Featured
How To Check Gut Health
Published: August 31, 2023
Learn how to check your gut health with our featured guide. Improve digestion and overall well-being. Take control of your gut health today!
Introduction
Gut health plays a crucial role in maintaining overall well-being. The gut, which refers to the digestive tract, is not just responsible for digesting food, but it is also closely connected to our immune system, mental health, and even skin condition. As more research emerges, the importance of maintaining a healthy gut becomes increasingly evident. In this article, we will explore what gut health is, why it is important, how it impacts overall health, and most importantly, how you can check your gut health.
Our digestive tract is home to trillions of tiny bacteria, known as the gut microbiome, which regulates digestion, nutrient absorption, and helps ward off pathogens. However, due to factors such as poor diet, stress, antibiotics, and environmental toxins, the balance of these gut bacteria can become disrupted, leading to an array of health issues.
From weight management to immune function, gut health affects numerous aspects of our well-being. Studies have shown that a healthy gut microbiome is associated with a stronger immune system, improved mood and mental health, reduced inflammation, and better nutrient absorption. On the other hand, an unhealthy gut can lead to digestive problems, allergies, skin issues, hormonal imbalances, and even chronic diseases like diabetes and autoimmune disorders.
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of poor gut health is crucial in order to take the necessary steps towards improving it. Common indicators include bloating, gas, diarrhea, constipation, food sensitivities, skin problems, fatigue, and frequent infections. However, it is important to note that these symptoms can be attributed to other health conditions as well, making it essential to check your gut health through specific tests and evaluations.
Fortunately, there are several methods that can help assess the health of your gut. These include food sensitivity testing, stool analysis, breath tests, microbiome testing, and digestive system evaluations, which we will delve into detail later in this article. By understanding how to check your gut health, you can gain valuable insights into the state of your digestive system and take appropriate action to restore balance and promote overall well-being.
What is Gut Health?
Gut health refers to the overall well-being and optimal functioning of the digestive tract. It is not just about the absence of digestive issues but encompasses the balance and diversity of the gut microbiome, the efficiency of digestion and nutrient absorption, as well as the absence of inflammation and gut-related diseases.
The gut, also known as the gastrointestinal tract, is a complex system that starts from the mouth and ends at the anus. It is responsible for breaking down food, extracting nutrients, and eliminating waste. Within the gut, there is a delicate ecosystem of microorganisms, including bacteria, yeasts, viruses, and fungi, collectively known as the gut microbiome.
The gut microbiome plays a vital role in gut health. It helps to break down complex carbohydrates, produce beneficial compounds like vitamins and short-chain fatty acids, regulate the immune system, and protect against harmful pathogens. A healthy gut microbiome is characterized by a diverse and balanced composition of these microorganisms.
When the gut microbiome is imbalanced or disrupted, often referred to as dysbiosis, it can lead to a variety of health issues. Imbalances in gut bacteria have been associated with digestive disorders such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD), and leaky gut syndrome. Furthermore, research has linked dysbiosis to chronic conditions like obesity, diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and even mental health disorders like depression and anxiety.
In addition to the gut microbiome, the integrity of the gut lining is crucial for optimal gut health. The gut lining is responsible for selectively allowing nutrients to enter the bloodstream while preventing harmful substances from crossing the barrier. When the gut lining becomes compromised, as in the case of leaky gut syndrome, undigested food particles, toxins, and bacteria can leak into the bloodstream, triggering inflammation and immune reactions throughout the body.
Maintaining a healthy gut involves nurturing the gut microbiome, supporting proper digestion and absorption, and protecting the gut lining. This can be achieved through a balanced and varied diet rich in fiber, prebiotics, and probiotics, stress management, regular physical activity, and avoiding excessive use of antibiotics and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
By understanding what gut health is and the factors that influence it, we can make informed choices to support and optimize our digestion, absorption, and overall well-being.
Why is Gut Health Important?
