Featured
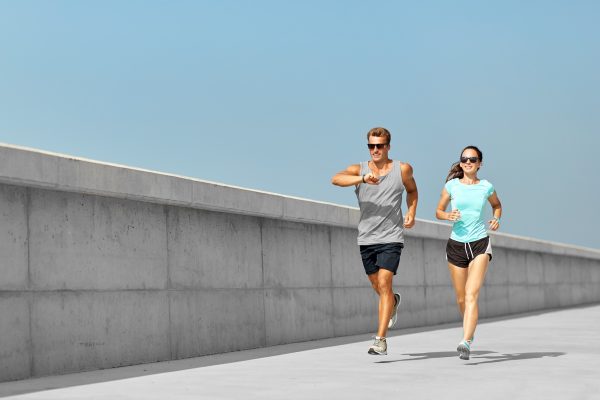
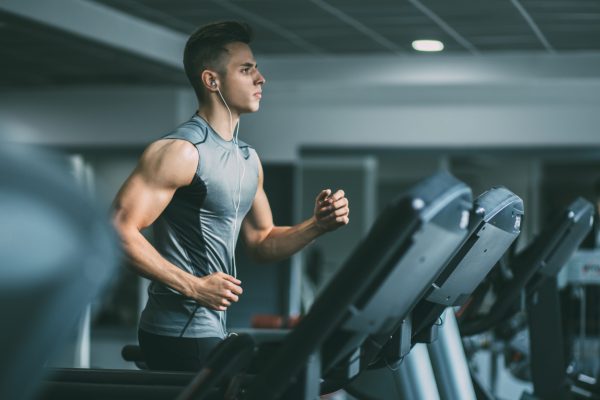
Why Do I Sweat A Lot When I Workout
Modified: January 2, 2024
Discover why you sweat excessively during workouts and how to manage it. Read our featured article on the causes and solutions for excessive sweating during exercise.
Introduction
When you engage in physical activity, you may notice that your body starts to produce sweat. Whether it’s a moderate workout or an intense training session, sweating is a natural response to exercise. But have you ever wondered why you sweat so much when you work out? In this article, we will dive into the fascinating world of sweat and explore the reasons behind your body’s powerful perspiration process during exercise.
Sweating is a normal bodily function that helps regulate your body temperature and keep you cool. It occurs when the sweat glands in your skin release a mixture of water and electrolytes onto the surface of your skin, which then evaporates and cools your body down. But sweating during exercise goes beyond just temperature regulation; it plays a crucial role in optimizing your workout performance and overall health.
Understanding the reasons behind excessive sweating during exercise will not only help you appreciate the incredible capabilities of your body but also provide insights into how you can enhance your workout experience. Whether you’re an avid athlete or someone who is just starting their fitness journey, this article will explore the mechanisms of sweat production during exercise and provide some tips for managing excessive sweating and staying comfortable throughout your workouts.
Understanding Sweat
Sweat is a clear, odorless liquid produced by special sweat glands in your skin called eccrine glands. These glands are located all over your body, but they are particularly concentrated in areas like your palms, soles of your feet, and forehead. When your body temperature rises, either due to external factors like high ambient temperature or internal factors like physical activity, the sweat glands are stimulated to produce sweat.
Sweat is primarily composed of water, but it also contains small amounts of minerals such as sodium, potassium, and chloride. These electrolytes help maintain the balance of fluids in your body and regulate various physiological processes. Additionally, sweat can contain trace amounts of toxins and waste products, making it an essential detoxification mechanism for the body.
The amount of sweat produced varies from person to person and depends on several factors, including genetics, fitness level, and environmental conditions. Some individuals naturally have more active sweat glands, leading to increased sweat production, while others may have a higher sweat threshold and start perspiring later during physical activity.
It is important to note that sweat is different from sebum, the oily substance produced by sebaceous glands in your skin. While sweat helps regulate body temperature, sebum lubricates and protects the skin. These two substances work together to maintain the health and functioning of your skin.
Now that we have a basic understanding of what sweat is and how it is produced, let’s delve into the reasons behind sweating during exercise and its role in optimizing your workouts.
