rich foods alongside iron-rich foods can help improve iron absorption and prevent iron deficiency anemia.
Citrus fruits, such as oranges, lemons, and grapefruits, are well-known sources of vitamin C. Other fruits, including kiwi, strawberries, and pineapples, are also rich in this essential vitamin. Vegetables like bell peppers, broccoli, and leafy greens, such as spinach and kale, are excellent sources of vitamin C as well.
While consuming vitamin C-rich foods is the ideal way to obtain this nutrient, supplementation can be considered when dietary intake may be insufficient. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the appropriate dosage and discuss any potential interactions with medications.
By incorporating vitamin C-rich foods into your diet and considering supplementation when necessary, you can support brain health, protect against oxidative stress, and promote optimal cognitive function.
Conclusion
Prioritizing brain health is essential for maintaining overall well-being and cognitive function. By incorporating specific vitamins into our diet, we can support optimal brain performance and reduce the risk of cognitive decline and neurodegenerative diseases.
The vitamin B complex, including vitamins B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B7, B9, and B12, plays a vital role in energy production, neurotransmitter synthesis, and brain development.
Vitamin D is crucial for maintaining strong bones and supporting immune function. It also plays a role in regulating calcium levels and supporting brain development and cognitive function.
Omega-3 fatty acids have numerous benefits for brain health, including supporting brain cell structure and function, reducing inflammation, and promoting memory and cognitive function.
Vitamin E acts as a potent antioxidant, protecting brain cells from oxidative stress and supporting healthy blood vessel function.
Antioxidants, such as vitamin C, help protect brain cells from oxidative stress, support neurotransmitter balance, and promote healthy blood flow to the brain.
While dietary sources are the ideal way to obtain these vitamins, supplementation may be necessary in certain situations. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the appropriate dosage and discuss any potential interactions with medications.
By incorporating these vitamins into our lifestyle and maintaining a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids, we can support brain health, enhance cognitive function, and promote overall well-being.
Remember, a healthy brain is instrumental in living a fulfilling and rewarding life, so let’s prioritize brain health and nourish our minds with the nutrients they need to thrive.