Gut health is vital for overall well-being and plays a crucial role in maintaining optimal physical and mental health. The health of our gut impacts various aspects of our body, from digestion and nutrient absorption to immune function and even our mood.
One of the primary reasons why gut health is important is its connection to the immune system. Around 70% to 80% of our immune cells reside in the gut. The gut microbiome helps to regulate immune responses, defend against harmful pathogens, and maintain a healthy balance between beneficial and harmful bacteria. When the gut microbiome is imbalanced, it can lead to immune dysregulation and increase the risk of infections, autoimmune diseases, and allergies.
In addition to immune support, a healthy gut is essential for proper digestion and nutrient absorption. The gut microbiome helps break down complex carbohydrates, fibers, and other indigestible compounds that our body cannot process on its own. It produces enzymes that aid in digestion and helps optimize the absorption of essential nutrients like vitamins, minerals, and fatty acids. Without a healthy gut, we may experience issues such as bloating, gas, indigestion, and nutrient deficiencies.
Furthermore, research has shown a strong connection between gut health and mental health. The gut and the brain communicate through what is known as the gut-brain axis, a bidirectional communication pathway. The gut microbiome produces neurotransmitters like serotonin, which plays a key role in regulating mood, sleep, and appetite. An imbalanced gut microbiome has been linked to mental health disorders such as depression, anxiety, and even cognitive decline.
Moreover, the gut microbiome also impacts weight management. Certain types of bacteria in the gut are associated with weight gain and obesity, while others are linked to weight loss. An imbalance in the gut microbiome can lead to increased inflammation, impaired metabolism, and difficulty in maintaining a healthy weight.
Furthermore, gut health is closely related to skin health. Studies have shown that certain skin conditions, such as acne, eczema, and psoriasis, can be influenced by an imbalanced gut microbiome. By improving gut health, it is possible to alleviate these skin issues and achieve a clearer complexion.
Overall, maintaining a healthy gut is crucial for optimal physical and mental health. It supports a strong immune system, proper digestion and nutrient absorption, balanced mood, healthy weight management, and even radiant skin. By prioritizing gut health, we can enhance our overall well-being and improve our quality of life.
How Does Gut Health Affect Overall Health?
Gut health has a significant impact on overall health and well-being. The health of our gut can influence various systems in our body, affecting everything from immune function to mental health and even skin condition.
One of the key ways that gut health affects overall health is through its influence on the immune system. The gut is home to a large portion of our immune cells, and the gut microbiome plays a crucial role in regulating immune responses. A healthy gut microbiome helps to promote immune balance, defend against pathogens, and prevent the development of autoimmune diseases. On the other hand, an imbalanced gut microbiome can weaken immune function and increase the risk of infections and autoimmune disorders.
In addition to immune function, the gut has a profound impact on mental health and brain function. The gut and the brain are intricately connected through the gut-brain axis. The gut microbiome produces neurotransmitters like serotonin, which is involved in mood regulation. It is estimated that around 90% of serotonin is actually produced in the gut. An imbalanced gut microbiome has been linked to mental health disorders such as depression, anxiety, and even cognitive decline. By nurturing a healthy gut, we can positively influence our mental well-being.
Gut health also plays a role in weight management and metabolism. Studies have shown that the composition of the gut microbiome can impact energy balance, fat storage, and the regulation of appetite. Certain types of bacteria in the gut are associated with weight gain and obesity, while others are linked to weight loss. An imbalance in the gut microbiome can lead to increased inflammation, impaired metabolism, and difficulties in maintaining a healthy weight.
The condition of our gut can also have a direct impact on our digestive system. A healthy gut microbiome aids in the breakdown and absorption of nutrients, ensuring that we get the maximum benefit from the food we eat. An imbalanced gut microbiome can lead to digestive issues such as bloating, gas, diarrhea, or constipation. It can also contribute to conditions like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
Furthermore, research has shown a clear connection between gut health and skin health. The gut microbiome is involved in the regulation of inflammation, which can impact the development of skin conditions such as acne, eczema, and psoriasis. By restoring gut health, it is possible to improve skin conditions and achieve healthier, clearer skin.