Why Do We Sweat?
Sweating is a vital mechanism that helps your body maintain its internal temperature within a narrow range, despite external fluctuations. When you engage in physical activity, your muscles generate heat, causing your body temperature to rise. In order to prevent overheating, your body initiates the sweat response.
The primary purpose of sweating during exercise is to cool your body down. As sweat evaporates from your skin, it carries away heat, leading to a cooling effect. This process is known as evaporative cooling. It allows your body to dissipate excess heat and maintain a stable core temperature, which is essential for optimal physiological functioning.
Additionally, sweating during exercise helps to maintain proper hydration levels in the body. Sweat contains water and electrolytes, such as sodium and potassium. When you sweat, you lose these important electrolytes along with water. Replenishing them through proper hydration is crucial to prevent dehydration and maintain overall health.
Another reason why we sweat during exercise is to improve grip and reduce friction. Sweat acts as a natural lubricant on the surface of your skin, making it easier for your hands to hold onto objects, such as weights or sports equipment. This increased grip helps enhance performance and reduce the risk of accidents or injuries.
Moreover, sweating during exercise serves as a way for your body to eliminate waste products and toxins. Through perspiration, your body can flush out impurities and maintain a healthy internal environment.
All in all, sweating during exercise is a dynamic and multifunctional process that goes beyond just temperature regulation. It plays a pivotal role in cooling your body, maintaining hydration, improving grip, and aiding in detoxification. Understanding why we sweat during exercise allows us to appreciate the incredible physiological adaptations that occur when we engage in physical activity.
The Role of Sweat in Exercise
Sweating plays a vital role in optimizing your exercise performance and maximizing the benefits you derive from your workouts. Let’s take a closer look at the various ways in which sweat impacts your exercise routine.
One of the primary roles of sweat during exercise is to help regulate your body temperature. As you engage in physical activity, your muscles generate heat, causing your core body temperature to rise. Sweating allows your body to cool down by dissipating this excess heat through evaporation. By maintaining a stable core temperature, your body can function more efficiently, allowing you to perform at your best.
Sweat also plays a crucial role in maintaining proper hydration during exercise. As mentioned earlier, sweat contains water and essential electrolytes. When you sweat, you lose both water and electrolytes, which need to be replenished to avoid dehydration. Ensuring adequate hydration before, during, and after exercise is essential for optimal performance, as dehydration can negatively impact your physical and cognitive abilities.
In addition, sweat acts as a natural lubricant, improving grip and reducing friction during exercise. Whether you’re lifting weights, gripping a sports implement, or performing bodyweight exercises, sweating allows for better traction, preventing slippage and enhancing overall performance. It also helps reduce discomfort and irritation caused by friction between your skin and clothing or equipment.
Furthermore, the production of sweat during exercise aids in the detoxification process. Sweating helps eliminate waste products and toxins from your body, promoting a healthier internal environment. This cleansing effect can have positive effects on various systems in your body, including your skin, kidneys, and liver.
Another important role of sweat during exercise is its psychological impact. Sweating can be seen as a sign of a challenging workout – a tangible indication that you’re pushing your limits and working hard. This can boost your motivation and sense of accomplishment, leading to increased dedication and adherence to your exercise routine.
In summary, sweat plays a multifaceted role in exercise. It helps regulate body temperature, ensures proper hydration, improves grip and reduces friction, aids in detoxification, and can have positive psychological effects. Understanding and embracing the role of sweat can significantly enhance your workout experience and overall fitness journey.
Factors Influencing Sweat Production During Exercise
The amount of sweat produced during exercise can vary significantly from person to person and is influenced by several factors. Understanding these factors can help you better manage sweat production and stay comfortable during your workouts. Let’s explore the key factors that influence sweat production during exercise.
1. Intensity and Duration of Exercise: The intensity and duration of your workout play a significant role in sweat production. Higher intensity exercises, such as running or HIIT workouts, usually result in more sweat due to increased metabolic heat production. Longer duration workouts also tend to lead to more sweating as your body works to maintain its core temperature throughout the extended period of activity.