Overall, the health of our gut is closely linked to our overall well-being. By supporting and nurturing a healthy gut through a balanced diet, stress management, and lifestyle choices, we can optimize our immune system, support our mental health, maintain a healthy weight, promote proper digestion, and even improve the condition of our skin. Taking care of our gut health is an essential aspect of promoting optimal overall health.
Signs and Symptoms of Poor Gut Health
The state of our gut health can be reflected in various signs and symptoms throughout the body. While these symptoms may not solely indicate poor gut health, they can serve as indicators that our digestive system is not functioning optimally. Recognizing these signs and seeking appropriate evaluation can help identify potential gut health issues. Here are some common signs and symptoms of poor gut health:
- Digestive Issues: Bloating, gas, constipation, diarrhea, and frequent indigestion are often signs of an imbalanced gut. These symptoms can indicate issues such as dysbiosis, impaired digestion, or inflammation in the digestive tract.
- Food Sensitivities and Intolerances: Developing sensitivities or intolerances to certain foods can be a sign of poor gut health. These reactions may manifest as bloating, gas, abdominal pain, skin issues, or other allergic-like symptoms after consuming specific foods.
- Chronic Fatigue and Low Energy: The gut has a significant influence on energy production and nutrient absorption. If the gut is not functioning optimally, it can lead to poor nutrient absorption and chronic fatigue.
- Mood and Mental Health Issues: There is a strong connection between the gut and the brain, known as the gut-brain axis. Imbalances in the gut can affect the production of neurotransmitters like serotonin, leading to mood disorders such as depression, anxiety, and even brain fog.
- Skin Problems: Skin conditions like acne, eczema, and psoriasis can be linked to an imbalanced gut. Chronic inflammation in the gut can contribute to inflammation in the skin, leading to various skin issues.
- Autoimmune Disorders: Poor gut health, specifically a leaky gut, has been associated with the development of autoimmune diseases. Conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and celiac disease may have roots in imbalances within the gut.
- Weight Fluctuations and Difficulty Losing Weight: An imbalanced gut can impact metabolism, hormone regulation, and fat storage. This can contribute to weight fluctuations and difficulties in losing weight, despite efforts to eat a healthy diet and exercise regularly.
- Weakened Immune System: The gut plays a significant role in immune function. If the gut microbiome is imbalanced, it can weaken the immune system and lead to increased susceptibility to infections, allergies, and autoimmune disorders.
It is essential to note that these symptoms can be indicative of other health conditions as well. Therefore, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional to evaluate the underlying causes and determine an appropriate plan of action to address gut health concerns.
How to Check Your Gut Health
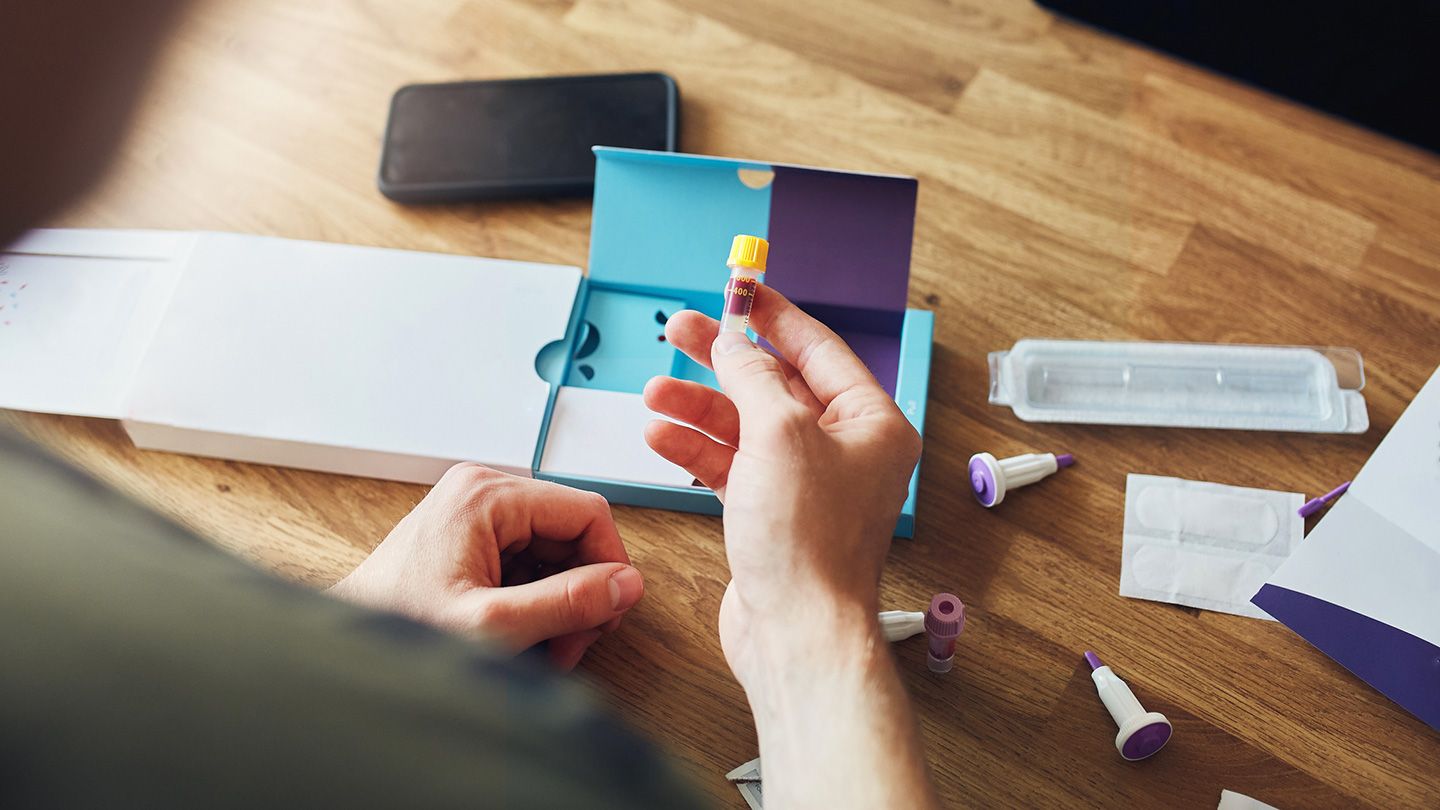
If you suspect that your gut health may be compromised, there are several methods available to assess and evaluate the state of your digestive system. These tests and evaluations can provide insights into the composition of your gut microbiome, the presence of any underlying conditions, and help guide appropriate treatment and intervention. Here are some common ways to check your gut health:
- Food Sensitivity Testing: Food sensitivity tests can help identify any specific foods that may be triggering immune reactions or affecting the health of your gut. These tests typically involve a blood sample or saliva collection to detect antibodies associated with food sensitivities.
- Stool Analysis: Stool analysis, also known as a comprehensive stool test, provides valuable information about the balance of bacteria in your gut, the presence of pathogens, and the overall health of your digestive system. This test can help identify any imbalances or markers of inflammation within the gut.
- Breath Tests: Breath tests are used to diagnose specific gut conditions such as small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO) or lactose intolerance. These tests involve consuming a specific substance and then measuring the levels of gases (such as hydrogen or methane) that are produced by bacteria in the gut.
- Gut Microbiome Testing: Gut microbiome testing analyzes the composition of bacteria and other microorganisms in your gut. This type of testing can provide insights into the diversity, balance, and abundance of different types of bacteria present in your gut microbiome. It can be helpful in identifying any imbalances or dysbiosis within the gut.