2. Environmental Factors: The ambient temperature and humidity level of your exercise environment can greatly impact how much you sweat. Hot and humid conditions make it more challenging for your sweat to evaporate, leading to increased perspiration. Similarly, exercising in a heated indoor environment or in direct sunlight can also intensify sweat production.
3. Fitness Level and Body Size: Your fitness level and body composition can influence how much you sweat during exercise. Fit individuals tend to produce more sweat because their bodies are better equipped at regulating temperature. Moreover, larger individuals generally have a higher sweat rate due to a larger body surface area.
4. Genetics: Genetic factors also contribute to individual differences in sweat production. Some individuals simply have more active sweat glands, leading to greater sweat rates during physical activity.
5. Clothing and Fabrics: The type of clothing you wear during exercise can impact sweat production. Tight-fitting synthetic fabrics can trap heat and hinder sweat evaporation, leading to increased sweating. On the other hand, loose-fitting, breathable clothing made from moisture-wicking materials can help keep you cool and facilitate sweat evaporation.
6. Hydration Status: Your hydration status plays a crucial role in sweat production. If you are dehydrated, your body will conserve water, leading to lower sweat rates. On the contrary, staying well-hydrated prior to exercise can help promote sweat production and maintain crucial electrolyte balance.
It’s important to note that individual variations and interactions between these factors can make it challenging to predict exactly how much you’ll sweat during a workout. However, being aware of these influencing factors can help you make informed choices about your exercise environment, clothing selection, and hydration practices to manage sweat production and optimize your exercise experience.
Physiological Benefits of Sweating During Workouts
Sweating during workouts is not just a natural bodily response; it also offers several physiological benefits that contribute to your overall health and fitness. Let’s explore some of the key advantages of sweating during exercise.
1. Temperature Regulation: Sweating plays a vital role in regulating your body temperature during exercise. As you sweat, the evaporation of perspiration from your skin helps cool your body down, preventing overheating. This thermoregulatory mechanism allows you to continue exercising in challenging environments and maintain optimal performance.
2. Toxin Elimination: Sweating during exercise promotes the elimination of toxins from your body. As you perspire, waste products and metabolites are expelled through your sweat glands. This detoxification process can help cleanse your body and support the health of vital organs, such as your liver and kidneys.
3. Enhanced Skin Health: Sweating can have positive effects on your skin. When you exercise and sweat, your pores open up, allowing dirt, oil, and impurities to be flushed out. This can help prevent clogged pores, acne breakouts, and other skin issues. Sweating also improves blood circulation to the skin, delivering essential nutrients and promoting a healthy complexion.
4. Improved Kidney Function: Sweating during exercise can contribute to better kidney function. When you sweat, your body gets rid of excess fluids and waste products, reducing the workload on your kidneys. This can help maintain proper kidney function and support overall kidney health.
5. Endorphin Release: Sweating during exercise is associated with the release of endorphins, often referred to as “feel-good” hormones. Endorphins not only improve your mood but also help reduce stress and anxiety. Sweating during workouts can thus contribute to a sense of happiness, well-being, and overall mental health.
6. Cardiovascular Conditioning: Sweat-inducing workouts, such as cardiovascular exercises, can have significant cardiovascular benefits. As your body sweats and your heart rate increases, your cardiovascular system is strengthened. This can improve cardiovascular endurance, lower resting heart rate, and enhance overall heart health.
7. Improved Exercise Performance: Sweating during workouts can positively impact your exercise performance. When you sweat, your body cools down, allowing you to keep exercising for longer durations without overheating. This can help increase your endurance, improve stamina, and enhance overall athletic performance.
These physiological benefits highlight the importance of sweating during workouts. It goes beyond just cooling your body down; it contributes to toxin elimination, improved skin health, kidney function, endorphin release, cardiovascular conditioning, and enhanced exercise performance. Embrace the sweat and enjoy the multitude of benefits it offers for your mind and body.