- Digestive System Evaluation: A comprehensive evaluation by a healthcare professional specializing in gut health can be helpful in assessing your gut health. They may utilize a combination of medical history, physical examination, and laboratory tests to evaluate the health of your digestive system and identify any underlying conditions or imbalances.
When checking your gut health, it is essential to work with a healthcare professional who specializes in gut health or functional medicine. They can guide you in selecting the most appropriate tests, interpreting the results, and developing a personalized plan to improve your gut health.
It is important to note that these tests are not always necessary for everyone. If you are not experiencing any specific symptoms or concerns related to your gut health, adopting a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, stress management, and adequate sleep, can significantly contribute to maintaining a healthy gut.
Food Sensitivity Testing
Food sensitivity testing is a diagnostic tool used to identify specific foods that may be causing negative reactions in your body. Unlike food allergies, which typically trigger an immediate and severe immune response, food sensitivities are characterized by a delayed, less obvious reaction that can manifest as various symptoms.
The purpose of food sensitivity testing is to identify potential triggers that may be contributing to gut-related issues, inflammation, skin problems, and other symptoms. By identifying and eliminating these trigger foods from your diet, you can alleviate symptoms and support your gut health.
There are different types of food sensitivity testing available, each with its own methodology and approach:
- Elimination Diet: While not a form of direct testing, an elimination diet involves removing potential trigger foods from your diet for a period of time, typically 2-4 weeks. Then, one by one, the eliminated foods are reintroduced to identify any adverse reactions. This method helps you personally identify specific foods causing sensitivities.
- IgG Antibody Testing: This blood test measures the levels of IgG antibodies, which are produced by the immune system in response to specific foods. High levels of IgG antibodies to certain foods may indicate a sensitivity or intolerance to those foods.
- IgE Antibody Testing: This blood test is used to diagnose immediate allergic reactions to foods. IgE antibodies are produced by the immune system in response to allergens, and elevated levels can indicate an allergic response to certain foods.
- Comprehensive Food Panels: These panels utilize a combination of blood or saliva tests to identify reactions to a wide range of common foods. They can provide a more comprehensive overview of your potential food sensitivities.
It’s important to note that food sensitivity testing is not definitive and can sometimes yield false positives or false negatives. The results should be interpreted in conjunction with your symptoms and clinical judgment. It is best to work with a healthcare professional, such as a registered dietitian or nutritionist, who specializes in food sensitivities to interpret the results accurately and guide you in creating a personalized dietary plan.
Once you have identified your trigger foods, the next step is to eliminate them from your diet. This elimination period can vary depending on the severity of your symptoms and the advice of your healthcare professional. By removing the offending foods, you can allow your gut to heal and reduce inflammation, leading to improved gut health and symptom relief.
Over time, you may be able to reintroduce some of the eliminated foods in moderation, depending on your individual tolerance levels. However, it’s important to listen to your body and be mindful of any recurrent symptoms or reactions that may occur.
Overall, food sensitivity testing can be a valuable tool in identifying trigger foods and supporting your gut health. By making informed dietary choices based on the results, you can optimize your gut health and improve your overall well-being.
Stool Analysis
Stool analysis, also known as a comprehensive stool test, is a diagnostic tool used to evaluate the health and composition of your gut microbiome, as well as identify any potential imbalances or abnormalities within the digestive system. This non-invasive test involves analyzing a sample of your stool to gather valuable information about your gut health.
Stool analysis can provide insights into various aspects of gut health, including:
- Gut Microbiome Composition: Stool analysis can assess the diversity and abundance of different bacteria present in your gut. An imbalanced or less diverse gut microbiome may indicate issues such as dysbiosis, which is associated with a variety of digestive disorders and health conditions.
- Digestive Function: This test can evaluate how well your digestive system is functioning by assessing parameters such as the presence of digestive enzymes, fat absorption, and the breakdown of proteins, carbohydrates, and fats. It can also identify any issues related to malabsorption.
- Presence of Pathogens: Stool analysis can detect the presence of harmful bacteria, parasites, or fungi that may be causing gut disturbances or infections. Identifying and treating these pathogens is essential for restoring gut health.
- Intestinal Inflammation: Chronic inflammation in the gut can contribute to digestive problems and other health conditions. Stool analysis can evaluate markers of inflammation, such as calprotectin or lactoferrin, which can indicate the presence of intestinal inflammation.
To perform a stool analysis, you will typically collect a small sample of your stool and send it to a laboratory for analysis. The laboratory will provide a detailed report that includes information about the composition of your gut microbiome, potential pathogens, any markers of inflammation, and digestive function.
Working with a healthcare professional, such as a gastroenterologist or functional medicine practitioner, is crucial in interpreting the results and understanding their implications for your gut health. Based on the findings, they can develop a personalized treatment plan that may include dietary modifications, probiotics, antimicrobial agents, or other interventions to restore gut health.
Stool analysis is a valuable tool for assessing gut health and identifying potential issues that may be contributing to digestive problems or other health conditions. By addressing imbalances or abnormalities detected through stool analysis, you can take proactive steps to improve your gut health and overall well-being.
Breath Tests
Breath testing is a non-invasive diagnostic method used to evaluate specific gastrointestinal disorders and conditions by measuring the gases produced by bacteria in the gut. These tests can provide insights into the presence of certain bacteria or the ability to digest specific substances, helping to identify conditions such as small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO) or lactose intolerance.
There are different types of breath tests available, each targeting specific gastrointestinal issues:
- Hydrogen Breath Test: This test is commonly used to diagnose small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO). SIBO occurs when there is an overgrowth of bacteria in the small intestine, leading to an imbalance in the gut microbiome. During the test, you consume a specific substance, usually lactulose or glucose, and then breathe into a device that measures the levels of hydrogen in your breath. Elevated levels of hydrogen indicate the presence of bacteria fermenting the substance in the small intestine.
- Methane Breath Test: Similar to the hydrogen breath test, this test measures the levels of methane gas produced by bacteria in the gut. It is used to diagnose methane-dominant SIBO. Some individuals may produce higher levels of methane instead of hydrogen when there is bacterial overgrowth in the small intestine.
- Lactose Intolerance Test: This breath test is used to determine lactose intolerance, a condition characterized by the inability to digest lactose, a sugar found in milk and dairy products. During the test, you consume a measured amount of lactose, and breath samples are collected over time. Elevated levels of hydrogen or methane in the breath may indicate an inability to digest lactose.
- Fructose Intolerance Test: This test assesses the ability to digest fructose, a naturally occurring sugar found in fruits and some sweeteners. It measures the levels of hydrogen or methane in the breath after consuming a fructose solution.
These breath tests are typically conducted in a clinical setting or under the guidance of a healthcare professional. It’s important to follow the specific instructions provided and avoid certain medications, foods, or substances that could interfere with the accuracy of the test.
Interpreting the results of a breath test requires the expertise of a healthcare professional who specializes in gastrointestinal disorders. They can analyze the gas patterns in your breath and determine if there is evidence of bacterial overgrowth or carbohydrate malabsorption. Based on the results, they can create a personalized treatment plan that may involve dietary modifications, targeted antimicrobial therapy, or other interventions to address the specific gut-related issue.
Breath tests offer a non-invasive and relatively simple way to assess and diagnose certain gastrointestinal conditions. By identifying the underlying causes of symptoms such as bloating, gas, or abdominal discomfort, these tests can help guide appropriate treatment and management strategies to improve gut health and overall well-being.
Gut Microbiome Testing
Gut microbiome testing involves analyzing the composition and diversity of bacteria and other microorganisms that reside in your digestive system. This type of testing provides insights into the unique ecosystem of your gut, shedding light on the balance of beneficial and potentially harmful microorganisms present.
Gut microbiome testing can be conducted through various methods:
- 16S rRNA Sequencing: This technique targets a specific region of bacterial DNA to identify and classify different species present in your gut. It provides valuable information about the diversity and relative abundance of bacteria but does not capture the full genetic information of the microorganisms.