Excessive Sweating During Exercise: Causes and Solutions
Sweating during exercise is normal and expected, but some individuals may experience excessive sweating, a condition known as hyperhidrosis. Excessive sweating can be uncomfortable and affect your confidence during workouts. Let’s explore some common causes and potential solutions for excessive sweating during exercise.
Causes of Excessive Sweating:
– Hyperactive Sweat Glands: Some individuals have sweat glands that are more active than others, leading to increased sweat production.
– Genetic Factors: Excessive sweating can run in families, indicating a genetic predisposition to hyperhidrosis.
– Hormonal Imbalance: Hormonal changes, such as those that occur during puberty or menopause, can lead to increased sweat production.
– Chronic Health Conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as hyperthyroidism, diabetes, or obesity, can cause excessive sweating.
– Medications: Some medications, like antidepressants or certain blood pressure medications, can cause excess sweating as a side effect.
Solutions for Excessive Sweating:
– Antiperspirants: Use clinical-strength antiperspirants containing aluminum chloride to help reduce sweating. Apply them to clean, dry skin before your workout.
– Clothing Choice: Wear moisture-wicking fabrics that draw sweat away from your skin and allow for better evaporation. Avoid tight-fitting clothes that can trap heat and moisture.
– Stay Hydrated: Proper hydration can help regulate sweat production. Drink enough water before, during, and after exercise to maintain a good fluid balance.
– Cool Environment: Exercise in well-ventilated or air-conditioned spaces to help lower your body temperature and minimize excessive sweating.
– Prescription Medications: If excessive sweating persists and significantly affects your quality of life, consult a healthcare professional who may prescribe medications, such as anticholinergics, to reduce sweat production.
– Botox Injections: In severe cases, Botox injections can be used to temporarily block the nerves responsible for sweat production.
– Lifestyle Changes: Reduce spicy food consumption, manage stress levels, and practice relaxation techniques, as these factors can contribute to excessive sweating for some individuals.
It’s important to note that while these solutions may help manage excessive sweating, it may not be possible to completely eliminate it. Additionally, if excessive sweating is accompanied by other symptoms or affects your daily life significantly, it is advisable to seek medical advice for further evaluation and treatment options.
Health Considerations for Those Who Sweat Profusely During Workouts
For individuals who sweat profusely during workouts, there are several health considerations to keep in mind to ensure their well-being and optimize their exercise experience. Understanding these considerations can help manage excessive sweating and maintain overall health during physical activity.
Hydration: Excessive sweating can lead to significant fluid loss. It’s crucial to stay well-hydrated before, during, and after exercise. Drink water regularly to replenish the fluids lost through sweat and maintain proper hydration levels. Electrolyte-rich beverages or sports drinks can also be beneficial, as they help replace essential minerals lost through perspiration.
Electrolyte Balance: Sweating not only results in fluid loss but also causes a decrease in electrolytes such as sodium, potassium, and chloride. An imbalance in electrolytes can lead to muscle cramps, fatigue, and even more serious complications. Consume foods rich in electrolytes or consider using electrolyte supplements to maintain a proper balance and support optimal physiological functioning.
Skin Care: Excessive sweating can increase the risk of skin infections and irritations. Take extra care of your skin by cleansing regularly and drying thoroughly after workouts. Use gentle, pH-balanced cleansers and moisturizers to keep your skin healthy. If you notice any rashes or infections, seek medical advice for proper treatment.
Heat-Related Illnesses: Individuals who sweat profusely are more susceptible to heat-related illnesses, such as heat exhaustion or heatstroke. Pay attention to signs of overheating, including dizziness, nausea, excessive fatigue, or an elevated heart rate. If you experience these symptoms, immediately rest in a cool environment, drink fluids, and seek medical attention if necessary.
Impact on Exercise Intensity: Excessive sweating can potentially affect exercise intensity and performance. As sweat acts as a cooling mechanism, it may allow you to exercise for longer durations or at higher intensities before reaching your limits. However, it’s important to listen to your body’s signals and adjust your workout intensity as needed to avoid overexertion and increase the risk of dehydration or heat-related illnesses.
Medical Evaluation: It’s advisable to consult a healthcare professional if excessive sweating persists or is accompanied by other concerning symptoms. They can evaluate your overall health, rule out any underlying medical conditions, and provide guidance on managing excessive sweating during exercise.
Remember, while sweating profusely during workouts may be uncomfortable, it is a natural bodily response. By taking appropriate precautions, staying hydrated, and paying attention to your body’s signals, you can navigate excessive sweating during exercise and prioritize your health and well-being.
Tips for Managing Excessive Sweating During Exercise
Experiencing excessive sweating during exercise can be challenging, but there are several strategies and tips you can implement to manage and minimize its impact. These tips can help you stay comfortable, confident, and motivated during your workouts. Here are some effective ways to manage excessive sweating:
1. Choose the Right Clothing: Opt for moisture-wicking, breathable fabrics that allow for better air circulation and faster evaporation of sweat. Loose-fitting clothing can also promote better airflow and reduce friction on your skin.
2. Use Antiperspirants: Apply antiperspirants containing aluminum chloride to clean, dry skin before your workout. Antiperspirants can help reduce sweat production by temporarily blocking sweat ducts.
3. Stay Hydrated: Proper hydration is essential to regulate sweat production and maintain fluid balance. Drink plenty of water before, during, and after exercise to replace the fluids lost through sweat.
4. Cool Down Your Environment: Exercise in a well-ventilated area or in a cool room with fans or air conditioning. Lowering the ambient temperature can help reduce overall sweat production and keep you more comfortable during your workouts.
5. Take Breaks and Rest: Listen to your body and take short breaks during intense workouts. This allows your body temperature to lower, reducing sweat production and preventing overheating.
6. Use Towels or Sweatbands: Carry a towel or wear sweatbands to wipe away excess sweat and prevent it from dripping into your eyes or onto your workout equipment. It can help you stay focused and reduce discomfort.
7. Monitor Exercise Intensity: Consider adjusting the intensity and duration of your workouts to avoid excessive sweating. Lower-intensity exercises or shorter workout sessions may help manage sweat production while still providing health benefits.
8. Shower and Change Clothes: After your workout, take a refreshing shower to cleanse your skin and remove any residual sweat. Change into fresh, clean clothes to prevent the accumulation of sweat and bacteria on your skin.
9. Consider Time of Day: If possible, schedule your workouts during cooler parts of the day, such as early morning or late evening. Exercising when the temperature is lower can help reduce sweat production and increase comfort.
10. Use Cooling Accessories: Consider using cooling towels, misting fans, or ice packs to help lower your body temperature and keep you cool during exercise. These accessories can provide temporary relief from excessive sweating.
Remember, while these tips can help manage excessive sweating, it’s essential to listen to your body, prioritize your comfort, and seek medical advice if you are concerned about your sweating patterns or if excessive sweating significantly impacts your daily life.
Conclusion
Sweating is a natural and essential process that occurs during exercise. It serves multiple purposes, including regulating body temperature, maintaining hydration, improving grip, aiding in detoxification, and promoting overall health and well-being.
Understanding the reasons behind sweating during exercise and its physiological benefits can help you appreciate the remarkable capabilities of your body. It also enables you to make informed choices to optimize your workouts and manage excessive sweating effectively.
If you find yourself sweating excessively during exercise, consider the factors influencing sweat production, such as exercise intensity, environmental conditions, genetics, and clothing choices. Implementing strategies like wearing moisture-wicking clothing, using antiperspirants, staying hydrated, and exercising in cooler environments can help manage excessive sweating and increase comfort.
It’s important to note that excessive sweating could be a sign of an underlying medical condition. If excessive sweating persists or is accompanied by other concerning symptoms, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional for further evaluation and guidance.
As you embark on your fitness journey, embrace the sweat as a testament to your hard work and commitment. Sweat is not just a sign of a challenging workout; it’s a reflection of your body’s incredible ability to adapt and perform. So, embrace the sweat, stay hydrated, and enjoy the many benefits that sweating during exercise brings to your mind, body, and overall health.