- Whole Genome Sequencing (Shotgun Sequencing): This method involves sequencing the entire genetic material found in a sample, providing a more comprehensive picture of the gut microbiome. It allows for the identification of bacteria as well as other microorganisms such as viruses, fungi, and archaea.
- Metagenomic Sequencing: Metagenomic sequencing combines the genetic material of all microorganisms in a sample, providing detailed information about their functional capacity and potential interactions. It offers insights into the genes present in the gut microbiome, allowing researchers to study the metabolic capabilities of the microbial community.
By analyzing the composition and function of the gut microbiome, this type of testing can help identify imbalances or dysbiosis in the gut. Imbalances in the gut microbiome have been associated with various health conditions, including gastrointestinal disorders, obesity, autoimmune diseases, and mental health disorders.
When considering gut microbiome testing, it’s essential to work with a healthcare professional or a laboratory specializing in this area. They can help interpret the results and provide actionable recommendations to improve gut health, such as dietary modifications, targeted probiotic or prebiotic supplementation, or other interventions tailored to your specific microbial composition.
It’s important to note that gut microbiome testing is still an evolving field, and the understanding of the complex interactions within the gut microbiome is constantly expanding. Therefore, the results of these tests should be interpreted with caution. The focus should be on identifying any imbalances or potential areas for improvement, rather than seeking a specific “ideal” microbiome composition.
Gut microbiome testing offers a glimpse into the intricate world of microorganisms residing in your gut. By harnessing this knowledge, you can take informed steps to support the health and diversity of your gut microbiome, which in turn can positively influence your overall well-being.
Digestive System Evaluation
A comprehensive evaluation of the digestive system is a thorough assessment conducted by a healthcare professional to assess the overall health and function of your digestive tract. This evaluation involves a combination of medical history review, physical examination, and specialized tests to identify any underlying conditions or imbalances that may be affecting your gut health.
The digestive system evaluation may include one or more of the following components:
- Medical History: Your healthcare professional will take a comprehensive medical history to understand your symptoms, previous diagnoses, medications, and lifestyle factors that may impact your digestive health. This information provides important insights into potential triggers and areas of concern.
- Physical Examination: A physical examination, particularly of the abdomen, may be performed to check for any signs of tenderness, distension, or abnormal sounds that could indicate issues such as inflammation, blockages, or swelling in the digestive system.
- Diagnostic Imaging: Imaging tests, such as an abdominal ultrasound, computed tomography (CT) scan, or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), may be utilized to visualize the digestive organs and identify any abnormalities, such as tumors, strictures, or structural issues.
- Endoscopy: An endoscopy is a procedure that uses a flexible tube with a camera on the end to visualize and examine the upper or lower gastrointestinal tract. This allows for the identification of conditions such as ulcers, inflammation, polyps, or signs of gastrointestinal bleeding.
- Biopsy: During an endoscopy or other invasive procedures, small tissue samples (biopsies) may be collected for further analysis. Biopsies can help identify specific conditions, such as celiac disease, inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), or cancer.
- Functional Testing: Functional tests assess the functional capacity of the digestive system. Examples include gastric emptying studies to evaluate the rate at which the stomach empties, esophageal motility studies to assess the movement of food through the esophagus, or manometry to measure pressure and muscle contractions in the digestive tract.
Based on the results of the evaluation, the healthcare professional can provide a diagnosis, recommend appropriate treatment options, and develop a personalized plan to improve gut health. This may include lifestyle modifications, dietary changes, medications, or further specialized interventions.
A digestive system evaluation is particularly beneficial if you are experiencing persistent or severe digestive symptoms, have a family history of digestive disorders, or have previously been diagnosed with certain conditions such as inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), gastrointestinal bleeding, or gastrointestinal cancers.
It is important to consult with a healthcare professional, such as a gastroenterologist or a specialist in functional medicine, to guide you through the digestive system evaluation process. They have the expertise to interpret the findings and guide you toward the appropriate interventions to optimize your gut health and overall well-being.
Tips to Improve Gut Health
Improving gut health is essential for maintaining overall well-being and supporting optimal digestion. Fortunately, there are several lifestyle and dietary approaches that you can implement to promote a healthy gut. Here are some tips to improve gut health:
- Eat a Balanced Diet: Focus on a diet rich in whole, unprocessed foods, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. This provides essential nutrients and a diverse range of fibers that nourish beneficial gut bacteria.
- Increase Fiber Intake: Consume a variety of plant-based foods to increase your fiber intake. Fiber acts as a prebiotic, feeding the beneficial bacteria in your gut and promoting their growth. Include sources such as legumes, whole grains, fruits, and vegetables.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking an adequate amount of water supports digestion and helps maintain regular bowel movements. Aim for at least 8 cups of water per day.
- Limit Processed and Sugary Foods: Highly processed foods and those high in added sugars can disrupt the balance of gut bacteria and contribute to inflammation. Minimize your intake of sugary drinks, refined grains, and processed snacks.
- Include Probiotics: Probiotics are beneficial bacteria that can help restore and maintain a healthy gut microbiome. Include foods such as yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, kimchi, and other fermented foods in your diet. Alternatively, you can consider taking a high-quality probiotic supplement.
- Manage Stress: Chronic stress can impact the gut-brain axis and disrupt gut function. Incorporate stress management techniques such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, yoga, or regular physical activity to help reduce stress levels and support gut health.
- Get Enough Sleep: Adequate sleep is crucial for gut health, as it helps regulate hormones that influence digestion and appetite. Aim for 7-8 hours of quality sleep each night.
- Exercise Regularly: Regular physical activity not only supports overall health but also helps maintain healthy digestion. Engage in moderate-intensity exercise, such as brisk walking, jogging, or cycling, for at least 150 minutes per week.
- Avoid Antibiotic Overuse: Antibiotics can disrupt the delicate balance of gut bacteria. Only take antibiotics when necessary and work with your healthcare provider to explore alternative options, such as probiotics, to support gut health during and after antibiotic use.
- Listen to Your Body: Pay attention to how you feel after consuming certain foods. Everyone’s gut is unique, so what works for others may not work for you. Identify and avoid any trigger foods or ingredients that may cause digestive discomfort or adverse reactions.
Remember, improving gut health is a gradual process, and it may take time to see noticeable improvements. Making these tips a part of your daily routine can help support a healthy gut and contribute to improved digestion, better nutrient absorption, and enhanced overall well-being.
Conclusion
Ensuring optimal gut health is crucial for overall well-being and can have a profound impact on various aspects of our health, including digestion, immune function, mental well-being, and more. By understanding what gut health is and how it can affect our overall health, we can take proactive steps to improve and maintain a healthy gut.
In this article, we explored the importance of gut health and how it is connected to various bodily systems. We discussed the signs and symptoms of poor gut health, emphasizing the need to pay attention to any digestive issues or imbalances that may indicate potential gut health concerns. We also delved into different methods to check your gut health, such as food sensitivity testing, stool analysis, breath tests, gut microbiome testing, and digestive system evaluations.
To support a healthy gut, we provided practical tips, including following a balanced diet, increasing fiber intake, staying hydrated, limiting processed foods, incorporating probiotics, managing stress, getting enough sleep, regular exercise, and being mindful of antibiotic use. Implementing these habits can contribute to a healthy gut microbiome, better digestion, nutrient absorption, and overall improved well-being.
While the information provided in this article serves as a guide, it is essential to remember that everyone’s gut health is unique. It is always recommended to consult with a healthcare professional who specializes in gut health or functional medicine to address specific concerns and receive personalized advice tailored to your individual needs.
By prioritizing and nurturing our gut health, we can take an active role in supporting our overall health and well-being. Remember, a healthy gut leads to a healthier you.